Custom Maternity Newborncare Proctored Exam
ATI Custom Maternity Newborncare Proctored Exam
Total Questions : 48
Showing 10 questions Sign up for moreThe nurse admits a newborn to the admission nursery and prepares to bathe the baby for the first time after assessing which of the following?
Explanation
A. This is not a primary consideration before bathing a newborn. The timing of the last feeding is more relevant to assessing the risk of hypoglycemia rather than determining readiness for a bath.
B. This temperature is slightly below the recommended range for newborns (36.5°C to 37.5°C). Bathing should be delayed until the newborn's temperature is stable.
C. While care of the umbilical cord is important, it does not determine the timing of the first bath. The cord can be kept dry even if the baby is bathed.
D. Ensuring that the newborn has maintained a stable body temperature for at least 2 hours is crucial before giving the first bath. Bathing can cause a drop in body temperature, so it's essential that the newborn's thermoregulation is stable to avoid hypothermia.
How do you prevent flat spots on the back of a baby's head?
Explanation
A. Back to sleep: While placing babies on their backs to sleep is essential for reducing the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), it does not prevent flat spots. Instead, tummy time while the baby is awake helps balance the time spent on their back.
B. Take the baby for walks: Taking a baby for walks is beneficial for overall development and stimulation but does not directly prevent flat spots on the head.
C. Keep them awake most of the day: This is not a safe or recommended practice. Babies need sufficient sleep for proper growth and development.
D. Tummy time helps prevent flat spots by reducing the amount of time the baby spends lying on their back. It also strengthens neck, shoulder, and arm muscles, encouraging the baby to move their head more freely and develop motor skills.
A nurse is caring for a newborn who was delivered by vacuum extraction and has swelling on his head that crosses the suture line. The newborn's mother asks about the swelling on her newborn's head. Which of the following responses should the nurse make?
Explanation
"This is a caput succedaneum, which is a collection of fluid from the pressure of the vacuum extractor.”.
Choice A rationale:
A Mongolian spot is a benign, flat, bluish-gray pigmented area often found on the sacral or gluteal area of some newborns with darker skin tones. It is not related to the swelling on the newborn's head caused by vacuum extraction.
Choice B rationale:
A caput succedaneum is a localized swelling on the baby's scalp that occurs due to pressure from the vacuum extractor during delivery. It is typically soft and may cross the suture lines. This explanation accurately describes the swelling the baby has on his head.
Choice C rationale:
Erythema toxicum is a common rash that appears as small red bumps with white or yellow centers. It is a benign and self-resolving condition that does not cause swelling on the head or involve the suture lines.
Choice D rationale:
A cephalhematoma is a collection of blood between the skull and the periosteum that does not cross the suture lines. It is caused by trauma during birth and may take weeks to months to resolve. This does not match the description of the swelling caused by vacuum extraction.
The nurse enters the room and notices that the room feels cold. The mother says, "He has been crying and kicking and now he seems very tired.”. What is the nurse's priority concern?
Explanation
A. This condition typically results from excessive loss of acid, often due to vomiting or diuretics. It is not the most likely concern in a cold environment with an infant who has been crying and kicking.
B. A cold environment can lead to nonshivering thermogenesis in newborns, where they metabolize brown fat to generate heat. This process can lead to increased lactic acid production, potentially causing metabolic acidosis. The infant's fatigue following crying and kicking may indicate that the body has expended significant energy to stay warm, making metabolic acidosis a priority concern.
C. While hunger could be a reason for crying, it is not the priority concern in this scenario where environmental cold and fatigue are present.
D. Overstimulation might cause crying, but the environmental cold and subsequent risk of metabolic acidosis are more critical concerns in this context.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching about phenylketonuria (PKU) testing with the parent of a newborn. Which of the following statements by the parent indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
"My baby will be placed under special lights if the test is elevated.”.
Choice A rationale:

This statement indicates a need for further teaching. Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a metabolic disorder that leads to the accumulation of phenylalanine in the body. If the PKU test is elevated, it means that the baby has high levels of phenylalanine, and immediate dietary intervention is required. The parent's statement about special lights suggests a confusion with jaundice treatment, which is not related to PKU.
Choice B rationale:
This statement is accurate. Before the PKU test is done, the baby needs to consume formula or breast milk to ensure accurate test results.
Choice C rationale:
This statement is also accurate. PKU is a genetic disorder that can be managed with a special diet low in phenylalanine. By adhering to the prescribed diet, the harmful effects of PKU can be minimized.
Choice D rationale:
This statement is accurate. It is common for the PKU test to be repeated at the 2-week check- up to confirm the initial results and ensure early detection and management of PKU if present.
A nurse is collecting data from a newborn. Which of the following anatomical landmarks should the nurse use to measure chest circumference?
Explanation
The nurse should use the lower ribcage border to measure chest circumference.
Choice A rationale:
The sternal notch is not an appropriate landmark for measuring chest circumference. It is a notch at the top of the sternum and not indicative of chest circumference.
Choice B rationale:
When measuring the chest circumference of a newborn, the correct anatomical landmark to use is the nipple line. This method ensures that the measurement is taken at a consistent and reproducible location across different individuals, providing an accurate assessment of the chest size relative to growth and development standards. It's important to position the measuring tape at the level of the nipples, encircling the chest at its largest point, which typically aligns with the nipple line.
Choice C rationale:
The lower ribcage border is also not suitable as it may vary significantly with respiratory movements and is not a stable landmark for consistent measurements.
Choice D rationale:
The axillae (armpits) are not used as a landmark for measuring chest circumference. It is not a standardized anatomical point for this purpose.
A nurse is assisting a client with breastfeeding her newborn. The nurse should explain that which of the following reflexes will initiate sucking?
Explanation
Rooting. Choice A rationale:
The Moro reflex is a startle reflex characterized by the infant's sudden extension and abduction of the arms in response to a loud noise or sudden movement. It is not involved in the initiation of sucking and is unrelated to breastfeeding.
Choice B rationale:
The rooting reflex is a crucial reflex that helps initiate sucking in newborns. When the infant's cheek is stroked or touched, they will turn their head toward the stimulus and open their mouth, preparing for feeding. This reflex helps the infant find the mother's nipple and begin breastfeeding effectively.
Choice C rationale:
The stepping reflex is a primitive reflex observed in newborns when held upright with their feet touching a solid surface. The baby will make stepping movements, mimicking walking. However, this reflex is not related to the initiation of sucking and breastfeeding.
Choice D rationale:
The Babinski reflex is a reflex in which the big toe extends upward and the other toes fan out when the sole of the foot is stimulated. This reflex is present in newborns and disappears as the child grows older. It is not involved in the initiation of sucking.
Which statement about fetal circulation is true?
Explanation
Fetal circulation continues until after the stress of labor.
Choice A rationale:
Fetal circulation undergoes significant changes at birth. It becomes ineffective as the transition from intrauterine to extrauterine life occurs. The foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus, which allow blood to bypass certain fetal circulatory pathways, close as the baby breathes for the first time.
Choice B rationale:
Fetal circulation does not continue until red blood cells are broken down. Red blood cells in a fetus have a shorter lifespan than those in adults and are continually replaced throughout gestation. However, their breakdown is not the reason for the changes in fetal circulation.
Choice C rationale:
The correct answer. Fetal circulation continues until after the stress of labor. During labor, the baby experiences increased stress and pressure, which helps trigger various physiological changes, including the closure of specific fetal circulatory shunts.
Choice D rationale:
Fetal circulation does not continue until adulthood. As mentioned earlier, the transition from fetal to adult circulation occurs during and after birth, with the closure of specific fetal shunts and the establishment of a fully functional adult circulatory system.
A nurse is caring for several newborn clients. For which of the following findings should the nurse notify the charge nurse?
Explanation
A. A blood glucose fingerstick of 40 mg/dL for an infant who is 1-hr old: A blood glucose level of 40 mg/dL is borderline low but expected in the immediate postnatal period, especially if the infant is asymptomatic. Feeding the infant is the first step to address this, and monitoring is usually sufficient unless symptoms of hypoglycemia develop.
B. A hematocrit of 60% in an infant who is 8-hr old: This value is at the upper end of normal for a newborn and may suggest mild polycythemia. However, it does not require urgent notification unless accompanied by symptoms such as respiratory distress or poor perfusion
C. Jaundice in an infant who is 4-hr old: Early-onset jaundice (within the first 24 hours) is not normal and suggests a potentially dangerous underlying condition, such as hemolytic disease of the newborn or infection. Immediate reporting and further evaluation, including bilirubin levels and possible treatment with phototherapy, are essential.
D. Acrocyanosis in an infant who is 2-hr old: Acrocyanosis (bluish discoloration of the hands and feet) is a common and benign finding in the first 24 to 48 hours after birth due to immature circulation. It does not require notification or intervention.
Exhibit 1. The names of the newborn reflexes are? Select all that apply.
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
The newborn reflex called "rooting”. is characterized by turning the head and opening the mouth when the cheek or mouth area is touched. This reflex helps the newborn find the mother's breast for feeding.
Choice B rationale:
"Stepping”. is a newborn reflex where they make stepping movements when held upright with their feet touching a solid surface. This reflex is present at birth but tends to disappear after a few weeks.
Choice C rationale:
The "Moro”. reflex is also known as the startle reflex. It is elicited by a sudden loss of support or loud noise, causing the newborn to throw their arms and legs out and then bring them back in. This reflex usually disappears around 3 to 4 months of age.
Choice D rationale:
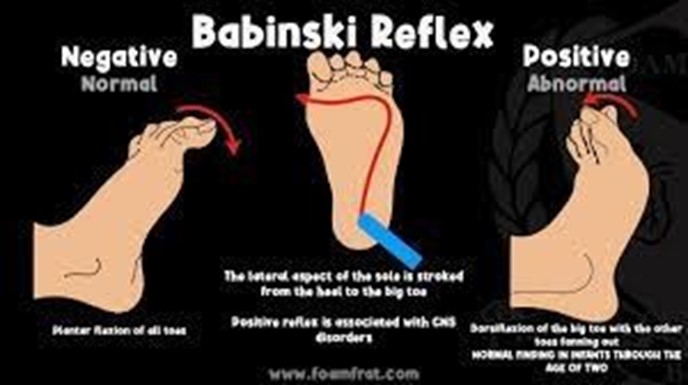
The "Babinski”. reflex is characterized by the extension of the big toe and fanning of the other toes when the sole of the foot is stroked. This reflex is present in newborns and should disappear by around 12 months of age.
Choice E rationale:
"Running”. is not a recognized newborn reflex. There is no reflex with this name related to newborns.
Choice F rationale:
The "gag”. reflex is present in newborns and helps protect the airway by causing a gagging response when the back of the throat is stimulated.
You just viewed 10 questions out of the 48 questions on the ATI Custom Maternity Newborncare Proctored Exam Exam. Subscribe to our Premium Package to obtain access on all the questions and have unlimited access on all Exams. Subscribe Now



