Please set your exam date
Newborn Nutrition
Study Questions
More Questions
A nurse is caring for a newborn who has jaundice and is receiving phototherapy.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Cover the newborn’s eyes with a mask or shield.This is because phototherapy can cause eye damage and the mask or shield protects the newborn’s eyes from the light.
Some additional explanations are:
• Choice A is wrong because increasing fluid intake by 25% to prevent dehydration is not necessary for a newborn receiving phototherapy.The newborn should be fed on demand or according to a regular schedule and monitored for signs of dehydration such as poor skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, sunken fontanels, and decreased urine output.
• Choice C is wrong because applying lotion or oil to the newborn’s skin to prevent drying is not recommended for a newborn receiving phototherapy.Lotion or oil can increase the absorption of light and cause skin burns.
• Choice D is wrong because turning off the phototherapy lights during feedings is not advised for a newborn receiving phototherapy.The lights should be on continuously to maximize the effectiveness of the treatment and reduce the duration of exposure.
A nurse is preparing to bottle feed a newborn who is formula fed.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Hold the newborn in a semi-upright position during feeding.This prevents the formula from flowing back into the baby’s ears and causing infections.It also helps the baby swallow less air and reduces the risk of choking.
Choice A is wrong because warming the formula in a microwave oven can create hot spots that can burn the baby’s mouth.The formula should be warmed by running it under warm tap water or placing it in a bowl of warm water.
Choice B is wrong because discarding any unused formula after 2 hours at room temperature is too long.Bacteria can grow rapidly in warm milk that is left sitting out and unused.The formula should be discarded after one hour at room temperature or within 24 hours if refrigerated.
Choice D is wrong because burping the newborn after finishing each ounce of formula is not necessary.Burping can interrupt the feeding and make the baby lose interest in finishing the bottle.The baby should be burped only when they show signs of discomfort or after finishing the feeding.
Normal ranges for formula intake vary depending on the baby’s age, weight and appetite.In general, newborn babies need around 150 to 200 ml per kilo of their weight a day until they’re 6 months old.The baby should be fed when they show signs of hunger, such as rooting, sucking or crying, and not forced to finish the bottle if they are full.
A nurse is reviewing laboratory results for a newborn who is breastfed.
Which of the following findings indicates adequate nutrition?
Explanation
Hemoglobin level of 11 g/dL.This is within the normal range for a newborn, which is 13.4-19.9 g/dL for the first month.
Hemoglobin is the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells.
Choice B is wrong because serum calcium level of 8 mg/dL is below the normal range for a newborn, which is 8.5-10.6 mg/dL for the first month.
Calcium is important for bone health and muscle function.
Choice C is wrong because serum bilirubin level of 15 mg/dL is above the normal range for a newborn, which is less than 12 mg/dL for the first week.
Bilirubin is a waste product from the breakdown of red blood cells.
High levels can cause jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Choice D is wrong because serum sodium level of 130 mEq/L is below the normal range for a newborn, which is 135-145 mEq/L.
Sodium is an electrolyte that helps regulate fluid balance and nerve impulses.
A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has dumping syndrome due to gastric bypass surgery.
Which of the following dietary modifications should the nurse recommend?
Explanation
Eat small, frequent meals throughout the day.This will help prevent dumping syndrome, which is a condition that occurs when food moves too fast from the stomach to the duodenum, causing symptoms such as abdominal cramps, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, flushing, dizziness and rapid heart rate.Eating small, frequent meals will reduce the amount of food that enters the small intestine at once and slow down gastric emptying.
Choice B is wrong because drinking fluids with meals rather than between meals will increase the volume of food that enters the small intestine and worsen dumping syndrome symptoms.Fluids should be consumed at least 30 minutes after a meal.
Choice C is wrong because increasing intake of simple carbohydrates such as fruit juice will cause a rapid rise and fall of blood sugar levels, leading to late dumping syndrome symptoms such as sweating, hunger, low blood sugar, fatigue, dizziness and weakness.Simple carbohydrates should be avoided and replaced with complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, fruits and vegetables.
Choice D is wrong because avoiding foods that are high in fat and protein will not help prevent dumping syndrome.In fact, fat and protein can slow down gastric emptying and stabilize blood sugar levels.A moderate amount of fat and protein should be included in each meal.However, too much fat at one time can have the opposite effect and trigger dumping syndrome symptoms.
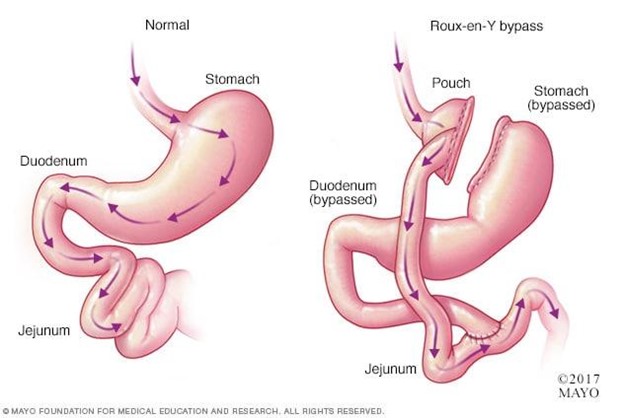
A nurse is evaluating a client’s understanding of a low-purine diet for gout management.
Which of the following food choices by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
Grilled cheese sandwich with tomato soup.This food choice indicates an understanding of the teaching because it is low in purines, which are chemicals that break down into uric acid and can trigger gout attacks.
Some additional information for the response are:
• Choice A.Liver and onions with mashed potatoes is wrong because liver is an organ meat that is high in purines and should be avoided by people with gout.
• Choice C.Roast beef with green beans and rice is wrong because roast beef is a red meat that is high in purines and should be limited by people with gout.
• Choice D.Sardines on whole wheat crackers with cheese is wrong because sardines are a type of oily fish that is high in purines and should be avoided by people with gout.
• A low-purine diet for gout management should include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and low-fat dairy products.It should also limit sugar, alcohol, and meat consumption.

A nurse is assisting a postpartum client who is breastfeeding her newborn for the first time 2 hr after birth.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
The nurse should assess for proper latch-on technique and encourage skin-to-skin contact between mother and infant.
These actions promote successful breastfeeding and bonding.
Choice C is wrong because limiting feeding time to 10 min per breast can interfere with the infant’s intake of hindmilk, which is rich in fat and calories.The infant should be allowed to nurse until satisfied, which may take longer than 10 min per breast.
Choice D is wrong because instructing the client to offer both breasts at each feeding can lead to nipple soreness and engorgement.The client should offer one breast until it is emptied, then switch to the other breast if the infant is still hungry.
Choice E is wrong because advising the client to feed the infant every 2 to 3 hr can disrupt the infant’s natural feeding cues and rhythms.The client should feed the infant on demand, which may be more or less frequent than every 2 to 3 hr.
A nurse is reviewing discharge instructions with a postpartum client who plans to breastfeed her newborn exclusively for at least 6 months.
Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
I will drink at least eight glasses of water every day.This statement indicates that the client understands the importance of hydration for breast milk production and the prevention of constipation.
Some possible explanations for the other choices are:
• Choice A is wrong because iron supplements are not necessary for breastfeeding mothers unless they have anemia.Iron supplements can also cause constipation and stomach upset in some women.
• Choice C is wrong because dairy products are not harmful for breastfeeding mothers or their infants, unless there is a history of allergy or intolerance.Dairy products can provide calcium, protein and vitamin D for the mother and the infant.
• Choice D is wrong because infants should not be given any solid foods before 6 months of age, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics.Introducing solids too early can interfere with breastfeeding, increase the risk of allergies and infections, and cause choking or aspiration.
A nurse is caring for a newborn who was born at 38 weeks of gestation, weighs 3 kg (6 lb 10 oz), and is receiving formula feedings every 3 hr.
The nurse should expect that at each feeding this newborn will consume how many mL?
Explanation
90 mL.According to the CDC, babies who are only getting infant formula and no breast milk need about2.5 ounces (75 mL) of formula per pound of body weight each day.
A newborn who weighs 3 kg (6 lb 10 oz) would need about15 ounces (450 mL) of formula per day, divided into 8 to 12 feedings.
This means that at each feeding, the newborn would consume about90 mLof formula.
Choice A is wrong because30 mLis too little for a newborn who weighs 3 kg.
This would only provide about10 ounces (300 mL) of formula per day, which is not enough for adequate growth and development.
Choice B is wrong because60 mLis also too little for a newborn who weighs 3 kg.
This would only provide about20 ounces (600 mL) of formula per day, which is still below the recommended amount.
Choice D is wrong because120 mLis too much for a newborn who weighs 3 kg.This would provide about40 ounces (1200 mL) of formula per day, which is more than the maximum amount of32 ouncesthat most babies need before they start solids.
Overfeeding can cause problems such as spitting up, gas, and obesity.
A nurse is assessing a postpartum client who delivered vaginally without complications and has chosen not to breastfeed her newborn infant.
Which of these findings would indicate that lactation suppression has been successful?
Explanation
Breasts are soft without engorgement or leakage.This indicates that lactation suppression has been successful and the woman is not experiencing any discomfort or risk of infection from milk accumulation.
Breasts are firm with mild tenderness or leakage is wrong because it suggests that lactation is still occurring and the woman may need to express some milk for comfort or use other non-pharmacological methods to suppress it.
Breasts are hard with moderate pain or leakage is wrong because it indicates that the woman is suffering from breast engorgement, which can lead to mastitis if not treated.The woman may need pharmacological intervention to suppress lactation and relieve pain.
Breasts are swollen with severe pain or leakage is wrong because it shows that the woman has developed mastitis, which is a bacterial infection of the breast tissue that requires antibiotics and analgesics.The woman may also need to drain the infected breast by expressing milk or using a pump.
Normal ranges for lactation suppression vary depending on the individual and the method used.Generally, lactation suppression can take from a few days to a few weeks.
A nurse is assessing a postpartum client who delivered vaginally without complications and has chosen not to breastfeed her newborn infant.
Which of these findings would indicate that lactation suppression has been successful?
Explanation
Breasts are soft without engorgement or leakage.This indicates that lactation suppression has been successful and the woman is not experiencing any discomfort or risk of infection from milk accumulation.
Breasts are firm with mild tenderness or leakage is wrong because it suggests that lactation is still occurring and the woman may need to express some milk for comfort or use other non-pharmacological methods to suppress it.
Breasts are hard with moderate pain or leakage is wrong because it indicates that the woman is suffering from breast engorgement, which can lead to mastitis if not treated.The woman may need pharmacological intervention to suppress lactation and relieve pain.
Breasts are swollen with severe pain or leakage is wrong because it shows that the woman has developed mastitis, which is a bacterial infection of the breast tissue that requires antibiotics and analgesics.The woman may also need to drain the infected breast by expressing milk or using a pump.
Normal ranges for lactation suppression vary depending on the individual and the method used.Generally, lactation suppression can take from a few days to a few weeks.
A nurse is teaching a group of parents about infant nutrition.
The nurse explains that iron-fortified infant formula is recommended for infants who are not breastfed because:
Explanation
Iron is essential for brain development.Iron helps red blood cells carry oxygen through the body and supports a child’s ability to learn.Iron deficiency can cause anemia, which is when there are not enough red blood cells in the body or the child’s ability to carry oxygen throughout the body is lowered.
Choice B is wrong because iron does not prevent constipation in infants.In fact, iron-fortified formula may cause constipation in some infants.
Choice C is wrong because iron does not enhance immune system function.Iron is important for hemoglobin production, but it does not directly affect the immune system.
Choice D is wrong because iron does not improve skin color and tone.Iron deficiency can cause pale skin, but iron supplementation does not change the natural color or tone of the skin.
A nurse is caring for a newborn who is receiving breast milk and supplemental vitamin D drops daily.
The nurse knows that vitamin D supplementation is necessary for breastfed infants because:
Explanation
Breast milk does not contain enough vitamin D for bone health.Vitamin D is needed to support healthy bone development and to prevent rickets, a condition that causes weak or deformed bones.Breast milk alone does not provide infants with an adequate amount of vitamin D.The Dietary Guidelines for Americans and American Academy of Pediatrics recommend breastfed and partially breastfed infants be supplemented with 400 IU per day of vitamin D beginning in the first few days of life.
Choice B is wrong because breast milk does not interfere with vitamin D absorption from sunlight.However, reducing sun exposure is important for preventing skin cancer, and other factors such as clothing, air pollution, and skin type can also decrease the amount of vitamin D a person can make from sunlight.
Choice C is wrong because breast milk does not increase vitamin D excretion in urine.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is stored in the body and not easily lost in urine.
Choice D is wrong because breast milk does not inhibit vitamin D synthesis in the liver.Vitamin D is synthesized in the skin from exposure to sunlight, and then activated in the liver and kidneys to its active form.
Breast milk does not affect this process.
A nurse is preparing to administer an oral liquid medication to a 3-month-old infant who is receiving powdered infant formula.
The nurse should:
Explanation
Use an oral syringe to squirt the medication into the side of the mouth.
This is because an oral syringe allows the nurse to measure the exact dose of the medication and deliver it slowly and safely into the infant’s mouth, avoiding choking or aspiration.
The other choices are wrong for the following reasons:
• Choice A) Mixing the medication with formula in a bottle can alter the taste and effectiveness of the medication, and also make it difficult to ensure that the infant receives the full dose.
• Choice C) Placing the medication on a pacifier can cause the infant to spit out the pacifier or the medication, and also increase the risk of infection from contaminated pacifiers.
• Choice D) Dipping a cotton swab in the medication and rubbing it on the gums can irritate the oral mucosa and cause pain or bleeding, and also waste some of the medication on the swab.
A nurse is planning to introduce complementary foods to an infant who is six months old and exclusively breastfed.
Which of the following foods should the nurse recommend as a good source of zinc?
Explanation
Meat is a good source of zinc for infants who are six months old and exclusively breastfed.Zinc is a mineral that is important for immune function, wound healing, and the senses of smell and taste.Children 7 to 24 months need 3 mg of zinc each day.
Choice B is wrong because yogurt is not a good source of zinc for infants.Yogurt is a dairy product that contains some zinc, but not as much as meat.
Choice C is wrong because broccoli is not a good source of zinc for infants.Broccoli is a vegetable that contains very little zinc.
Choice D is wrong because mango is not a good source of zinc for infants.Mango is a fruit that contains almost no zinc.
A nurse is educating a mother about complementary feeding for her infant who is eight months old.
Which of the following statements by the mother indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
“I will give my baby soft finger foods that he can pick up and eat by himself.” This statement indicates an understanding of the teaching because it shows that the mother knows how to provide appropriate complementary foods for her infant who is eight months old.Complementary feeding, also known as weaning, mixed feeding or introduction of solid foods, should begin for infants by six months of age (26 weeks) but not before 17 weeks.Breast milk or infant formula should continue during the complementary feeding period with amounts gradually reduced as the variety of foods increases.WHO and UNICEF recommend that infants start receiving complementary foods at 6 months of age in addition to breast milk.Initially, they should receive complementary foods 2–3 times a day between 6–8 months and increase to 3–4 times daily between 9–11 months and 12–24 months of age.Complementary foods should be nutritionally adequate, safe, and properly fed.
Choice A is wrong because pureed foods are not suitable for an eight-month-old infant who can handle more textured foods.
Pureed foods are recommended for infants who are just starting complementary feeding at around six
A nurse is reviewing the dietary intake of an infant who is receiving complementary foods and drinks along with breast milk.
Which of the following foods should the nurse instruct the mother to limit or avoid to prevent dental caries?
Explanation
Honey should be limited or avoided to prevent dental caries in infants.
Honey is a type of sugar that can feed the bacteria that cause cavities, especially if it is left on the teeth for a long time.Honey can also contain spores of a bacterium that can cause botulism, a serious illness, in infants.
Choice B is wrong because cheese is not a risk factor for dental caries in infants.Cheese can actually help prevent cavities by stimulating saliva production and neutralizing acids in the mouth.
Choice C is wrong because avocado is not a risk factor for dental caries in infants.Avocado is a healthy fat that does not contain sugars that can feed cavity-causing bacteria.
Choice D is wrong because green leafy vegetables are not a risk factor for dental caries in infants.Green leafy vegetables are rich in vitamins and minerals that can support oral health and general health.
A nurse is promoting exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life and continued breastfeeding for up to two years or beyond.
Which of the following benefits of breastfeeding should the nurse include in her education?
Explanation
Breastfeeding provides optimal nutrition and immunological protection for infants.This is because breastmilk contains all the energy and nutrients that the infant needs for the first six months of life, and it also contains antibodies that help protect against many common childhood illnesses.
Choice A is wrong because breastfeeding reduces the risk of infections, allergies, and chronic diseases in infants and children, but this is not the only benefit of breastfeeding.Breastfeeding also has benefits for mothers, such as reducing the risk of breast and ovarian cancers.
Choice B is wrong because breastfeeding enhances maternal-infant bonding and attachment, but this is not the only benefit of breastfeeding.Breastfeeding also has benefits for the environment, such as reducing waste and greenhouse gas emissions.
Choice C is wrong because breastfeeding helps mothers lose weight and prevent postpartum hemorrhage, but this is not the only benefit of breastfeeding.Breastfeeding also has benefits for society, such as reducing health care costs and improving productivity.
A nurse is supporting a mother to continue breastfeeding or formula feeding when she returns to work or school.
Which of the following strategies should the nurse suggest to help the mother maintain her milk supply?
Explanation
The nurse should suggest all of these strategies to help the mother maintain her milk supply when she returns to work or school.
Choice A is correct because pumping or expressing milk at least every 3 to 4 hours during work or school hours stimulates the production of prolactin, the hormone that regulates milk synthesis.
Choice B is correct because storing milk in clean glass or plastic containers with tight-fitting lids in a refrigerator or freezer preserves the quality and safety of the milk.
Choice C is correct because labeling milk containers with the date and time of expression and using them in order of oldest to newest ensures that the milk is used before it spoils.
Choice D is correct because it includes all of the above strategies.
A nurse is referring a mother and her infant to specialized care for severe diseases or complications related to nutrition and feeding.
Which of the following conditions would warrant such a referral?
Explanation
All of these conditions would warrant a referral to specialized care for severe diseases or complications related to nutrition and feeding.
Choice A is wrong because phenylketonuria (PKU) in the infant is a genetic disorder that causes an amino acid called phenylalanine to build up in the body.This can lead to intellectual disability, seizures, and other neurological problems if not treated with a special diet that limits phenylalanine.
Choice B is wrong because gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in the mother is a condition where the mother has high blood sugar levels during pregnancy.This can increase the risk of complications for both the mother and the baby, such as preeclampsia, macrosomia, birth injuries, and neonatal hypoglycemia.
Choice C is wrong because cleft lip or palate in the infant is a birth defect where the upper lip or roof of the mouth does not form properly.This can affect the infant’s ability to feed, speak, and breathe, and may require surgery and other interventions.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching about growth and development evaluation to a group of parents of preschoolers.
Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Growth and development evaluation should be done annually until adulthood, plotted on appropriate growth charts and compared with expected norms for age and sex, and used to identify any deviations from normal or expected patterns of growth and development.
Choice A is wrong because growth and development evaluation should not be done only annually, but also at specific ages recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), such as 9 months, 18 months, 24 months, and 30 months.
Choice B is wrong because growth and development evaluation should not only be plotted on appropriate growth charts and compared with expected norms for age and sex, but also include developmental milestones in playing, learning, speaking, behaving, and moving.
Choice C is wrong because growth and development evaluation should not only be used to identify any deviations from normal or expected patterns of growth and development, but also to monitor the child’s progress and provide early intervention if needed.
A nurse is assessing an 18-month-old toddler’s gross motor development during a well-child visit.
Which of the following actions by the toddler indicates normal development?
Explanation
Runs with a wide stance.This indicates normal gross motor development for an 18-month-old toddler.Gross motor skills are the abilities to use large muscles for movements such as walking, running, jumping, and climbing.
Choice A is wrong because walking up and down stairs with assistance is a skill that most toddlers can do by 24 months.
Choice C is wrong because kicking a ball forward without falling is a skill that most toddlers can do by 24 months.
Choice D is wrong because jumping in place with both feet is a skill that most toddlers can do by 30 months.
A nurse is collecting data from a 3-year-old child during a well-child visit.
Which of the following findings should alert the nurse to a possible developmental delay?
Explanation
The child has frequent temper tantrums.This is because temper tantrums are not a normal part of a 3-year-old child’s development and can indicate emotional or behavioral problems.According to the height and weight chart for children, a 3-year-old child should be able to do the following:
• Speak in three-word sentences
• Copy a circle with a crayon
• Ride a tricycle using pedals
Therefore, choices A, B and C are wrong because they are expected developmental milestones for a 3-year-old child.
A nurse should collect data from the child and the parents to determine the cause and frequency of the temper tantrums and provide appropriate interventions and referrals.
Introduction
A nurse is teaching a new mother about the benefits of breastfeeding.
Which of the following statements by the nurse is correct?
Explanation
Breastfeeding reduces the risk of infection by providing IgA antibodies and other immune factors.These antibodies help the baby fight off viruses and bacteria by forming a protective layer in the baby’s nose, throat, and digestive system.Breastfeeding also lowers the baby’s risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), obesity, and cardiovascular disease in adulthood.
Choice B is wrong because breastfeeding does not promote rapid brain growth due to large amounts of protein and fat.Breast milk contains the right amount of nutrients for the baby’s needs, but it does not have more protein and fat than formula.
Choice C is wrong because breastfeeding does not require iron supplementation for the newborn after 3 months of age.Breast milk has enough iron for the baby’s first 6 months of life, and after that solid foods can provide additional iron.
Choice D is wrong because breastfeeding is recommended exclusively for the first 6 months of age by the American Academy of Pediatrics, not 4 months.After 6 months, breastfeeding can continue along with solid foods until at least 1 year or longer.
A nurse is assessing a newborn who is formula fed.
Which of the following findings indicates adequate hydration?
Explanation
Pale yellow or clear urine indicates adequate hydration in a newborn.
The other choices are wrong because:
• Choice A: Weight loss of 8% in the first week is excessive and may indicate dehydration or inadequate feeding.
• Choice B: Urine output of 1 to 2 mL/kg/hr is too low for a newborn.The normal range is 2 to 5 mL/kg/hr.
• Choice C: Sunken fontanels and dry mucous membranes are signs of dehydration and should be reported to the provider.
Normal ranges for urine output vary by age.For a newborn, the normal range is 2 to 5 mL/kg/hr.
For a toddler, it is 1.5 mL/kg/hr, and for an older child

A nurse is planning to feed a newborn who is breastfed.
Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Explanation
Feed the newborn when he shows signs of hunger, such as rooting or sucking.This is the best way to ensure that the newborn gets enough breast milk and that the mother’s milk supply is maintained.Breastfeeding on demand also helps prevent engorgement and mastitis.
Choice A is wrong because feeding the newborn every 4 to 5 hours during the day and night is too infrequent and may lead to insufficient weight gain, dehydration, jaundice, and low milk supply.Breastfed newborns should be fed at least every 2 to 3 hours or 8 to 12 times in 24 hours.
Choice B is wrong because feeding the newborn on one breast for 10 minutes and then switching to the other breast may not allow the newborn to get enough of the hindmilk, which is richer in fat and calories than the foremilk.The newborn should be allowed to nurse on one breast until it is emptied or until the baby releases it, and then offered the other breast.
Choice D is wrong because feeding the newborn 4 to 5 ounces of breast milk per feeding is too much for a newborn’s stomach capacity and may cause overfeeding, spitting up, or colic.
A nurse is calculating the fluid intake for a healthy newborn who weighs 3 kg.
How much fluid does the newborn need per day?
Explanation
360 to 504 mL.This is because the fluid intake for a healthy newborn is about120 to 168 mL/kg/day.
Since the newborn weighs 3 kg, the fluid intake per day is 3 x 120 to 3 x 168 mL, which equals 360 to 504 mL.
Choice A is wrong because 300 to 420 mL is too low for a 3 kg newborn.
Choice B is wrong because 330 to 462 mL is also too low for a 3 kg newborn.
Choice D is wrong because 390 to 546 mL is too high for a 3 kg newborn.
Normal ranges for fluid intake vary depending on the age and weight of the infant.For example, infants 0–6 months of age need about700 mLof fluid per day, assumed to be from milk.Infants 7–12 months of age need about800 mLof fluid per day from milk and complementary foods and beverages.Children 1–3 years of age need about1300 mLof fluid per day.
A nurse is providing teaching to a mother who is breastfeeding and is a vegetarian who excludes meat, fish, and dairy products from her diet.
Which of the following supplements should the nurse recommend for the mother to provide to her newborn?
Explanation
Vitamin B12.The mother should provide vitamin B12 supplements to her newborn because vitamin B12 is only found in animal products and is essential for the development of the nervous system and the production of red blood cells.A deficiency of vitamin B12 can cause anemia, weakness, fatigue, and neurological problems.
Choice A is wrong because vitamin D can be obtained from sunlight exposure, fortified foods, or supplements.
The mother and the newborn should get enough vitamin D from these sources.
Choice C is wrong because vitamin C is abundant in plant foods, such as fruits and vegetables.
The mother and the newborn should get enough vitamin C from their diet.
Choice D is wrong because vitamin K is produced by bacteria in the gut and is also found in green leafy vegetables.
The mother and the newborn should get enough vitamin K from these sources.However, all newborns are given a vitamin K injection at birth to prevent bleeding disorders.
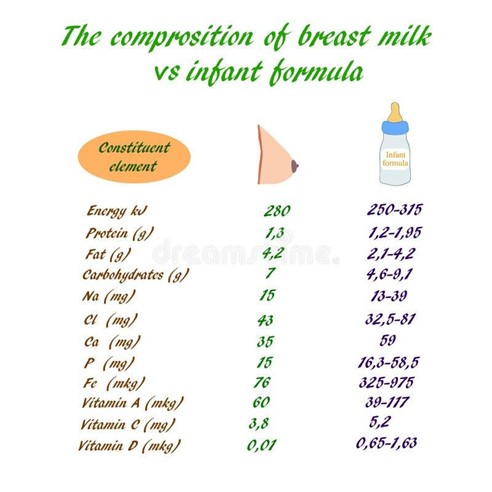
Breast Milk
A nurse is teaching a postpartum client about the benefits of breastfeeding.
Which of the following statements by the client indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
Breastfeeding will make my baby smarter and more attached to me.
This statement indicates a need for further teaching because it is not based on scientific evidence and may create unrealistic expectations for the mother and the baby.Breastfeeding does not directly affect the baby’s intelligence or attachment, although it may provide some benefits for cognitive development and bonding.
Choice A is wrong because breastfeeding will help the uterus contract and reduce bleeding.This is a benefit of breastfeeding that helps the mother recover from childbirth and prevent postpartum hemorrhage.
Choice B is wrong because breastfeeding will lower the risk of breast and ovarian cancer.This is another benefit of breastfeeding that reduces the mother’s exposure to estrogen and other hormones that may promote cancer growth.
Choice C is wrong because breastfeeding will protect the baby from infections and allergies.This is a benefit of breastfeeding that provides the baby with antibodies and other immune factors that help fight off diseases and reduce the risk of allergies.
A nurse is assessing a newborn who is breastfeeding for the first time.
The nurse observes that the newborn’s nose, cheeks, and chin are touching the mother’s breast during feeding.
What should the nurse do next?
Explanation
Encourage the mother to continue feeding as usual.This is because the newborn’s nose, cheeks, and chin touching the mother’s breast during feeding indicates a good latch and positioning.A good latch and positioning help the baby to get enough milk and prevent nipple soreness for the mother.
Choice A is wrong because repositioning the newborn to avoid suffocation is not necessary.The newborn’s nose should not be squashed against the mother’s breast, but it should be clear and able to breathe.
Choice C is wrong because instructing the mother to burp the newborn frequently is not related to the newborn’s latch and positioning.Burping the newborn may help to release air that they swallow during feeding, but it does not affect how well they feed.
Choice D is wrong because suggesting the mother to switch to another position is not helpful.The mother may use different positions to breastfeed, but the most important thing is that the baby is well attached and comfortable.If the mother and baby are happy with their current position, there is no need to change it.

A nurse is caring for a postpartum client who had a cesarean section and is breastfeeding her newborn.
The nurse notices that the client is holding her newborn in a football hold position.
What is an appropriate response by the nurse?
Explanation
Praise the client for choosing a suitable position for breastfeeding.The football hold is a common and comfortable breastfeeding position that allows the mother to support the baby’s head and help with latching.It is especially good for mothers who had a cesarean section, have large breasts, or are breastfeeding twins.
Choice B is wrong because there is no need to change to a cradle hold position if the mother and baby are comfortable with the football hold.
Different positions may work better for different mothers and babies.
Choice C is wrong because the mother does not need to support her breast with her hand during feeding.
This may interfere with the baby’s latch and cause nipple soreness.
Choice D is wrong because asking the client if she is experiencing pain or discomfort in her incision may imply that she is doing something wrong by holding her baby in that position.
It may also make the mother feel anxious or guilty about her pain.
The nurse should assess the incision site regularly and provide pain relief as needed, but not question the mother’s choice of breastfeeding position.
A nurse is educating a pregnant client about the phases of lactation and breast milk composition.
The nurse explains that colostrum is the first milk produced during pregnancy and the first few days postpartum.
Which of the following information should the nurse include about colostrum? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A, C, D, and E. Here is why:
• Choice A is correct because colostrum is thick, yellowish, and high in protein, vitamins, minerals, immune cells, and immunoglobulins.Immunoglobulins are antibodies that provide passive immunity to the newborn.
• Choice B is wrong because it describes the characteristics of mature milk, not colostrum.Mature milk is thin, whiter, and higher in fat, carbohydrates, lactose, water, vitamins, immunoglobulins, and growth factors.
• Choice C is correct because colostrum protects the infant’s gastrointestinal tract from infections and helps establish normal flora.Normal flora are beneficial bacteria that aid in digestion and immunity.
• Choice D is correct because colostrum has a laxative effect that helps clear meconium and prevent jaundice.Meconium is the first stool of the newborn, which contains waste products from the fetal life.Jaundice is a yellowing of the skin and eyes caused by excess bilirubin, a breakdown product of red blood cells.
• Choice E is correct because colostrum meets all the nutritional needs of the newborn during the first few days of life.Colostrum is rich in calories and nutrients and provides adequate hydration to the newborn.
A nurse is counseling a breastfeeding mother about her dietary intake.
The nurse informs the mother that she should consume enough calories, fluids, protein, calcium, iron, folate, vitamin B12, vitamin D, iodine, selenium, zinc, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants to support milk production and quality.
Which of the following foods should the nurse recommend to the mother as good sources of these nutrients? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A, B and E.These foods are good sources of protein, calcium, iron, folate, vitamin B12, vitamin D, iodine, selenium, zinc, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants that are essential for milk production and quality.
Choice C is wrong because coffee, tea, soda, energy drinks, chocolate, and alcohol are not nutritious foods and can have negative effects on the mother and the baby.They can cause dehydration, irritability, insomnia, poor weight gain, and fetal alcohol syndrome.
Choice D is wrong because whole grains, fruits, vegetables, vegetable oils, and herbs are not sufficient to provide all the nutrients needed by the mother and the baby.They are good sources of carbohydrates, fiber, vitamin C, vitamin E, and phytochemicals, but they lack protein, calcium, iron, folate, vitamin B12, vitamin D, iodine, selenium, and zinc.
The normal ranges for these nutrients are:
• Protein: 71 g/day for lactating women
• Calcium: 1000 mg/day for lactating women
• Iron: 9 mg/day for lactating women
• Folate: 500 mcg/day for lactating women
• Vitamin B12: 2.8 mcg/day for lactating women
• Vitamin D: 15 mcg/day for lactating women
• Iodine: 290 mcg/day for lactating women
• Selenium: 70 mcg/day for lactating women
• Zinc: 12 mg/day for lactating women
• Omega-3 fatty acids: 1.3 g/day for lactating women
• Antioxidants: no specific recommendation but fruits and vegetables are good sources
Infant formula
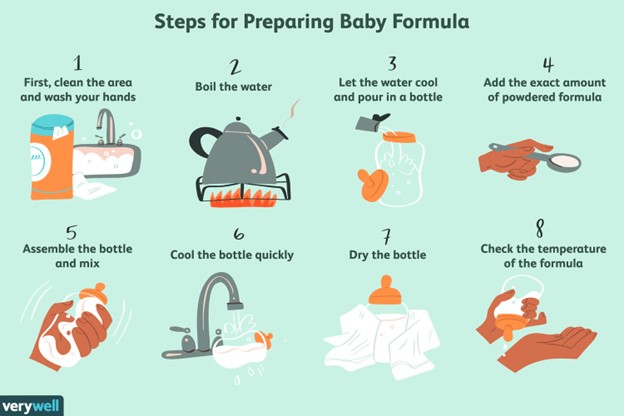
A nurse is teaching a new mother how to prepare powdered infant formula for her baby.
Which of the following instructions should the nurse include?
Explanation
Shake the bottle well to dissolve any clumps.
This is because clumps of powder can clog the nipple and make it hard for the baby to drink.Clumps can also cause inaccurate measurements of formula and water, which can affect the baby’s nutrition and hydration.
Choice A is wrong because tap water may contain harmful bacteria or contaminants that can cause infections or illnesses in the baby.Tap water should be boiled first and then cooled to kill any germs before mixing with powdered formula.
Choice B is wrong because one scoop of powder should be mixed with one ounce of water, not two.
Mixing too much water with the powder can dilute the formula and make it less nutritious for the baby.Mixing too little water can make the formula too concentrated and cause dehydration or kidney problems in the baby.
Choice D is wrong because leftover formula should not be stored at room temperature for more than one hour.
Bacteria can grow quickly in warm formula and make the baby sick.Leftover formula should be discarded or refrigerated immediately and used within 24 hours.
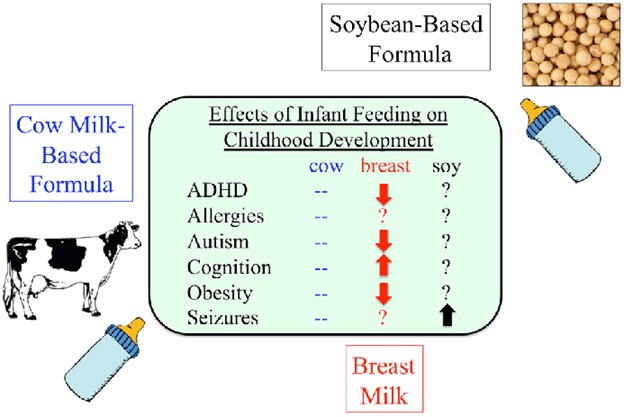
A client is considering switching from breast milk to soy-based infant formula for her 4-month-old infant who has a cow’s milk allergy.
What should the nurse inform the client about soy-based infant formula?
Explanation
It may increase the risk of developing peanut allergy later in life.According to a study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, infants who were fed soy-based formula had a higher risk of developing peanut allergy than those who were fed cow’s milk formula or breast milk.
This may be because soy and peanut are both legumes and share some common proteins that can trigger allergic reactions.
Choice A is wrong because soy-based formula may causelessgas and bloating than cow’s milk formula, since it does not contain lactose, which some babies have trouble digesting.
Choice C is wrong because soy-based formula provides adequate iron and calcium for the infant’s growth, as well as other nutrients such as protein, fat, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals.Soy-based formula is also fortified with iron to prevent iron deficiency anemia.
Choice D is wrong because soy-based formula does not interfere with thyroid function and hormone synthesis in healthy infants.However, infants with congenital hypothyroidism who are taking thyroid medication may need to adjust their dosage if they are fed soy-based formula, since soy can affect the absorption of the medication.
Therefore, these infants should be monitored closely by their doctor.
A nurse is assessing a 6-month-old infant who is exclusively fed with ready-to-use infant formula.
Which of the following findings should alert the nurse to a possible complication of this type of formula?
Explanation
Dental caries, also known as tooth decay or cavities, are a possible complication of ready-to-use infant formula.This type of formula is a liquid breast milk substitute that does not need to be mixed with water and is sterile and safe for babies.However, it may contain more sugar than powdered or concentrated formula and can cause tooth decay if the baby’s teeth are exposed to it for long periods of time.For example, if the baby falls asleep with a bottle of ready-to-use formula in his or her mouth, the sugar can pool around the teeth and erode the enamel.To prevent dental caries, the baby should not be put to bed with a bottle of formula and should have his or her teeth cleaned regularly with a soft cloth or a baby toothbrush.
Choice A is wrong because poor weight gain is not a complication of ready-to-use infant formula.This type of formula provides adequate nutrition and calories for normal growth and development of infants.Poor weight gain may be caused by other factors, such as illness, feeding difficulties, or inadequate intake.
Choice C is wrong because iron deficiency anemia is not a complication of ready-to-use infant formula.This type of formula is fortified with iron and can prevent or treat iron deficiency anemia in infants who are not breastfed or are partially breastfed.
Iron deficiency anemia may be caused by other factors, such as blood loss, infection, or low iron intake from complementary foods.
Choice D is wrong because constipation is not a complication of ready-to-use infant formula.This type of formula has a similar composition and consistency to powdered or concentrated formula and does not cause constipation in infants.
Constipation may be caused by other factors, such as dehydration, low fiber intake, or medication.
A nurse is caring for a 9-month-old infant who has diarrhea and dehydration due to gastroenteritis.
The infant’s mother asks if she can continue to feed her baby with liquid concentrate formula diluted with water.
How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
The nurse should advise the mother to stop feeding her baby with diluted formula and switch to undiluted formula or breast milk.This is because diluted formula does not provide enough calories and nutrients for the infant and may worsen the dehydration by increasing the osmotic load in the gut.Undiluted formula or breast milk can help maintain the infant’s nutrition and hydration status while also providing some protection against infection.
Choice A is wrong because diluted formula is not recommended for infants with diarrhea and dehydration, and oral rehydration solution (ORS) should be given in addition to, not instead of, breast milk or formula.
Choice B is wrong because oral rehydration solution alone is not sufficient to meet the infant’s nutritional needs and may lead to weight loss and malnutrition.ORS should be used to correct fluid and electrolyte losses, but not as the sole source of hydration.
Choice C is wrong because adding sugar and salt to diluted formula is dangerous and can cause serious complications such as hypernatremia, hyponatremia, hyperglycemia, or cerebral edema.ORS has a specific concentration of sugar and electrolytes that has been shown to increase the absorption of fluid and electrolytes in the gut.
A nurse is reviewing the label of a powdered infant formula with a parent who wants to know what ingredients are in it.
The nurse explains that most powdered infant formulas are made from modified cow’s milk or soy protein that contain added nutrients such as:
Explanation
Vitamins, minerals, and carbohydrates.Most powdered infant formulas are made from modified cow’s milk or soy protein that contain added nutrients such as proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals.Carbohydrates are usually from lactose, glucose, or corn syrup, and they supply calories and sweetness.Vitamins and minerals are added to meet the nutritional requirements of infants.
Choice A is wrong because antibodies, enzymes, and growth factors are not added to powdered infant formulas.These are components of breast milk that help protect the baby from infections and support digestion and development.
Choice C is wrong because hormones, probiotics, and antioxidants are not added to powdered infant formulas.Hormones are not needed for infant nutrition and may have adverse effects.Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that may help with gut health, but they are not required for infant formulas.Antioxidants are substances that protect cells from damage, but they are not added to infant formulas.
Choice D is wrong because fats, amino acids, and fiber are not added to powdered infant formulas.
Fats are usually from vegetable oils, and they provide energy and fatty acids
Feeding Cues and Patterns
A nurse is teaching a new mother about feeding cues for her newborn.
Which of the following statements by the mother indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
The mother should feed her baby when he shows early signs of hunger, such as sucking on his fingers, rooting, bringing his hand to his mouth, or opening and closing his mouth.
These are feeding cues that indicate the baby is ready to feed and will latch on well.
Choice B is wrong because sucking on fingers is an early sign of hunger and not a sign of needing further teaching.
Choice C is wrong because turning his head toward the breast is an early sign of hunger and not a sign of needing further teaching.
Choice D is wrong because opening and closing his mouth is an early sign of hunger and not a sign of needing further teaching.
Choice A is the only statement that indicates a need for further teaching because crying is a late sign of hunger and not an ideal time to feed the baby.
Crying can make it harder for the baby to latch on and feed effectively.The mother should try to feed her baby before he starts to cry by looking for the early signs of hunger
A nurse is assessing a 2-month-old infant who is bottle-fed.
The nurse observes that the infant pushes away the bottle and falls asleep after drinking 3 ounces of formula.
The nurse should recognize this as an example of which of the following feeding cues?
Explanation
Satiety cue.
A satiety cue is a sign that the infant is full and satisfied after feeding.Pushing away the bottle and falling asleep are examples of satiety cues.
Hunger cue is wrong because hunger cues are signs that the infant is hungry and wants to feed.Hunger cues include rooting, sucking, crying, and bringing hands to mouth.
Distress cue is wrong because distress cues are signs that the infant is upset or uncomfortable and needs soothing.Distress cues include arching back, turning away, grimacing, and fussing.
Discomfort cue is wrong because discomfort cues are signs that the infant is experiencing pain or physical discomfort and needs relief.Discomfort cues include squirming, flailing, grunting, and crying.
The normal range of formula intake for a 2-month-old infant is about 4 to 5 ounces per feeding, every 3 to 4 hours.
However, this may vary depending on the infant’s weight, growth rate, and individual needs.
The nurse should assess the infant’s growth and development, as well as the caregiver’s feeding practices and concerns.
A nurse is planning to teach a group of parents about feeding patterns for infants.
Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
Explanation
Newborns should be fed about 15 to 20 minutes per breast or 2 to 3 ounces per bottle.This is because breast milk or formula provides the optimal nutrition for newborns and they need about 110 kcal/kg/day for the first 3 months.
Choice A is wrong because newborns do not need to be fed every 2 to 3 hours during the day and night.They should be fed on cue, which means responding to their signs of hunger, such as sucking on fists, lip smacking, or fussing.
Feeding on cue can help establish a good milk supply and prevent overfeeding or underfeeding.
Choice C is wrong because newborns should not be fed on a strict schedule rather than on cue.Feeding on a schedule can interfere with the natural regulation of hunger and satiety cues and can lead to feeding problems later on.
Feeding on cue can also promote bonding and attachment between the parent and the newborn.
Choice D is wrong because newborns should be fed at least 6
A nurse is caring for a 4-month-old infant who is breastfed.
The mother reports that her baby feeds about six times a day and sleeps through the night.
The nurse should evaluate this feeding pattern as which of the following?
Explanation
Normal for the infant’s age and weight.According to the CDC, breastfed babies may feed as often as every 1 to 3 hours in the first days, and then about every 2 to 4 hours on average by 4 months of age.
The number of feedings may vary depending on the baby’s needs and cues.Breastfeeding six times a day and sleeping through the night is within the normal range for a 4-month-old infant who is breastfed.
Choice B is wrong because the infant’s growth rate and needs are not solely determined by the frequency of breastfeeding, but also by the amount of milk intake, weight gain, and diaper output.If the infant is gaining weight, seems content, and has several wet and dirty diapers a day, then he or she is likely getting enough breast milk.
Choice C is wrong because there is no evidence that the infant is overfed or overweight.Breastfed babies are less likely to overeat than formula-fed babies, as they can regulate their own milk intake according to their hunger and satiety signals.
The infant’s weight should be monitored by a pediatrician and compared to a growth chart for breastfed babies.
Choice D is wrong because there is no standard or regular feeding pattern for breastfed babies.Breastfeeding on demand, or following the baby’s cues, is recommended by the CDCand other health organizations.
The infant’s feeding pattern may change over time as he or she grows and starts eating solid foods.
The mother should not worry about the irregularity of the feeding pattern as long as the infant is healthy and thriving.
A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a newborn who weighs 3 kg (6 lb 10 oz) at birth.
The nurse should expect the newborn to have which of the following feeding patterns by day 10 of life?
Explanation
Feed every 2 hours and take 60 mL (2 oz) per feeding.This is because newborns need about 150 to 200 mL of formula per kilo of their weight a day until they’re 6 months old.
A newborn who weighs 3 kg would need about 450 to 600 mL of formula a day.
Dividing this by 24 hours, the newborn would need about 19 to 25 mL of formula per hour.
Feeding every 2 hours would provide about 38 to 50 mL of formula per feeding, which is close to the recommended amount of 60 mL (2 oz).
Choice A is wrong because feeding every 4 hours and taking 90 mL (3 oz) per feeding would provide too much formula at once and not enough throughout the day.
The newborn would get about 540 mL of formula a day, which is on the lower end of the recommended range, but would also risk overfeeding and spitting up.
Choice C is wrong because feeding every 3 hours and taking 75 mL (2.5 oz) per feeding would also provide too much formula at once and not enough throughout the day.
The newborn would get about 600 mL of formula a day, which is on the higher end of the recommended range, but would also risk overfeeding and spitting up.
Choice D is wrong because feeding every hour and taking 30 mL (1 oz) per feeding would provide too little formula at once and too much throughout
Nursing Interventions and Education
A nurse is assessing the nutritional status of a pregnant woman who is in her second trimester.
Which of the following factors should the nurse consider when evaluating the adequacy of the woman’s weight gain?
Explanation
The woman’s pre-pregnancy BMI is a factor that the nurse should consider when evaluating the adequacy of the woman’s weight gain.
BMI is a measure of body fat calculated from weight and height.The amount of weight a woman should gain during pregnancy depends on her BMI before pregnancy.For example, a woman with a normal BMI (18.5-24.9) should gain 25-35 pounds, while a woman with an obese BMI (30 or more) should gain 11-20 pounds.
Choice B is wrong because the woman’s age and parity are not factors that affect the recommended weight gain during pregnancy.The weight gain recommendations are the same for all women regardless of their age or how many children they have had.
Choice C is wrong because the woman’s food preferences and cravings are not factors that determine the adequacy of the woman’s weight gain.Food preferences and cravings may influence what and how much a woman eats, but they do not change the amount of weight she should gain for a healthy pregnancy.
Choice D is wrong because the woman’s activity level and lifestyle are not factors that affect the recommended weight gain during pregnancy.Activity level and lifestyle may influence how a woman gains weight, but they do not change the amount of weight she should gain for a healthy pregnancy.Physical activity and healthy eating habits are important for all pregnant women to maintain their health and well-being.

A nurse is providing individualized counseling to a mother who wants to breastfeed her infant.
The nurse teaches the mother how to position the infant for optimal attachment.
Which of the following statements by the mother indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
“I should push my baby’s chin down if he doesn’t latch on properly.” This statement indicates a need for further teaching because pushing the baby’s chin down can cause pain and damage to the nipple and interfere with the baby’s ability to suckle effectively.The mother should wait for the baby to open his mouth wide before bringing him to her breast and then gently guide his lower jaw onto the breast.
Choice A is correct because holding the baby close to the body with his nose opposite the nipple helps him to latch on well and stimulates the rooting reflex.
Choice B is correct because supporting the breast with a C-shape below the areola prevents the fingers from compressing the milk ducts and allows the baby to grasp more of the breast tissue.
Choice C is correct because waiting for the baby to open his mouth wide ensures that he takes a large mouthful of breast tissue and forms a good seal around the nipple and areola.
Normal ranges for breastfeeding frequency and duration are 8-12 times in 24 hours and 15-20 minutes on each side.
A nurse is helping a mother overcome common breastfeeding problems.
The mother reports having sore nipples that are cracked and bleeding.
Which of the following interventions should the nurse recommend?
Explanation
Applying lanolin cream or hydrogel pads to the nipples after each feeding can help soothe and heal sore nipples that are cracked and bleeding.Lanolin cream is safe for the baby and does not need to be washed off before feeding.Hydrogel pads can also provide cooling relief and create a moist wound healing environment.
Choice B is wrong because washing the nipples with soap and water before and after each feeding can dry out and irritate the skin, making the problem worse.The nipples do not need to be washed more than once a day with plain water.
Choice C is wrong because switching to formula feeding until the nipples heal completely can interfere with the establishment of breastfeeding and reduce the milk supply.Formula feeding can also increase the risk of infections and allergies for the baby.Breastfeeding should be continued as much as possible, even with sore nipples, as long as the baby is latched on correctly.
Choice D is wrong because using a nipple shield or a breast pump for every feeding can also affect the milk supply and the baby’s ability to breastfeed effectively.Nipple shields and breast pumps should only be used temporarily and under the guidance of a lactation consultant.They do not address the underlying cause of sore nipples, which is usually a poor latch.
A nurse is educating a mother on how to feed her infant on cue, following his hunger and satiety signals.
Which of the following behaviors by the infant indicates that he is hungry?
Explanation
Sucking on his fingers or fists.This is a feeding readiness cue that indicates that the infant is hungry and ready to eat.
Some possible explanations for the other choices are:
• Choice A is wrong because turning his head away from the breast or bottle is a sign of satiety or fullness, not hunger.
• Choice C is wrong because falling asleep or becoming drowsy is a sign of fatigue or satisfaction, not hunger.
• Choice D is wrong because spitting up or burping is a sign of air swallowing or overfeeding, not hunger.
Normal ranges for infant feeding frequency and duration vary depending on the type of feeding (breastfeeding or formula feeding), the age and weight of the infant, and the individual needs and preferences of the infant and the mother.
However, some general guidelines are:
• Breastfed infants should feed 8 to 12 times in 24 hours, with each feeding lasting 10 to 15 minutes per breast.
• Formula-fed infants should feed 6 to 10 times in 24 hours, with each feeding lasting 15 to 20 minutes and providing about 2 to 3 ounces of formula per pound of body weight per day.
A nurse is advising a mother on the appropriate timing and types of complementary foods and drinks to introduce to her infant after six months of age.
Which of the following foods or drinks should the nurse recommend as the first complementary food for the infant?
Explanation
Iron-fortified infant cereal.According to the World Health Organization (WHO), infants should start receiving complementary foods at 6 months of age in addition to breast milk.Iron-fortified infant cereal is a good source of iron, which is essential for the development of the infant’s brain and blood cells.
Choice A is wrong because cow’s milk or juice are not recommended as the first complementary foods for infants.Cow’s milk can cause iron deficiency anemia and allergic reactions, and juice can cause dental caries and diarrhea.
Choice B is wrong because pureed fruits or vegetables are not enough to meet the infant’s iron needs.Fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins and minerals, but they do not provide enough iron for the growing infant.
Choice D is wrong because yogurt or cheese are not suitable as the first complementary foods for infants.Yogurt or cheese can cause allergic reactions and lactose intolerance, and they do not provide enough iron for the infant.
Growth and Development Evaluation
A nurse is collecting data from a 6-month-old infant during a well-child visit.
Which of the following findings should the nurse report to the provider?
Explanation
BMI increased by 5% since last visit.
BMI is a measure of body fat based on height and weight.A 5% increase in BMI since the last visit indicates excessive weight gain or growth failure, which should be reported to the provider.
Choice A is wrong because head circumference increased by 2 cm since last visit is normal for a 6-month-old infant.The head circumference should increase by 1.5 cm per month for the first 6 months.
Choice B is wrong because weight increased by 50% since birth is normal for a 6-month-old infant.The weight should double by 5 months and triple by 12 months.
Choice C is wrong because length increased by 25% since birth is normal for a 6-month-old infant.The length should increase by 50% by 12 months.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching about developmental milestones to the parents of a 9-month-old infant.
Which of the following skills should the nurse expect the infant to perform? (Select all that apply)
Explanation
These are the developmental milestones that a 9-month-old infant should be able to perform according to the Denver II Developmental Screening Test.
Some explanations for each choice are:
• Choice A is correct because a 9-month-old infant should be able to pull up to a standing position by holding on to furniture or other objects.
• Choice B is correct because a 9-month-old infant should be able to say “mama” and “dada” nonspecifically, meaning they do not associate the words with specific people yet.
• Choice C is correct because a 9-month-old infant should be able to use a pincer grasp to pick up small objects, such as cereal or raisins, with the thumb and index finger.
• Choice D is wrong because a 9-month-old infant should not be able to point to objects or pictures when named.This skill usually develops around 12 months of age.
• Choice E is correct because a 9-month-old infant should be able to crawl on hands and knees, although some infants may use other methods of locomotion, such as scooting or rolling.
A nurse is assisting with a developmental screening on a 4-year-old child.
Which of the following cognitive skills should the nurse expect the child to perform?
Explanation
Classify objects by size, shape, and color.A 4-year-old child should be able to recognize and name a few colors, starting with primary colors of red, yellow and blue.He should also be able to sort objects according to various characteristics, such as color, shape and size.
Choice B is wrong because the concept of conservation of matter is not understood by 4-year-olds.
This is the ability to recognize that the quantity of a substance remains the same even if its shape or appearance changes.
For example, a 4-year-old might think that a ball of clay has more clay than a flattened piece of clay.This concept is usually developed around 7 to 8 years of age.
Choice C is wrong because abstract reasoning is not a cognitive skill that 4-year-olds can perform.
Abstract reasoning is the ability to think beyond the concrete and literal, and use symbols, logic, and imagination to solve problems.
For example, a 4-year-old might not understand what a metaphor or a joke means.
This skill is usually developed around 11 to 12 years of age.
A nurse is reinforcing teaching about nutrition to the parents of a 2-year-old toddler.
Which of the following statements by the parents indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
All of the above.
This statement indicates that the parents understand the nutrition needs of a 2-year-old toddler.
Choice A is correct because a 2-year-old should eat three healthy meals a day, plus one or two snacks.
Choice B is correct because a 2-year-old should limit milk intake to 16 oz per day to avoid displacing other foods and nutrients.A 2-year-old can drink lower-fat dairy products, such as 2% or 1% milk, unless advised otherwise by a doctor.
Choice C is correct because a 2-year-old should avoid foods that are potential choking hazards, such as nuts, seeds, popcorn, hard candy, grapes, hot dogs, and raw carrots.A 2-year-old can eat the same food as the rest of the family, but may prefer finger foods instead of soft ones.
A nurse is collecting data from a 12-year-old child who has Turner syndrome.
Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? (Select all that apply)
Explanation
Turner syndrome is a genetic disorder in which a female is partially or completely missing an X chromosome.This can cause various physical and developmental problems, such as a webbed neck, low position of posterior hairline, shield-shaped chest with wide space between the nipples, short stature and delayed puberty.
Choice D is wrong because Turner syndrome does not cause tall stature.In fact, most girls and women with Turner syndrome are shorter than average.
Exams on Newborn Nutrition
Custom Exams
Login to Create a Quiz
Click here to loginLessons
 Naxlex
Just Now
Naxlex
Just Now
Notes Highlighting is available once you sign in. Login Here.
Objectives
- Describe the benefits and composition of breast milk and infant formula
- Explain the feeding cues and patterns of newborns
- Identify the nursing interventions and education for breastfeeding and bottle-feeding mothers
- Discuss the introduction of complementary foods and drinks to infants
- Recognize the signs and risks of dehydration, overhydration, and failure to thrive in infants
- Evaluate the growth and development of infants using appropriate charts and indicators
Introduction
- Newborn nutrition is vital for healthy growth and development during the first two years of life
- Newborns need adequate calories and nutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals
- Newborns can meet their nutritional needs by either breast milk or iron-fortified infant formula
- Breast milk is the preferred source of nutrition for most infants as it provides many advantages for both the mother and the infant
- Infant formula is an alternative for infants who cannot or should not receive breast milk
- Newborns should be fed on cue, following their hunger and satiety signals
- Newborns should be fed at least 8 to 12 times in 24 hours, with each feeding lasting about 15 to 20 minutes per breast or 2 to 3 ounces per bottle
- Newborns may lose 5 to 10% of their body weight right after birth, but they should regain it by 10 to 14 days of age
- Newborns should be monitored for adequate hydration, weight gain, growth, and development

Breast Milk
-
Breast milk is a complex fluid that contains all the nutrients, antibodies, hormones, enzymes, and growth factors that an infant needs for optimal health
-
Breast milk has many benefits for both the mother and the infant, such as:
-
Reducing the risk of infections, allergies, asthma, diabetes, obesity, leukemia, and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) in infants
-
Promoting brain growth, cognitive development, and emotional bonding in infants
-
Helping the uterus contract, reducing postpartum bleeding and lowering the risk of breast and ovarian cancer in mothers
-
Saving time, money, and resources for mothers
-
-
Breast milk composition varies with each phase of lactation, maternal diet, time of day, and duration of feeding
-
The three phases of lactation are:
-
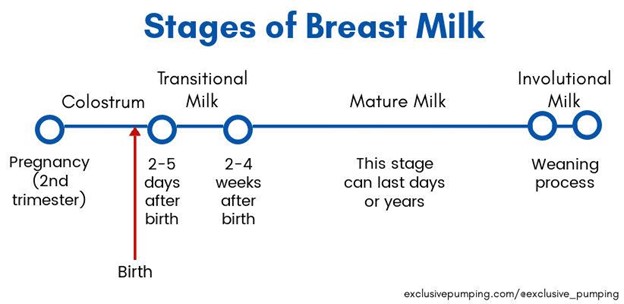
Colostrum: The first milk produced during pregnancy and the first few days postpartum. It is thick, yellowish, high in protein, vitamins, minerals, immune cells, and immunoglobulins (especially IgA). It is low in fat and carbohydrates. It protects the infant’s gastrointestinal tract from infections and helps establish normal flora. It also has a laxative effect that helps clear meconium and prevent jaundice. It meets all the nutritional needs of the newborn during the first few days of life
-
Transitional milk: The milk produced between two to five days postpartum. It is thinner, whiter, higher in fat and carbohydrates than colostrum. It also contains more vitamins, immunoglobulins (especially IgG), lactose, and water. It provides more calories and hydration for the growing infant
-
Mature milk: The milk produced after five days postpartum. It is composed of two types: foremilk and hindmilk. Foremilk is the milk that comes out at the beginning of each feeding. It is watery, low in fat and high in lactose. It quenches the infant’s thirst. Hindmilk is the milk that comes out at the end of each feeding. It is creamy, high in fat and low in lactose. It satisfies the infant’s hunger.
-
-
Breast milk production is regulated by supply and demand. The more often and effectively an infant nurses, the more milk is produced by the mother
-
Breastfeeding mothers should follow a balanced diet that provides enough calories, fluids, protein, calcium, iron, folate, vitamin B12, vitamin D, iodine, selenium, zinc, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants
-
Breastfeeding mothers should avoid or limit alcohol, caffeine, nicotine, drugs, herbal supplements, mercury-containing fish, spicy foods, allergens, or any foods that may cause adverse reactions in their infants

Infant formula
- Infant formula is a food designed to feed babies and infants less than 12 months of age who cannot or should not receive breast milk
- Infant formula is made from cow’s milk or soy protein that has been modified to resemble breast milk in terms of nutrients, calories, and composition
-
Infant formula has some disadvantages compared to breast milk, such as:
-
It does not contain antibodies, hormones, enzymes, or growth factors that protect the infant from infections and promote development
-
It is more expensive, less convenient, and less environmentally friendly than breast milk
-
It may increase the risk of allergies, asthma, diabetes, obesity, and other chronic diseases in infants
-
It may cause more digestive problems, such as constipation, gas, spit-up, diarrhea, or colic in infants
-
-
Infant formula comes in three forms: ready-to-use, liquid concentrate, and powdered
-
Ready-to-use formula is the most convenient but also the most expensive. It does not need to be mixed with water and can be fed directly to the infant after opening
-
Liquid concentrate formula needs to be mixed with equal parts of water before feeding. It is cheaper than ready-to-use formula but still more costly than powdered formula
-
Powdered formula is the cheapest and most widely used form of formula. It needs to be mixed with a specific amount of water according to the instructions on the label. It can be stored for longer periods of time than the other forms of formula
-
-
Infant formula should be iron-fortified to prevent iron deficiency anemia in infants
-
Infant formula should be prepared and stored carefully to prevent contamination and spoilage
-
Formula should be prepared with clean water that has been boiled for one minute and cooled before mixing
-
Formula should be mixed well to avoid clumps or air bubbles that can cause choking or gas in infants
-
Formula should be fed to the infant within one hour of preparation or refrigerated for up to 24 hours
-
Formula should not be microwaved as it can cause hot spots that can burn the infant’s mouth or throat
-
Formula should not be reused or rewarmed once it has been fed to the infant as it can harbor bacteria that can cause illness
-
Feeding Cues and Patterns
-
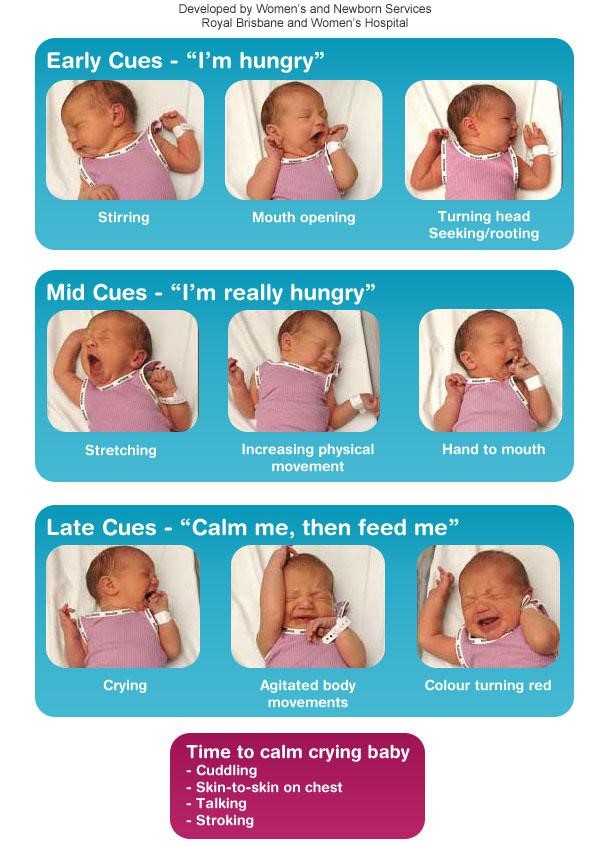
Feeding cues are signs that indicate when an infant is hungry or full
-
Hunger cues include:
-
Smacking or licking lips
-
Opening and closing mouth
-
Sucking on lips, tongue, hands, fingers, toes, toys, or clothing
-
Moving head from side to side
-
Turning head toward the breast or bottle
-
Fussing or crying
-
-
Satiety cues include:
-
Closing mouth
-
Turning head away from the breast or bottle
-
Relaxed hands and arms
-
Falling asleep
-
Pushing away the breast or bottle
-
-
Feeding patterns are the frequency and duration of feedings for an infant
-
Feeding patterns vary depending on the infant’s age, weight, growth rate, and individual needs
-
In general, newborns should be fed on cue, following their hunger and satiety signals, rather than on a strict schedule
-
Newborns should be fed at least 8 to 12 times in 24 hours, with each feeding lasting about 15 to 20 minutes per breast or 2 to 3 ounces per bottle
-
Newborns should not go longer than four hours without feeding during the day or six hours at night
-
As infants grow older, they may feed less often but take more milk at each feeding
-
By six months of age, most infants can go four to six hours between feedings during the day and eight to twelve hours at night
Nursing Interventions and Education
-
Nursing interventions and education are aimed at supporting and promoting optimal nutrition for mothers and infants
-
Nursing interventions and education include:
-
Assessing the nutritional status, feeding practices, and growth patterns of mothers and infants
-
Providing individualized counseling and guidance on breastfeeding or formula feeding, based on the mother’s preferences, needs, and challenges
-
Teaching mothers how to initiate and maintain breastfeeding or formula feeding, including proper positioning, attachment, expression, storage, and hygiene
-
Helping mothers overcome common breastfeeding problems, such as sore nipples, engorgement, mastitis, low milk supply, or inverted nipples
-
Encouraging mothers to feed their infants on cue, following their hunger and satiety signals
-
Educating mothers on the signs of adequate hydration, weight gain, growth, and development in infants
-
Advising mothers on the appropriate timing and types of complementary foods and drinks to introduce to infants after six months of age
-
Promoting exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of life and continued breastfeeding for up to two years or beyond
-
Supporting mothers to continue breastfeeding or formula feeding when they return to work or school
-
Referring mothers and infants to specialized care when needed for severe diseases or complications
-
Advocating for the protection, promotion, and support of breastfeeding in health facilities, workplaces, and communities
-
Growth and Development Evaluation
-
Growth and development evaluation is the process of measuring and monitoring the physical and mental progress of infants and children
-
Growth and development evaluation includes assessing the following parameters:
-
Length or height: The distance from the top of the head to the bottom of the feet. Length is measured in infants who cannot stand, while height is measured in children who can stand. Length or height reflects the growth of the long bones and is influenced by genetic, nutritional, hormonal, and environmental factors
-
Weight: The force of gravity on the body mass. Weight reflects the balance between energy intake and expenditure and is influenced by genetic, nutritional, hormonal, metabolic, and environmental factors
-
Head circumference: The distance around the largest part of the head. Head circumference reflects the growth of the brain and skull and is influenced by genetic, nutritional, hormonal, and neurological factors
-
Body mass index (BMI): The ratio of weight to height squared. BMI reflects the relative proportion of fat and lean tissue in the body and is influenced by genetic, nutritional, hormonal, metabolic, and environmental factors
-
Developmental milestones: The skills or abilities that infants and children acquire at certain ages. Developmental milestones include motor, language, cognitive, social, emotional, and behavioral domains and are influenced by genetic, nutritional, hormonal, neurological, psychological, and environmental factors
-
-
Growth and development evaluation should be done regularly and systematically using standardized tools and methods
-
Growth and development evaluation should be done at the following ages:
-
Birth
-
Within one week after delivery
-
1 month
-
2 months
-
4 months
-
6 months
-
9 months
-
12 months
-
15 months
-
18 months
-
24 months
-
30 months
-
36 months
-
Annually thereafter until adulthood
-
-
Growth and development evaluation should be plotted on appropriate growth charts and compared with the expected norms for age and sex. Growth charts are graphical tools that show how infants and children grow over time in relation to a reference population. Growth charts can help identify normal or abnormal patterns of growth and development. The World Health Organization (WHO) growth charts are recommended for infants and children up to two years of age. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) growth charts are recommended for children from two to twenty years of age
-
Growth and development evaluation should be interpreted in the context of the individual child’s history, physical examination, family background, cultural background, medical conditions, medications, or other factors that may affect growth and development
-
Growth and development evaluation should be used to identify any deviations from the normal or expected patterns of growth and development. Deviations may include:
-
Growth failure: A condition characterized by inadequate or impaired growth due to insufficient nutrition, chronic disease, genetic disorder, endocrine disorder, psychosocial stress, or other causes. Growth failure may manifest as low birth weight, small for gestational age, failure to thrive, short stature, underweight, wasting, stunting, or microcephaly
-
Growth excess: A condition characterized by excessive or accelerated growth due to overnutrition, genetic disorder, endocrine disorder, tumor, or other causes. Growth excess may manifest as large for gestational age, macrosomia, tall stature, overweight, obesity, or macrocephaly
-
Developmental delay: A condition characterized by a significant lag or deviation in one or more domains of development compared with the expected norms for age. Developmental delay may be caused by genetic disorder, chromosomal abnormality, metabolic disorder, congenital anomaly, prenatal exposure to drugs or toxins, perinatal complications, prematurity, low birth weight, malnutrition, infection, brain injury, hypoxia, hypoglycemia, hypothyroidism, hearing loss, vision loss, autism spectrum disorder (ASD), cerebral palsy (CP), intellectual disability (ID), learning disability (LD), attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), emotional disorder (ED), behavioral disorder (BD), or environmental deprivation
-
-
Growth and development evaluation should be used to guide further assessment, diagnosis, intervention, referral, follow-up, counseling, education, or support for infants and children with growth or developmental problems
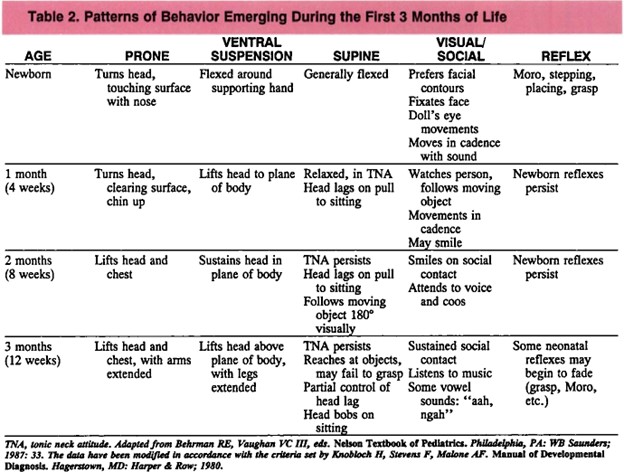
Conclusion
Proper nutrition is crucial for newborns to thrive and develop optimally. Breastfeeding offers numerous benefits, including reduced infection risk, essential nutrients, and support for brain growth. It is essential to follow recommended feeding practices, such as breastfeeding right after birth, observing adequate wet diapers, and introducing solid foods at the appropriate age. Additionally, proper storage and handling of breast milk and formula, along with safe sleep practices, contribute to the overall well-being of the newborn.
Naxlex
Videos
Login to View Video
Click here to loginTake Notes on Newborn Nutrition
This filled cannot be empty
Join Naxlex Nursing for nursing questions & guides! Sign Up Now


