Please set your exam date
Cesarean delivery
Study Questions
Introduction
A nurse is reviewing the medical records of four pregnant clients who are scheduled for cesarean delivery.
Which client has the highest risk of developing a postoperative infection?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.A client with gestational diabetes mellitus has a higher risk of developing a postoperative infection after cesarean section because diabetes impairs wound healing and increases susceptibility to infection.
Choice B is wrong because active herpes virus infection does not increase the risk of surgical site infection after cesarean section.
Choice C is wrong because placenta previa is not a risk factor for postoperative infection after cesarean section.
Choice D is wrong because fetal breech presentation does not increase the risk of surgical site infection after cesarean section.
Some of the other risk factors for postoperative infection after cesarean section are high body mass index, intrapartum fever, prolonged rupture of membranes, prolonged labor, chorioamnionitis, anemia, and vertical skin incision.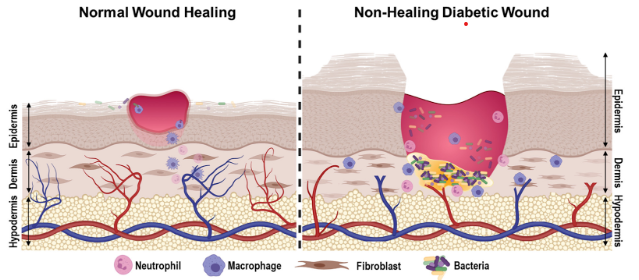
A nurse is caring for a client who had an emergency cesarean delivery due to fetal distress.
The nurse notices that the client has a large amount of bright red blood on her perineal pad.
What is the nurse’s priority action?
Explanation
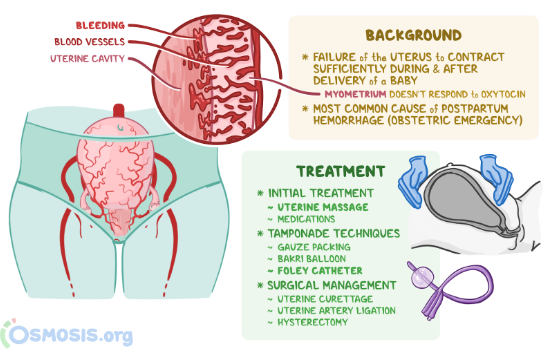
The correct answer is choice B. Massage the client’s fundus and check for firmness.This is because the most common cause of postpartum hemorrhage is uterine atony, which is a lack of contraction of the uterus after delivery.Massaging the fundus stimulates the uterus to contract and reduces bleeding from the placental site.Checking for firmness ensures that the uterus is not distended by blood clots or retained placental fragments, which can also cause hemorrhage.
Choice A is wrong because assessing the client’s vital signs and level of consciousness is not a priority action.
These are important indicators of blood loss and shock, but they do not address the source of bleeding.The nurse should first try to stop the bleeding by massaging the fundus and then assess the client’s status.
Choice C is wrong because notifying the provider and preparing for a blood transfusion are not priority actions.
These are interventions that may be needed if the bleeding does not stop with fundal massage or if the client develops signs of severe hemorrhage or shock.However, they are not the first steps to take in managing postpartum hemorrhage.
Choice D is wrong because administering oxytocin as prescribed to stimulate uterine contractions is not a priority action.Oxytocin is a uterotonic medication that can help prevent and treat postpartum hemorrhage by causing sustained uterine contractions.
However, it is not the first intervention to try in case of bleeding.The nurse should first massage the fundus and check for firmness, and then administer oxytocin if ordered by the provider.
Normal ranges for blood loss after delivery are less than 500 mL for vaginal birth and less than 1000 mL for cesarean birth.Normal ranges for vital signs and level of consciousness vary depending on the individual client, but some signs of hypovolemia and shock include tachycardia, hypotension, tachypnea, pallor, cold clammy skin, oliguria, anxiety, confusion, and loss of consciousness.Normal range for uterine firmness is a well-contracted uterus that feels like a hard ball at or below the umbilicus.
A nurse is teaching a prenatal class about the indications for cesarean delivery.
The nurse should include that which of the following conditions can lead to a cesarean delivery? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A, C, D and E. These are all conditions that can lead to a cesarean delivery.
Choice A is correct because cephalopelvic disproportion (CPD) means that the baby’s head or body is too large to fit through the mother’s pelvis.This can cause prolonged or obstructed labor and fetal distress.
Choice B is wrong because gestational hypertension (high blood pressure during pregnancy) is not a direct indication for a cesarean delivery.However, it can be associated with other complications such as preeclampsia, placental abruption or fetal growth restriction that might require a cesarean delivery.
Choice C is correct because fetal malposition means that the baby is not in the optimal position for vaginal delivery.
This includes breech (feet or buttocks first), transverse (sideways) or oblique (diagonal) presentations.These can increase the risk of cord prolapse, fetal injury or uterine rupture.
Choice D is correct because placenta abruption means that the placenta separates from the uterine wall before delivery.
This can cause severe bleeding, fetal hypoxia or stillbirth.A cesarean delivery is usually performed to save the mother and the baby.
Choice E is correct because cord prolapse means that the umbilical cord slips through the cervix ahead of the baby.
This can compress the cord and cut off the blood supply to the baby.A cesarean delivery is usually performed as an emergency to prevent fetal death.
A nurse is preparing a client for a planned cesarean delivery.
The nurse should explain that which of the following types of anesthesia is most commonly used for this procedure?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B.Spinal anesthesia is the most commonly used type of anesthesia for cesarean delivery.It is administered around the spinal cord using a needle and it numbs the lower body for three to four hours.It has the advantages of being fast-acting, providing good operating conditions, and having minimal effects on the fetus.
Choice A is wrong because general anesthesia is rarely used for cesarean delivery unless there is an emergency or a contraindication for regional anesthesia.It involves putting the mother to sleep with drugs that can cross the placenta and affect the fetus.
Choice C is wrong because epidural anesthesia is not as commonly used as spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery.It is administered around the nerves in the lower back and it requires a larger dose and a longer time to work than spinal anesthesia.
Choice D is wrong because local anesthesia is rarely used for cesarean delivery and only for minor procedures such as repairing a wound or removing stitches.It involves injecting a drug into the skin or tissue to numb a small area.
A nurse is assessing a client who had a cesarean delivery 24 hours ago.
The nurse should identify that which of the following findings is a potential complication of this procedure?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.Urinary output of 40 mL/hr is a potential complication of cesarean delivery because it indicates inadequate fluid intake, blood loss, or urinary tract injury.The normal range of urinary output is 30 to 60 mL/hr.
Choice B is wrong because incision site with serous drainage is a normal finding after cesarean delivery and does not indicate infection or bleeding.
Choice C is wrong because abdominal pain relieved by analgesics is also a normal finding after cesarean delivery and does not indicate any complication.
Choice D is wrong because uterus palpable at the umbilicus is an expected finding after cesarean delivery and indicates that the uterus is contracting and returning to its pre-pregnancy size.
A nurse is assessing a patient’s medical history before Cesarean delivery.
What should the nurse assess?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. The patient’s allergies.
The nurse should assess the patient’s allergies before Cesarean delivery to prevent any adverse reactions to medications, anesthesia, or latex products that may be used during the procedure.
Allergies can cause serious complications such as anaphylaxis, which can be life-threatening for both the mother and the baby.
Choice B is wrong because the patient’s age is not a relevant factor for Cesarean delivery.
Age does not affect the surgical technique or the outcome of the operation.
Choice C is wrong because the patient’s height is not a relevant factor for Cesarean delivery.
Height does not affect the size of the incision or the amount of blood loss during the surgery.
Choice D is wrong because the patient’s weight is not a relevant factor for Cesarean delivery.
Weight does not affect the type of anesthesia or the risk of infection after the surgery.
Normal ranges for vital signs and laboratory values are not applicable for this question.
A client is scheduled for Cesarean delivery.
What should the nurse do to support the client emotionally?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. Address any concerns or anxieties the client may have regarding the procedure.Emotional support is a critical aspect of quality care throughout pregnancy and childbirth.Women who have a cesarean section may experience a range of emotions, such as depression, regret, or lower self-esteem.
The nurse should provide emotional support by listening to the client’s feelings, answering their questions, and reassuring them about the procedure.
Choice A is wrong because educating the client about the surgical procedure is not enough to support them emotionally.
The client may still have fears or worries that need to be addressed.
Choice B is wrong because administering prescribed medications as ordered by the healthcare provider is not directly related to emotional support.
Medications may help with pain relief or infection prevention, but they do not address the client’s psychological needs.
Choice D is wrong because ensuring that informed consent has been obtained from the client is a legal and ethical requirement, but it does not necessarily imply emotional support.
The client may still feel coerced, uninformed, or unhappy about the procedure.
A nurse is performing a physical examination on a patient before Cesarean delivery.
What should the nurse pay special attention to?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C. The patient’s abdomen and pelvic area.
The nurse should pay special attention to the patient’s abdomen and pelvic area before Cesarean delivery because this is where the surgery will take place.
The nurse should assess the size and position of the uterus, the fetal heart rate and movement, and any signs of infection or bleeding in the abdominal and pelvic area.
The nurse should also prepare the patient for the surgery by shaving the pubic hair, inserting a urinary catheter, and administering prophylactic antibiotics if ordered.
Choice A is wrong because the patient’s medical history is not as relevant as the current physical examination before Cesarean delivery.
The nurse should review the medical history for any risk factors or complications, but this is not the main focus of the examination.
Choice B is wrong because the patient’s allergies are not as important as the patient’s abdomen and pelvic area before Cesarean delivery.
The nurse should ask about any allergies to medications, latex, or iodine, but this is not the primary concern of the examination.
Choice D is wrong because the patient’s height is not as significant as the patient’s abdomen and pelvic area before Cesarean delivery.
The nurse should measure the patient’s height and weight to calculate the body mass index (BMI), but this is not the main objective of the examination.
A nurse is administering prescribed medications before Cesarean delivery.
What medication should the nurse administer?
Explanation
Prophylactic antibiotics and antacids are commonly given before a Cesarean delivery to prevent infection and reduce the risk of aspiration.Antibiotics can reduce the incidence of postoperative endometritis and wound infection.Antacids can neutralize the stomach acid and lower the pH, which can minimize the lung injury if aspiration occurs.
Choice B is wrong because painkillers and sedatives are not routinely given before a Cesarean delivery.Painkillers are usually given after the surgery or during the surgery if regional anesthesia is used.Sedatives are not recommended because they can cause respiratory depression and cross the placenta to affect the baby.
Choice C is wrong because antidepressants and antipsychotics are not indicated for a Cesarean delivery unless the woman has a psychiatric condition that requires them.These medications can have adverse effects on the mother and the baby, such as bleeding, hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, sedation, withdrawal symptoms, and neurobehavioral changes.
Choice D is wrong because antihistamines and decongestants are not relevant for a Cesarean delivery.Antihistamines can cause sedation, dry mouth, and urinary retention, and decongestants can cause hypertension, tachycardia, and insomnia.These medications can also cross the placenta and affect the baby’s health.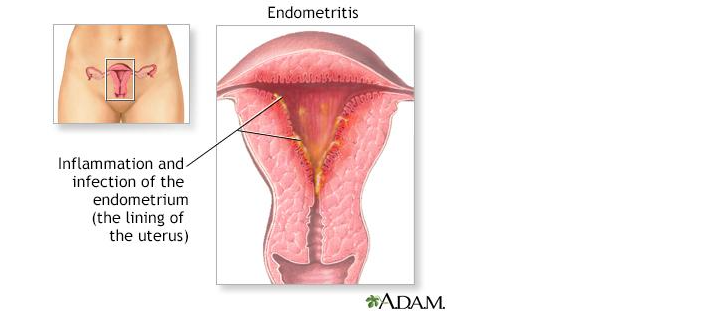
A nurse is educating a patient about Cesarean delivery before surgery.
What should the nurse educate the patient about?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice D. All of the above.
The nurse should educate the patient about the risks, benefits and expected outcomes of Cesarean delivery before surgery.
Choice A is wrong because it is not enough to inform the patient only about the risks of surgery, such as infection, bleeding, injury to organs or anesthesia complications.
The patient also needs to know the benefits and expected outcomes of surgery.
Choice B is wrong because it is not enough to inform the patient only about the benefits of surgery, such as avoiding labor complications, delivering a healthy baby or having a planned date of birth.
The patient also needs to know the risks and expected outcomes of surgery.
Choice C is wrong because it is not enough to inform the patient only about the expected outcomes of surgery, such as the length of hospital stay, the recovery process or the wound care.
The patient also needs to know the risks and benefits of surgery.
Complications of Cesarean delivery
A nurse is caring for a client who had a cesarean delivery 24 hours ago.
The nurse notices that the client has a fever of 38.2°C, increased redness and swelling at the incision site, and foul-smelling lochia.
What is the most likely cause of these findings?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Infection.The client’s fever, increased redness and swelling at the incision site, and foul-smelling lochia are all signs of infection, which is a common complication of cesarean delivery.
Choice B. Hemorrhage is wrong because hemorrhage would cause excessive bleeding, low blood pressure, and rapid pulse, which are not mentioned in the question.
Choice C. Deep vein thrombosis is wrong because deep vein thrombosis would cause pain, swelling, and tenderness in the legs, which are not mentioned in the question.
Choice D. Wound dehiscence is wrong because wound dehiscence would cause separation of the incision edges, drainage of serous fluid, and exposure of underlying tissues, which are not mentioned in the question.
Normal ranges for lochia are as follows:
• Lochia rubra: bright red blood and clots that last for 3 to 4 days after delivery
• Lochia serosa: pinkish-brown discharge that lasts for 4 to 10 days after delivery
• Lochia alba: yellowish-white discharge that lasts for 10 to 14 days after delivery
Foul-smelling lochia indicates infection and should be reported to the health care provider.


A nurse is assessing a client who had a cesarean delivery 12 hours ago.
The nurse observes that the client has soaked two perineal pads in one hour, has a heart rate of 120 beats per minute, and has a blood pressure of 90/60 mmHg.
What is the priority intervention for this client?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Apply pressure to the bleeding site.This is because the client is showing signs of postpartum hemorrhage (PPH), which is severe vaginal bleeding after childbirth.PPH can occur up to 12 weeks postpartum, but it is more common within the first 24 hours.PPH can be caused by uterine atony, retained placenta, or trauma to the reproductive organs.
Applying pressure to the bleeding site can help to control the blood loss and prevent shock.
Choice B. Encourage early ambulation is wrong because it can worsen the bleeding and increase the risk of fainting.Early ambulation is beneficial for preventing thromboembolism and promoting recovery, but it should be done after the bleeding is stabilized.
Choice C. Apply sterile dressings to the incision is wrong because it does not address the source of bleeding, which is likely from the vagina or uterus.The incision site may also bleed, but it is usually less than the vaginal bleeding.
Applying sterile dressings to the incision can help to prevent infection, but it is not a priority intervention for PPH.
Choice D. Encourage frequent voiding is wrong because it can cause bladder distension and interfere with uterine contraction.A full bladder can displace the uterus and prevent it from compressing the blood vessels where the placenta was attached.
Encouraging frequent voiding can help to maintain bladder function and reduce discomfort, but it is not a priority intervention for PPH.
Normal ranges for heart rate are 60-100 beats per minute and for blood pressure are 90/60-120/80 mmHg.Normal blood loss after cesarean delivery is less than 1000 mL.
A nurse is teaching a client who had a cesarean delivery about measures to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? (Select all that apply.).
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A, B, C and D. These are all measures to prevent deep vein thrombosis (DVT) after cesarean delivery.DVT is a blood clot that forms in the deep veins of the legs or arms and can break off and travel to the lungs, causing a life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism (PE).
Choice A is correct because wearing anti-embolism stockings as prescribed can help improve blood flow and reduce swelling in the legs.
Choice B is correct because avoiding crossing your legs when sitting or lying down can prevent pressure on the veins and reduce the risk of blood clots.
Choice C is correct because performing ankle and calf exercises every hour while awake can stimulate blood circulation and prevent blood from pooling in the lower extremities.
Choice D is correct because drinking at least 3 liters of fluid per day can help prevent dehydration, which can thicken the blood and increase the risk of clotting.
Choice E is wrong because elevating your legs above your heart level when resting can impair venous return and increase the risk of DVT.This position is recommended for patients with arterial insufficiency, not venous insufficiency.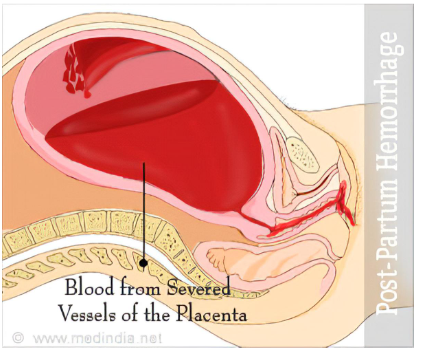
A nurse is assisting a client who had a cesarean delivery to get out of bed for the first time.
The nurse notices that the client’s incision site has opened and there is visible bowel protruding from the wound.
What is the appropriate action for the nurse to take?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B. Cover the wound with a sterile, moist dressing and notify the healthcare provider.
This is because the client has a wound dehiscence with evisceration, which is a serious complication that requires immediate medical attention.
The sterile, moist dressing will help prevent infection and keep the bowel tissue moist until surgery can be performed.
Choice A is wrong because pushing the bowel back into the abdomen can cause further damage and increase the risk of infection and peritonitis.
Choice C is wrong because irrigating the wound with normal saline and applying an antibiotic ointment can also introduce bacteria and irritate the bowel tissue.
Choice D is wrong because leaving the wound exposed to air can cause the bowel tissue to dry out and necrose, which can lead to sepsis and shock.
A nurse is evaluating a client who had a cesarean delivery for urinary retention.
Which of the following findings should alert the nurse to this complication?
Explanation
Answer and explanation..
The correct answer is choice D. All of the above.Urinary retention is a common complication after cesarean delivery, and it can be detected by measuring the postvoid residual bladder volume (PVRBV) with an ultrasound scan.A PVRBV of more than 150 mL is considered abnormal and indicative of urinary retention.
The following findings should alert the nurse to this complication:
• Inability to void within 6 hours after delivery: This is a sign of overt urinary retention, which occurs in about 7.4% of women who had a cesarean delivery.It may be caused by factors such as pain, anxiety, anesthesia, or bladder trauma.
• Distended bladder palpable above the symphysis pubis: This is a sign of covert urinary retention, which occurs in about 16.7% of women who had a cesarean delivery.It means that the bladder is overfilled but the woman does not feel the urge to void or has difficulty initiating micturition.
• Urinary output of less than 30 mL per hour: This is a sign of inadequate bladder emptying, which may lead to urinary tract infection, bladder damage, or renal impairment.It may be due to factors such as morphine-related postoperative analgesia, multiple pregnancy, or low body mass index, which are associated with increased risk of urinary retention after cesarean delivery.
Normal ranges for PVRBV and urinary output are:
• PVRBV: less than 150 mL
• Urinary output: more than 30 mL per hour
Patient Education
A nurse is providing discharge instructions to a client who had a cesarean delivery.
Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A.“I will avoid lifting anything heavier than my baby for the next 6 weeks.” This statement indicates that the client understands the importance of limiting physical activity and protecting the incision site from strain or injury.Lifting heavy objects can increase the risk of bleeding, infection, or wound dehiscence.
Choice B is wrong because resuming regular exercise routine as soon as getting home is not advisable after a C-section.The client should gradually increase activity levels and avoid strenuous exercises until cleared by the healthcare provider.
Choice C is wrong because ibuprofen may not be sufficient for pain relief after a C-section.The client may need stronger pain medications prescribed by the healthcare provider and should follow the instructions on how to take them safely.
Choice D is wrong because removing the dressing from the incision site tomorrow is too soon.The client should keep the incision site clean and dry and follow the healthcare provider’s instructions on when and how to change the dressing.Removing the dressing too early can increase the risk of infection or wound dehiscence.
A nurse is monitoring a client who had a cesarean delivery for signs of thromboembolism.
Which of the following findings should alert the nurse to this complication?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Shortness of breath and chest pain are signs of pulmonary embolism (PE), which is a life-threatening complication of deep vein thrombosis (DVT).DVT is a type of blood clot that can occur in the legs or arms, especially during pregnancy and postpartum.PE happens when a blood clot breaks off and travels to the lungs, blocking blood flow.
Choice B is wrong because nausea and vomiting are not specific signs of thromboembolism.
They can be caused by many other conditions, such as morning sickness, food poisoning, or medication side effects.
Choice C is wrong because headache and blurred vision are not typical signs of thromboembolism.
They can be associated with other pregnancy complications, such as preeclampsia or eclampsia.
Choice D is wrong because fever and chills are not common signs of thromboembolism.
They can indicate an infection or inflammation, such as mastitis or endometritis.
Pregnant women have a higher risk of developing DVT and PE because of hormonal changes, increased blood clotting factors, reduced blood flow to the legs, and other factors.The risk is even higher after a cesarean delivery.
Therefore, it is important to know the signs and symptoms of thromboembolism and seek immediate medical attention if they occur.Thromboembolism can be prevented and treated with anticoagulant medications, compression stockings, and physical activity.
A nurse is evaluating the bonding between a client who had a cesarean delivery and her newborn.
Which of the following behaviors by the client indicates effective bonding? (Select all that apply.).
Explanation
A. "Holding the newborn close to her chest" indicates effective bonding. Physical closeness is important for establishing a connection between the mother and newborn. This promotes emotional attachment and comfort for the baby.
B. "Making eye contact with the newborn" is a key indicator of bonding. Eye contact fosters connection and attachment and is often an early behavior seen in positive bonding.
C. "Talking to the newborn in a soft voice" also reflects positive bonding behavior. Talking to the newborn helps with emotional connection, promotes early communication, and establishes comfort for the baby.
D. "Handing the newborn to a family member when crying" does not indicate effective bonding. While it may be appropriate to ask for help, consistent delegation of newborn care can suggest a lack of emotional connection or reluctance to care for the infant.
E. "Stroking the newborn’s hair and skin" is another indicator of effective bonding. Physical touch, such as stroking, is soothing and promotes attachment between the mother and her newborn.
A client is scheduled for a cesarean section (C-section).
Which nursing intervention should be included in preoperative care?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice C) Encouraging coughing and deep breathing exercises.
This is because coughing and deep breathing exercises can help prevent atelectasis and pneumonia, which are common postoperative complications of C-section.
Coughing and deep breathing exercises also promote oxygenation and circulation.
Choice A) Administering an opioid analgesic is wrong because opioids can cause respiratory depression and sedation, which are not desirable before surgery.
Opioids can also cross the placenta and affect the fetus.
Choice B) Assessing for signs of deep vein thrombosis is wrong because this is not a priority intervention before surgery.
Deep vein thrombosis is more likely to occur after surgery due to immobility and venous stasis.
Choice D) Providing a high-carbohydrate meal is wrong because this can increase the risk of aspiration during surgery.
The client should be kept NPO (nothing by mouth) for at least 6 hours before surgery.
Which nursing intervention is most important for preventing respiratory complications such as pneumonia and atelectasis in a postoperative client?
Explanation
The correct answer is choiceD) Use of incentive spirometry.Incentive spirometry is a device that helps patients take slow, deep breaths to expand their lungs and prevent respiratory complications such as pneumonia and atelectasis.Incentive spirometry also helps clear mucus and fluids from the lungs and improves ventilation.
Choice A is wrong because controlling anxiety and agitation may not directly prevent respiratory complications, although it may help patients breathe more comfortably.
Choice B is wrong because adequate nutrition and fluids are important for general health and recovery, but they do not specifically prevent respiratory complications.
Choice C is wrong because adequate pain control may help patients breathe more deeply and cough more effectively, but it is not enough to prevent respiratory complications by itself.
Choice E is wrong because early ambulation may improve blood circulation and reduce the risk of thromboembolism, but it does not directly prevent respiratory complications.
Which nursing intervention is most important for preventing surgical site infections in clients undergoing surgery?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A) Administering prophylactic antibiotics as ordered.According to the WHO guidelines for the prevention of surgical site infection (SSI), prophylactic antibiotics should be given within 60 minutes before skin incision and discontinued within 24 hours after surgery.
This reduces the risk of SSI by preventing bacterial colonization of the surgical site.
Choice B) Encouraging coughing and deep breathing exercises is wrong because this intervention is mainly for preventing respiratory complications, not SSI.Coughing and deep breathing exercises help to clear secretions and prevent atelectasis and pneumonia.
Choice C) Providing adequate pain control is wrong because this intervention is mainly for improving patient comfort and recovery, not SSI.Pain control may reduce stress and inflammation, but it does not directly affect the risk of SSI.
Choice D) Assessing for signs of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is wrong because this intervention is mainly for preventing venous thromboembolism (VTE), not SSI.
DVT is a condition where a blood clot forms in a deep vein, usually in the legs.
It can cause pain, swelling, and redness.If the clot breaks off and travels to the lungs, it can cause a pulmonary embolism (PE), which can be life-threatening.
Some other intraoperative interventions for preventing SSI include using an alcohol-based skin prep, maintaining body temperature, using impervious wound protectors, and performing SSI surveillance.
A nurse is caring for a client who had an unscheduled cesarean delivery due to fetal distress.
Which of the following interventions should the nurse implement in the immediate postoperative period?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice D. All of the above interventions should be implemented in the immediate postoperative period after a cesarean delivery.
Choice A is correct because assessing the client’s fundus for firmness and position is important to prevent postpartum hemorrhage and monitor uterine involution.The fundus should be firm and at the level of the umbilicus one hour after delivery and descend into the pelvis at a rate of approximately 1 cm per day.
Choice B is correct because encouraging early ambulation can prevent thromboembolism, which is a potential complication of cesarean delivery.Early mobilization can also reduce pain, ileus, and urinary retention.
Choice C is correct because monitoring the client’s intake and output can help detect fluid imbalance, dehydration, or urinary tract infection.
Fluid intake should be adequate to maintain hydration and support lactation.Urinary output should be at least 30 mL per hour.
Therefore, choice D is correct because all of the above interventions are appropriate for postoperative care after a cesarean delivery.
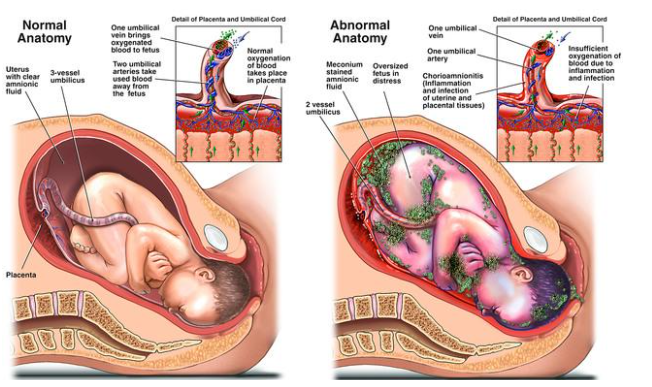
A nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of a client who is scheduled for a cesarean delivery.
Which of the following values should the nurse report to the provider?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B. The client can use patient-controlled analgesia to self-administer opioids.This is a form of multimodal analgesia, which is the core principle for cesarean delivery pain management.
Patient-controlled analgesia allows the client to have control over their pain relief and adjust the dose according to their needs.
Choice A is wrong because the client may experience delays in receiving analgesics if they have to request them from the nurse, which can lead to inadequate pain relief and increased opioid consumption.
Choice C is wrong because ice packs are not recommended for cesarean delivery pain management, as they may interfere with wound healing and increase the risk of infection.
Choice D is wrong because deep breathing and relaxation exercises are not sufficient to manage acute postoperative pain, although they may be helpful as adjuncts to pharmacologic methods.
A nurse is monitoring a patient who had a cesarean delivery for signs of infection.
Which of the following findings should alert the nurse to a possible infection? (Select all that apply.).
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A and B.A temperature of 38°C (100.4°F) or higher and foul-smelling lochia or increased lochia are signs of infection after a C-section.A C-section is a major surgery that involves making incisions in the abdomen and uterus, which can get infected by bacteria.An infection can also affect the lining of the uterus (endometritis) or the urinary tract.
Choice C is wrong because tenderness or hardness in the lower abdomen is normal after a C-section and does not indicate an infection.
Choice D is wrong because a decreased white blood cell count is not a sign of infection.In fact, an increased white blood cell count is more likely to occur with an infection.
Choice E is wrong because increased thirst or dry mouth is not a sign of infection.It could be due to dehydration, medication, or hormonal changes.
A nurse is providing discharge instructions to a patient who had a cesarean delivery.
Which of the following statements by the patient indicates an understanding of the teaching?
Explanation
“I can take ibuprofen or acetaminophen for pain relief.” This is because these are safe and effective medications for pain management after a C-section.
Choice A is wrong because driving is not recommended until the incision is healed and the pain is gone, which can take 4 to 6 weeks.
Choice B is wrong because lifting anything heavier than the baby can strain the incision and cause bleeding or infection.
Choice C is wrong because sexual intercourse should be avoided until the vaginal bleeding stops and the incision is healed, which can take 4 to 6 weeks or longer.
A nurse is evaluating the bonding between a patient who had a cesarean delivery and her newborn.
Which of the following behaviors by the patient indicates positive bonding?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice A. Holding the baby close to her chest and stroking his hair indicates positive bonding between the mother and the newborn.This behavior shows that the mother is attentive, affectionate, and responsive to her baby’s needs.
Choice B is wrong because looking away from the baby and talking to the visitors suggests that the mother is not interested in or attached to her baby.She may be distracted, overwhelmed, or depressed.
Choice C is wrong because handing the baby to the nurse whenever he cries implies that the mother is not willing or able to comfort her baby.She may be avoiding contact or feeling helpless.
Choice D is wrong because feeding the baby with a bottle and avoiding eye contact indicates that the mother is not engaging with her baby.She may be missing an opportunity to bond through eye contact, touch, and voice.
The health care team member is providing preoperative education to a patient who is having a planned cesarean delivery.
The patient asks, “When will I be able to see my baby?” The health care team member is aware that promoting maternal bonding during the recovery period is especially important for postcesarean patients.
Why is this true?
Explanation
The correct answer is choice B. Mothers may be at increased risk for poor bonding with the newborn.This is because cesarean delivery can interfere with the natural hormonal and physiological processes that facilitate maternal-infant attachment, such as skin-to-skin contact, breastfeeding initiation, and oxytocin release.Cesarean delivery can also cause more pain, stress, and anxiety for the mother, which can affect her emotional availability and responsiveness to the newborn.
Choice A is wrong because mothers do not necessarily have more problems with parenting skills after cesarean delivery.
Parenting skills depend on many factors, such as education, support, personality, and motivation.
Cesarean delivery may pose some challenges for postpartum recovery and care, but it does not imply that mothers are less competent or capable of parenting.
Choice C is wrong because mothers can breastfeed right away after cesarean delivery, unless there are medical contraindications or complications.
Breastfeeding is beneficial for both the mother and the newborn, as it provides nutrition, immunity, comfort, and bonding.However, breastfeeding after cesarean delivery may require more assistance and support from health care providers and family members, as well as alternative positions and techniques to avoid pain and discomfort.
Choice D is wrong because mothers do not necessarily resent the health care team member for keeping the newborn in the nursery.
Mothers may appreciate the help and care that the health care team member provides for them and their newborns.
However, keeping the newborn in the nursery may delay or reduce the opportunities for maternal-infant interaction and bonding.
Therefore, it is recommended to promote early and frequent contact between the mother and the newborn after cesarean delivery, as long as it is safe
As a patient is arriving in the recovery area following a cesarean delivery, the health care team member receives a hand-off report from the anesthesia provider.
Which information should be included in this report? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
The correct answer is choices A, B, C and D. The type of anesthesia used, the estimated blood loss during surgery, the vital signs and oxygen saturation, and the allergies and medications given are all important information to be included in the hand-off report from the anesthesia provider to the recovery area staff.
These information help to assess the patient’s condition, monitor for complications, and plan for appropriate interventions.
Choice E is wrong because the Apgar scores of the newborn are not relevant to the patient’s recovery from cesarean delivery.
The Apgar scores are used to evaluate the newborn’s physical condition at birth and are usually reported by the neonatal team.
The recovery area staff should focus on the patient’s postoperative care and pain management.
The following statement(s) is/are true about the risks of Cesarean section:.
Explanation
The correct answer is choiceD.A planned Cesarean section increases the rate of unexplained stillbirths at or after 34 weeks in future pregnancies.This is because a prior Cesarean section can cause placental abnormalities such as placenta previa and placenta accreta, which are associated with increased risk of stillbirth.
Choice A is wrong because the evidence comparing the risks of planned Cesarean section and vaginal delivery is mainly low or moderate quality.There are many confounding factors that can affect the outcomes of different modes of delivery, and most studies are observational and not randomized.
Choice B is wrong because the immediate maternal risks from a planned Cesarean section are not significantly higher than those of a planned vaginal delivery.However, a planned Cesarean section is associated with higher risks of infection, thromboembolism, wound complications, and longer hospital stay than a planned vaginal delivery.
Choice C is wrong because a vaginal birth is not associated with a comparable or higher maternal mortality rate than planned Cesarean section.The maternal mortality rate for planned Cesarean section is 0.01% and for planned vaginal delivery is 0.02%, which means there is no significant difference between the two modes of delivery.
Choice E is wrong because there is no evidence that an association exists between a prior Cesarean section and subsequent preterm birth, fetal growth restriction and spontaneous miscarriage.
These outcomes are more likely to be influenced by other factors such as maternal age, medical conditions,
Exams on Cesarean delivery
Custom Exams
Login to Create a Quiz
Click here to loginCaesarean Delivery
Lessons
 Naxlex
Just Now
Naxlex
Just Now
Login to View Cesarean delivery Study Video
Notes Highlighting is available once you sign in. Login Here.
Objectives
Objectives
-
Understand the indications for a cesarean delivery.
-
Identify the preoperative nursing interventions for a cesarean delivery.
-
Describe the intraoperative nursing interventions for a cesarean delivery.
-
Recognize the postoperative nursing care for a patient who has undergone a cesarean delivery.
-
Explain the potential complications associated with a cesarean delivery.
-
Demonstrate knowledge of patient education regarding cesarean delivery.
Introduction
-
Cesarean delivery, also known as cesarean section or C-section, is the delivery of a neonate by surgical incision through the abdomen and uterus.
-
It is one of the most common major surgical procedures worldwide and in the United States.
-
It may occur under planned, unplanned or emergency conditions depending on the indications.
-
Indications for cesarean delivery may include:
-
Abnormal labor (e.g., dystocia, failure to progress, fetal malposition)
-
Cephalopelvic disproportion (e.g., macrosomia, hydrocephalus)
-
Gestational hypertension or diabetes mellitus
-
Active maternal herpes virus infection
-
Fetal compromise (e.g., distress, cord prolapse, breech presentation)
-
Placenta previa or abruptio placentae
-
Multiple gestation or previous uterine surgery
-
Maternal request or preference
-
Introduction
Introduction
-
Cesarean delivery, also known as cesarean section or C-section, is the delivery of a neonate by surgical incision through the abdomen and uterus.
-
It is one of the most common major surgical procedures worldwide and in the United States.
-
It may occur under planned, unplanned or emergency conditions depending on the indications.
-
Indications for cesarean delivery may include:
-
Abnormal labor (e.g., dystocia, failure to progress, fetal malposition)
-
Cephalopelvic disproportion (e.g., macrosomia, hydrocephalus)
-
Gestational hypertension or diabetes mellitus
-
Active maternal herpes virus infection
-
Fetal compromise (e.g., distress, cord prolapse, breech presentation)
-
Placenta previa or abruptio placentae
-
Multiple gestation or previous uterine surgery
-
Maternal request or preference
-
Nursing Interventions
1. Preoperative Nursing Interventions for Cesarean delivery:
-
Assess the patient's medical history, including any previous surgeries, medical conditions, and allergies.
-
Obtain vital signs and perform a thorough physical examination, paying special attention to the abdomen and pelvic area.
-
Administer prescribed medications, such as prophylactic antibiotics and antacids, as ordered by the healthcare provider.
-
Educate the patient about the surgical procedure, including the risks, benefits, and expected outcomes.
-
Ensure that informed consent has been obtained from the patient.
-
Support the patient emotionally and address any concerns or anxieties she may have regarding the procedure.
Postoperative Nursing Interventions for Caesarean delivery
2. Intraoperative Nursing Interventions for Cesarean delivery:
-
Assist the surgical team in preparing the patient for surgery, ensuring proper positioning and providing sterile draping.
-
Monitor the patient's vital signs closely throughout the procedure.
-
Anticipate the need for blood transfusions, if necessary, and have blood products readily available.
-
Maintain aseptic technique and prevent infection by following strict surgical hand hygiene protocols.
-
Assist the anesthesiologist in administering anesthesia, whether it is general or regional anesthesia (e.g., epidural or spinal).
-
Communicate effectively with the surgical team, providing any necessary information and advocating for the patient's safety.
Postoperative Nursing Interventions for Caesarean delivery
3. Postoperative Nursing Care for Cesarean delivery:
-
Monitor the patient's vital signs frequently, paying particular attention to blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature.
-
Assess the incision site for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or drainage.
-
Promote pain management by administering prescribed analgesics and utilizing non-pharmacological measures, such as positioning and relaxation techniques.
-
Encourage early ambulation and deep breathing exercises to prevent complications such as atelectasis and thromboembolism.
-
Assist the patient with breastfeeding, ensuring proper latch and positioning to promote successful nursing.
-
Provide emotional support and address any concerns or questions the patient may have regarding her recovery or caring for her newborn.
Complications of Cesarean delivery
Complications of Cesarean delivery:
-
Infection: Monitor for signs of infection at the incision site, including increased redness, swelling, warmth, and purulent drainage. Administer prescribed antibiotics as ordered.
-
Hemorrhage: Monitor for excessive bleeding and signs of hypovolemic shock, such as tachycardia, hypotension, and pallor. Initiate appropriate interventions, such as applying pressure to the bleeding site and administering intravenous fluids or blood products as needed.
-
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): Assess for signs of DVT, such as calf pain, swelling, and warmth. Encourage early ambulation and provide prophylactic measures, such as anti-embolism stockings or intermittent pneumatic compression devices.
-
Wound dehiscence: Assess the incision site for signs of dehiscence, including separation of the wound edges. Apply sterile dressings as needed and notify the healthcare provider promptly.
-
Urinary retention: Monitor the patient's urinary output and assess for signs of urinary retention, such as inability to void, distended bladder, and discomfort. Encourage frequent voiding and provide assistance as needed, such as with the use of a bedpan or urinal.
-
Respiratory complications: Monitor the patient's respiratory status closely, assessing for signs of respiratory distress, such as increased respiratory rate, shallow breathing, and decreased oxygen saturation. Encourage deep breathing exercises and use incentive spirometry to promote optimal lung expansion.
Patient Education
-
Provide detailed instructions to the patient regarding wound care, including proper cleansing, dressing changes, and signs of infection to watch for.
-
Educate the patient on pain management techniques, such as using prescribed analgesics, applying cold packs, and utilizing relaxation techniques.
-
Teach the patient about the importance of early ambulation to prevent complications and promote healing.
-
Discuss breastfeeding techniques and positions with the patient, addressing any concerns or difficulties she may have.
-
Provide information on postpartum emotions and the importance of seeking support if experiencing postpartum depression or anxiety.
Summary:
-
Cesarean delivery is a surgical procedure performed when vaginal delivery is not recommended or poses a risk to the mother or baby.
-
Preoperative nursing interventions include assessing the patient's medical history, administering medications, and educating the patient about the procedure.
-
Intraoperative nursing interventions involve assisting the surgical team, monitoring vital signs, and ensuring aseptic technique.
-
Postoperative nursing care includes monitoring vital signs, assessing the incision site, promoting pain management, and providing support for breastfeeding and emotional well-being.
-
Potential complications of cesarean delivery include infection, hemorrhage, deep vein thrombosis, wound dehiscence, urinary retention, and respiratory complications.
-
Patient education should cover wound care, pain management, ambulation, breastfeeding, and postpartum emotions.
Summary
Introduction
-
Cesarean delivery, also known as cesarean section or C-section, is the delivery of a neonate by surgical incision through the abdomen and uterus.
-
It is one of the most common major surgical procedures worldwide and in the United States.
-
It may occur under planned, unplanned or emergency conditions depending on the indications.
-
Indications for cesarean delivery may include:
-
Abnormal labor (e.g., dystocia, failure to progress, fetal malposition)
-
Cephalopelvic disproportion (e.g., macrosomia, hydrocephalus)
-
Gestational hypertension or diabetes mellitus
-
Active maternal herpes virus infection
-
Fetal compromise (e.g., distress, cord prolapse, breech presentation)
-
Placenta previa or abruptio placentae
-
Multiple gestation or previous uterine surgery
-
Maternal request or preference
-
Summary:
-
Cesarean delivery is a surgical procedure performed when vaginal delivery is not recommended or poses a risk to the mother or baby.
-
Preoperative nursing interventions include assessing the patient's medical history, administering medications, and educating the patient about the procedure.
-
Intraoperative nursing interventions involve assisting the surgical team, monitoring vital signs, and ensuring aseptic technique.
-
Postoperative nursing care includes monitoring vital signs, assessing the incision site, promoting pain management, and providing support for breastfeeding and emotional well-being.
-
Potential complications of cesarean delivery include infection, hemorrhage, deep vein thrombosis, wound dehiscence, urinary retention, and respiratory complications.
-
Patient education should cover wound care, pain management, ambulation, breastfeeding, and postpartum emotions.
Naxlex
Videos
Login to View Video
Click here to loginTake Notes on Cesarean delivery
This filled cannot be empty
Join Naxlex Nursing for nursing questions & guides! Sign Up Now


