Please set your exam date
Integumentary System
Study Questions
Acne Vulgaris
Explanation
Explanation: Acne vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects the hair follicles and sebaceous glands. It is characterized by the formation of comedones (blackheads and whiteheads), papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts. While it is not caused by a viral, bacterial, or fungal infection, it is associated with factors such as hormonal imbalances, increased sebum production, and inflammation of the hair follicles.
Incorrect choices: a. A viral skin infection - This is incorrect because acne vulgaris is not caused by a viral infection. It is primarily a result of the abnormal keratinization of hair follicles and excessive sebum production.
b. A bacterial skin infection - This is incorrect because although bacteria can play a role in the development of acne, it is not the primary cause. Propionibacterium acnes, a type of bacteria, is commonly found on the skin and can contribute to inflammation in acne lesions, but it is not the initial cause of acne.
d. A fungal skin infection - This is incorrect because acne vulgaris is not caused by a fungal infection. It is not related to fungi or yeast but is rather a disorder of the pilosebaceous unit in the skin.
Explanation
Explanation: Acne vulgaris most commonly affects adolescents and young adults. It is estimated that up to 85% of individuals between the ages of 12 and 24 years experience acne at some point. During puberty, there is an increase in androgen hormones that can lead to an overproduction of sebum, leading to the development of acne.
Incorrect choices: a. Infants and young children - This is incorrect because acne vulgaris is rare in infants and young children. Acne in this age group may be a result of other underlying conditions and requires further evaluation by a healthcare provider.
c. Middle-aged adults - This is incorrect because acne vulgaris typically decreases with age. While some adults may still experience acne, it is less common compared to adolescents and young adults.
d. Elderly individuals - This is incorrect because acne vulgaris is rare in elderly individuals. It is more common in younger age groups due to hormonal changes and increased sebum production during adolescence and early adulthood.
Explanation
Explanation: The primary cause of acne vulgaris is hormonal imbalances, specifically an increase in androgen hormones during puberty. Androgens stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce more sebum, which can clog the hair follicles and lead to the development of acne. While bacteria (Propionibacterium acnes) can contribute to inflammation in acne lesions, it is not the primary cause of acne.
Incorrect choices: a. Bacterial infection - This is incorrect because while bacteria can contribute to the inflammation seen in acne, it is not the primary cause. Acne develops due to the abnormal process of keratinization of hair follicles and increased sebum production.
c. Excessive sun exposure - This is incorrect because while excessive sun exposure can exacerbate some skin conditions, it is not the primary cause of acne vulgaris. In fact, mild sun exposure can sometimes improve acne temporarily, but excessive sun exposure can lead to other skin issues and should be avoided.
d. Allergic reactions to skincare products - This is incorrect because while allergic reactions to skincare products can cause skin irritation, redness, and rashes, it is not the primary cause of acne vulgaris. Acne develops due to hormonal factors and other underlying mechanisms in the skin.
Explanation
Explanation: Acne vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects the hair follicles and sebaceous glands. It is characterized by the formation of comedones (blackheads and whiteheads), papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts. While hygiene and diet may play a role in acne development, they are not the sole causes. Acne is primarily influenced by hormonal factors, excessive sebum production, abnormal keratinization of hair follicles, and inflammation.
Incorrect choices: a. A skin condition caused by a lack of proper hygiene - This choice is incorrect because while proper hygiene is essential for maintaining skin health, acne is not solely caused by poor hygiene practices. Other factors like hormonal imbalances and inflammation play a more significant role in acne development.
b. A bacterial infection resulting from poor diet - This choice is incorrect because acne is not a bacterial infection caused by diet alone. While bacteria, particularly Propionibacterium acnes, are associated with acne lesions, the primary causes are related to hormonal changes and abnormal sebum production.
d. A viral skin infection transmitted through direct contact - This choice is incorrect because acne is not a viral infection and is not transmitted through direct contact. Acne is a non-communicable skin condition influenced by various internal and external factors, but not by a virus.
Explanation
Explanation: The clinical manifestation described in option c (erythematous, raised plaques with silver scales) is not commonly seen in acne vulgaris. This description is characteristic of psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune skin condition. Acne vulgaris is characterized by the presence of comedones (blackheads and whiteheads), papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts on the skin, primarily affecting the face, neck, chest, and back.
Incorrect choices: a. Comedones (blackheads and whiteheads) - This choice is incorrect. Comedones are a hallmark clinical feature of acne vulgaris, and they occur when hair follicles become clogged with sebum and dead skin cells.
b. Papules and pustules - This choice is incorrect. Papules are small, red, inflamed bumps, while pustules are pus-filled lesions. Both are common manifestations of acne vulgaris.
d. Nodules and cysts - This choice is incorrect. Nodules and cysts are severe forms of acne vulgaris, characterized by larger, painful, and deeper lesions beneath the skin's surface. They are more likely to cause scarring and require medical intervention.
Explanation
Explanation: The small, white bumps on the patient's forehead and chin are characteristic of closed comedones, also known as whiteheads. Comedones are non-inflammatory lesions and are one of the primary clinical manifestations of acne vulgaris.
Incorrect choices: a. Papules - Papules are small, red, inflamed bumps that may be present in acne vulgaris. However, they are not associated with the small, white bumps described in this question.
b. Pustules - Pustules are pus-filled lesions seen in acne vulgaris, but they are not the correct term for the small, white bumps in this scenario.
d. Nodules - Nodules are large, painful, solid lesions that extend deeper into the skin. They are not the correct term for the white bumps described in the question.
Explanation
Explanation: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly an increase in androgen hormones during adolescence, play a significant role in the development of acne vulgaris. Androgens stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce more sebum, which can clog hair follicles and lead to the formation of acne lesions.
Incorrect choices: a. Bacterial infection - While bacteria, specifically Propionibacterium acnes, may contribute to the inflammation and worsening of acne lesions, it is not the primary cause of acne vulgaris.
b. Excessive sun exposure - Excessive sun exposure can exacerbate acne lesions, but it is not the primary cause of acne vulgaris.
d. Allergic reaction to cosmetics - Allergic reactions to cosmetics can cause skin irritation and rashes but are not the primary cause of acne vulgaris.
Explanation
Explanation: Pustules are inflamed, tender, and pus-filled lesions commonly seen in acne vulgaris. They are a result of bacterial infection and inflammation within the blocked hair follicles.
Incorrect choices: a. Comedones - Comedones are non-inflammatory lesions that may be open (blackheads) or closed (whiteheads) and are not inflamed or pus-filled.
b. Nodules - Nodules are larger, solid, and painful lesions that extend deeper into the skin. They are more severe than pustules and papules.
c. Papules - Papules are small, red, inflamed bumps on the skin but are not pus-filled like pustules.
Explanation
Explanation: The primary pathogenesis of acne vulgaris involves increased keratinization (abnormal skin cell turnover) and follicular plugging. Excess sebum production, along with dead skin cells and bacteria, can lead to the formation of comedones, which are a hallmark of acne vulgaris.
Incorrect choices: a. Excessive skin hydration - Excessive skin hydration is not the primary pathogenesis of acne vulgaris. In fact, excessive oil production contributes to the development of acne lesions.
c. Overproduction of melanin - Overproduction of melanin is not the primary cause of acne vulgaris. Melanin is responsible for skin pigmentation, but it does not directly contribute to acne formation.
d. Allergic reaction to environmental allergens - Acne vulgaris is not primarily caused by an allergic reaction to environmental allergens. While allergens can exacerbate skin conditions, they are not the underlying cause of acne vulgaris.
Explanation
Explanation: The primary diagnostic criterion for acne vulgaris is the presence of comedones, which are non-inflammatory lesions that occur when hair follicles become clogged with sebum and dead skin cells. Comedones can be either open (blackheads) or closed (whiteheads) and are a hallmark of acne vulgaris.
Incorrect choices: b. Appearance of pustules - Pustules are inflammatory lesions seen in acne vulgaris, but they are not the primary diagnostic criterion.
c. Erythematous, raised plaques with silver scales - This description is characteristic of psoriasis, not acne vulgaris. Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition.
d. Nodules and cysts on the skin - Nodules and cysts are severe forms of acne vulgaris, but they are not the primary diagnostic criterion. They may develop in later stages of the condition.
Explanation
Explanation: The presence of a rash on the hands and feet is not a common diagnostic criterion for acne vulgaris. Acne vulgaris primarily affects the face, neck, chest, and back, and rashes on the hands and feet are not characteristic of this condition.
Incorrect choices: a. Family history of acne - A family history of acne is a relevant diagnostic criterion as there can be a genetic predisposition to developing acne.
b. Skin biopsy - A skin biopsy may be used in some cases to confirm the diagnosis of acne vulgaris and rule out other skin conditions with similar presentations.
d. Physical examination of the skin - Physical examination of the skin is a standard diagnostic approach for identifying acne vulgaris. It involves assessing the presence of comedones, papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts on the skin.
Explanation
Explanation: The distribution of the lesions is a key diagnostic criterion used to differentiate acne vulgaris from acne rosacea. Acne vulgaris commonly affects the face, neck, chest, and back, while acne rosacea typically presents with erythema (redness) and affects the central areas of the face, such as the cheeks and nose.
Incorrect choices: a. Presence of comedones - The presence of comedones is common in both acne vulgaris and acne rosacea, and it does not help differentiate between the two conditions.
b. Age of the patient - While age can provide some clues, it is not a definitive diagnostic criterion as both acne vulgaris and acne rosacea can affect individuals of different age groups.
d. Severity of skin redness - The severity of skin redness is a characteristic of acne rosacea, but it alone does not differentiate it from acne vulgaris. The distribution of lesions is more specific for distinguishing between the two conditions.
Explanation
Explanation: The description of small, red, inflamed bumps on the face and back is consistent with papules, which are a common clinical manifestation of acne vulgaris.
Incorrect choices: a. Presence of nodules and cysts - Nodules and cysts are deeper, larger, and more severe lesions that extend into the skin. They are not characteristic of the small, red, inflamed bumps described.
b. Appearance of comedones - Comedones are non-inflammatory lesions and do not present as red, inflamed bumps.
c. Distribution of pustules - Pustules are pus-filled lesions, and the description of the patient's skin lesions does not specifically mention pustules.
Explanation
Explanation: The diagnostic criteria for acne vulgaris typically include the identification of both comedones (blackheads and whiteheads) and inflammatory lesions (papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts). These manifestations are characteristic of acne vulgaris and help distinguish it from other skin conditions.
Incorrect choices: a. Scalp lesions - Scalp lesions are not specific to acne vulgaris and may be associated with other skin conditions or scalp disorders.
b. Yellowish-brown nodules - Yellowish-brown nodules are not commonly associated with acne vulgaris. These nodules may indicate a different skin condition.
c. Erythematous plaques with silver scales - This description is characteristic of psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune skin condition, and is not indicative of acne vulgaris.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice b is correct because non-comedogenic makeup products are formulated not to clog pores, which can help prevent further acne breakouts. Other makeup products may contribute to pore blockages and exacerbate acne.
Incorrect choices: a. "Apply oil-based moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated." - Oil-based moisturizers can be heavy and may contribute to clogged pores, worsening acne in some cases.
c. "Exfoliate the skin daily to remove dead skin cells." - Daily exfoliation can irritate the skin and may lead to increased inflammation and breakouts. Gentle exfoliation, no more than two to three times per week, is recommended.
d. "Use hot water to wash your face for better results." - Hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils and lead to dryness and irritation. Lukewarm water is preferable for cleansing the face to avoid exacerbating acne symptoms.
The nurse is caring for a client with acne vulgaris. Which intervention is appropriate for nursing management of acne vulgaris?
Explanation
While some medications for acne (like retinoids) can increase sensitivity to the sun, and sun exposure can worsen acne or lead to hyperpigmentation, this is a beneficial recommendation.
Incorrect choices:
a. Squeezing and popping acne lesions to release pus. - This intervention can lead to infection and scarring, as well as exacerbate inflammation and further spread bacteria.
b. Recommending the use of abrasive facial scrubs daily. - Daily use of abrasive facial scrubs can irritate the skin and worsen acne symptoms. Gentle cleansing is preferred for individuals with acne-prone skin.
d. Applying over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream to the affected areas. - Hydrocortisone cream is a topical steroid and is not recommended for routine use on acne lesions. It may cause skin thinning and other side effects if used improperly.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice c indicates a need for further teaching because applying a thick layer of moisturizer before bedtime can potentially clog pores and worsen acne. While moisturizing is essential for preventing dryness, it is essential to use non-comedogenic, oil-free moisturizers that are suitable for acne-prone skin.
Incorrect choices: a. "I will cleanse my face with a mild, non-soap cleanser twice a day." - This statement is correct as cleansing the face with a mild, non-soap cleanser twice a day helps remove dirt, excess oil, and debris without drying out the skin excessively.
b. "I will use a topical retinoid as prescribed by my healthcare provider." - This statement is correct as topical retinoids are a common treatment for acne vulgaris and help promote skin cell turnover and prevent clogged pores.
d. "I will avoid picking or squeezing acne lesions to prevent scarring." - This statement is correct as picking or squeezing acne lesions can lead to infection, inflammation, and scarring.
Explanation
Explanation: Regular monitoring of liver function is essential for clients receiving oral antibiotics for acne vulgaris because some antibiotics may have the potential to cause hepatotoxicity (liver damage). Monitoring liver function helps detect any adverse effects and ensures the client's safety during treatment.
Incorrect choices: a. Encourage the client to avoid consuming dairy products during antibiotic treatment. - There is no specific evidence that links dairy consumption with the effectiveness of oral antibiotics for acne vulgaris. Dairy restriction is not typically indicated for clients on acne treatment.
b. Educate the client on the importance of sun exposure for vitamin D synthesis. - While sun exposure can contribute to vitamin D synthesis, it is not specifically relevant to the client's treatment with oral antibiotics for acne vulgaris. In fact, sun exposure should be minimized or accompanied by sunscreen due to the potential for photosensitivity caused by some antibiotics.
d. Recommend the use of topical benzoyl peroxide in combination with oral antibiotics. - This may be a valid treatment option; however, the question specifically asks for a nursing management action related to the oral antibiotics. The nurse's responsibility is to monitor the client's response to the prescribed oral antibiotics and potential side effects, not topical treatment recommendations.
Explanation
Explanation: The nurse's role in addressing the client's concern about potential scarring is to provide emotional support and encouragement. Acne can have a significant impact on self-esteem, especially in teenagers. Encouraging open communication and offering support can help the client cope with the emotional aspect of acne and its potential effects on self-image.
Incorrect choices: a. Apply a topical retinoid liberally to prevent scarring. - While topical retinoids are used in the treatment of acne vulgaris, they are not specifically applied to prevent scarring. Their primary role is to promote skin cell turnover and prevent clogged pores.
b. Recommend using oil-based makeup products to cover acne scars. - Using oil-based makeup products may worsen acne and is not a recommended strategy for covering scars. Non-comedogenic makeup products are preferable for individuals with acne-prone skin.
c. Educate the client on avoiding sun exposure to minimize scarring. - While avoiding sun exposure is essential to protect the skin from UV damage, it does not specifically minimize scarring caused by acne. Preventing acne lesions and avoiding picking or squeezing existing lesions are more effective strategies to prevent scarring.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice a indicates a need for further teaching because washing the face several times a day can strip the skin of its natural oils and lead to dryness and irritation. Over-washing can also worsen acne by disrupting the skin's natural barrier and increasing oil production.
Incorrect choices: b. "I will use oil-free and non-comedogenic makeup products." - This statement is correct as using oil-free and non-comedogenic makeup products can help prevent clogged pores and further acne breakouts.
c. "I will avoid picking or squeezing my acne lesions to prevent scarring." - This statement is correct as picking or squeezing acne lesions can lead to infection, inflammation, and scarring.
d. "I will apply a thick layer of petroleum jelly to moisturize my skin." - This statement is incorrect because petroleum jelly is not recommended for acne-prone skin. Non-comedogenic, oil-free moisturizers are preferred for individuals with acne vulgaris.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice d indicates a need for further teaching because there is some evidence linking dairy consumption to an increased risk of acne development. It is generally recommended to limit dairy intake in individuals with acne vulgaris.
Incorrect choices: a. "I will avoid eating fried and greasy foods." - This statement is correct as fried and greasy foods can exacerbate acne by increasing oil production and clogging pores.
b. "I will increase my intake of fruits and vegetables." - This statement is correct as fruits and vegetables provide essential nutrients and antioxidants that support skin health.
c. "I will limit my consumption of sugary and processed foods." - This statement is correct as sugary and processed foods can contribute to inflammation and worsen acne symptoms.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice d indicates a need for further teaching because avoiding communication and bottling up stress can lead to increased emotional distress, which may actually worsen acne symptoms. Open communication and seeking support from friends and loved ones can be beneficial in managing stress.
Incorrect choices: a. "I will practice stress-reducing techniques like deep breathing and meditation." - This statement is correct as stress-reducing techniques can help manage stress, which may have a positive impact on acne symptoms.
b. "I understand that stress can worsen my acne symptoms." - This statement is correct as stress is known to trigger or worsen acne symptoms in some individuals.
c. "I will engage in regular physical activity to manage stress." - This statement is correct as regular physical activity can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice c indicates a need for further teaching because using tanning beds can increase the risk of skin damage and worsen acne symptoms. Tanning beds emit harmful UV rays, which can lead to premature aging and increase the risk of skin cancer.
Incorrect choices: a. "I will use sunscreen with at least SPF 30 daily." - This statement is correct as using sunscreen with at least SPF 30 daily is essential to protect the skin from harmful UV rays and prevent skin damage.
b. "I will avoid sun exposure during peak hours." - This statement is correct as avoiding sun exposure during peak hours (usually 10 am to 4 pm) reduces the risk of sunburn and other skin damage.
d. "I understand that some acne medications can increase sun sensitivity." - This statement is correct as certain acne medications, such as retinoids, can increase the skin's sensitivity to the sun. It is essential to take extra precautions and use sun protection when using these medications.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice b indicates a need for further teaching because scrubbing the face vigorously can irritate the skin and worsen acne lesions. Gentle cleansing is recommended to avoid skin irritation and inflammation.
Incorrect choices: a. "I will cleanse my face with a gentle, non-abrasive cleanser twice daily." - This statement is correct as gentle cleansing with a non-abrasive cleanser can help remove excess oil, dirt, and debris from the skin without causing irritation.
c. "I will avoid using oil-based moisturizers on my face." - This statement is correct as oil-based moisturizers can clog pores and worsen acne. Non-comedogenic, oil-free moisturizers are recommended for acne-prone skin.
d. "I will avoid picking or squeezing my acne lesions." - This statement is correct as picking or squeezing acne lesions can lead to infection, inflammation, and scarring. It is important to leave acne lesions untouched and let them heal naturally.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice a indicates a need for further teaching because salicylic acid is a common ingredient in many acne treatments and is known for its exfoliating and acne-fighting properties. Avoiding skincare products with salicylic acid may limit the client's access to effective acne treatments.
Incorrect choices: b. "I will wash my face twice daily with a gentle cleanser." - This statement is correct as regular face washing with a gentle cleanser can help remove excess oil and dirt, preventing clogged pores and reducing the risk of acne breakouts.
c. "I will change my pillowcase every week to prevent bacterial buildup." - This statement is correct as changing pillowcases regularly can prevent the accumulation of oils and bacteria that can contribute to acne development.
d. "I will avoid touching my face frequently to prevent the spread of bacteria." - This statement is correct as touching the face frequently can transfer bacteria and dirt from the hands to the face, increasing the risk of acne breakouts.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice c indicates a need for further teaching because while moderate sun exposure can help the body produce vitamin D, spending excessive time outdoors without sun protection can lead to sunburn and skin damage. Sunburn can exacerbate acne and increase the risk of skin cancer.
Incorrect choices: a. "I will avoid consuming foods high in sugar and processed carbohydrates." - This statement is correct as a diet high in sugar and processed carbohydrates can trigger inflammation and worsen acne symptoms.
b. "I will ensure to get enough sleep and rest to support skin health." - This statement is correct as adequate sleep and rest promote overall health and can positively impact skin health.
d. "I will wash my hair regularly to prevent oil transfer to my face." - This statement is correct as washing the hair regularly can help prevent excess oil and hair care products from transferring to the face, which can clog pores and lead to acne breakouts.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice c indicates a need for further teaching because petroleum jelly is not recommended for acne-prone skin. It can clog pores and potentially worsen acne symptoms.
Incorrect choices: a. "I will use a water-based moisturizer to keep my skin hydrated." - This statement is correct as water-based moisturizers are recommended for acne-prone skin as they do not clog pores and help keep the skin hydrated.
b. "I will avoid squeezing my acne lesions to prevent scarring." - This statement is correct as squeezing acne lesions can lead to infection, inflammation, and scarring.
d. "I will use oil-free sunscreen to protect my skin from harmful UV rays." - This statement is correct as using oil-free sunscreen can protect the skin from sunburn and damage without clogging pores and worsening acne.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice d indicates a need for further teaching because hormones play a significant role in the development of acne. Hormonal changes during puberty and the menstrual cycle can lead to increased oil production and clogged pores, contributing to acne development.
Incorrect choices: a. "Hormonal changes during puberty can lead to increased oil production in the skin." - This statement is correct as hormonal changes during puberty can increase the skin's sebum production, which can contribute to acne development.
b. "Hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle can worsen my acne." - This statement is correct as hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle can exacerbate acne symptoms in some individuals.
c. "Hormonal contraceptives can help regulate hormone levels and improve acne." - This statement is correct as hormonal contraceptives can be prescribed to manage acne in some cases by regulating hormone levels.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice c indicates a need for further teaching because applying acne cream all over the face is unnecessary and can lead to skin irritation. Acne creams should be applied only to the affected areas to avoid over-drying and irritating healthy skin.
Incorrect choices: a. "I will apply the acne cream on my face after washing and drying my skin." - This statement is correct as applying the acne cream on clean and dry skin enhances its effectiveness.
b. "I will apply a thin layer of the acne cream only on the affected areas." - This statement is correct as applying a thin layer of acne cream on the affected areas allows for targeted treatment without over-applying and potentially irritating the skin.
d. "I will avoid using any other skincare products while using the acne cream." - This statement is correct as using multiple acne treatments or skincare products simultaneously can lead to skin irritation and adverse reactions. It is best to follow a simple skincare routine and avoid combining products without medical advice.
More questions
Explanation
Explanation: Choice a indicates a need for further teaching because acne is not caused by poor hygiene practices alone. While keeping the skin clean is important, acne results from a combination of factors, including hormonal changes, excess oil production, and clogged pores.
Incorrect choices: b. "Hormonal changes can trigger acne breakouts." - This statement is correct as hormonal fluctuations, especially during puberty, can lead to increased sebum production, contributing to acne development.
c. "Certain foods, like chocolate, can worsen acne." - This statement is correct as certain foods may exacerbate acne symptoms in some individuals, though the effect varies from person to person.
d. "Stress and anxiety can worsen acne symptoms." - This statement is correct as stress can trigger hormonal responses that influence acne development and worsen existing symptoms.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice a indicates a need for further teaching because using a cleanser with exfoliating beads can be too harsh for acne-prone skin and may lead to irritation and worsen acne symptoms.
Incorrect choices: b. "I will avoid cleansers with harsh chemicals and fragrances." - This statement is correct as harsh chemicals and fragrances can irritate the skin and worsen acne symptoms.
c. "I will wash my face twice daily to keep my skin clean and fresh." - This statement is correct as washing the face twice daily with a gentle cleanser can help remove excess oil and dirt, preventing clogged pores and reducing the risk of acne breakouts.
d. "I will pat my skin dry with a clean towel after washing my face." - This statement is correct as patting the skin dry with a clean towel is gentler on the skin and reduces friction that can worsen acne.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice a indicates a need for further teaching because applying acne cream on the entire face is unnecessary and can lead to skin irritation. Acne treatments should be applied only to the affected areas to avoid over-drying and irritating healthy skin.
Incorrect choices: b. "I will use the acne treatment as directed and avoid over-applying." - This statement is correct as over-applying acne treatments can lead to skin irritation and adverse reactions. Following the instructions on the product label is essential for safe and effective use.
c. "I will perform a patch test before using any new acne product." - This statement is correct as patch testing helps determine if a new product may cause an allergic reaction or irritation, especially for individuals with sensitive skin.
d. "I will discontinue the acne treatment once my skin clears up." - This statement is correct as acne treatments should be used consistently, even if the skin clears up, to prevent future breakouts and maintain results.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice b indicates a need for further teaching because while moderate sun exposure can be beneficial, excessive sunlight can worsen acne and lead to skin damage.
Incorrect choices: a. "I will avoid touching my face frequently to prevent bacterial transfer." - This statement is correct as touching the face frequently can transfer bacteria and dirt from the hands to the face, increasing the risk of acne breakouts.
c. "I will practice stress-reducing techniques to support my skin health." - This statement is correct as stress can trigger hormonal responses that influence acne development. Managing stress can help reduce the frequency and severity of acne breakouts.
d. "I will follow a well-balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables." - This statement is correct as a well-balanced diet with fruits and vegetables provides essential nutrients that support skin health and may help reduce acne symptoms.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice d indicates a need for further teaching because acne does not cause excessive production of skin oils; rather, it results from an increase in sebum production, which can clog pores and contribute to acne development.
Incorrect choices: a. "Untreated severe acne can lead to permanent scarring and skin damage." - This statement is correct as untreated severe acne can leave permanent scars and cause skin damage, especially if the lesions are deep and inflamed.
b. "Severe acne can increase the risk of developing skin infections." - This statement is correct as open acne sores can serve as entry points for bacteria, increasing the risk of skin infections.
c. "Untreated acne may cause psychological and emotional distress." - This statement is correct as severe acne can have a significant impact on a person's self-esteem and cause psychological and emotional distress.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice d indicates a need for further teaching because acne vulgaris is not primarily caused by a deficiency of vitamins and minerals. Acne results from a combination of factors such as increased sebum production, clogged hair follicles, bacterial colonization, and inflammation.
Incorrect choices: a. "Acne vulgaris is caused by bacterial infections on the skin." - This statement is partially correct. Bacteria, particularly Propionibacterium acnes, play a role in the inflammation and exacerbation of acne, but they are not the sole cause.
b. "Acne vulgaris results from an overproduction of sebum by the sebaceous glands." - This statement is correct. An excess production of sebum contributes to the development of acne by clogging pores and promoting
bacterial growth.
c. "Acne vulgaris is a result of hormonal changes during puberty." - This statement is correct. Hormonal changes during puberty can lead to increased sebum production and contribute to the development of acne.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice a indicates a need for further teaching because washing the face with hot water can actually lead to skin irritation and exacerbate acne. Hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and potential inflammation.
Incorrect choices: b. "I will use a gentle cleanser to wash my face twice daily." - This statement is correct. A gentle cleanser can effectively remove excess oil and debris without causing irritation.
c. "I will avoid scrubbing my face vigorously to prevent skin irritation." - This statement is correct. Vigorous scrubbing can irritate the skin and worsen acne symptoms.
d. "I will moisturize my skin regularly to prevent dryness." - This statement is correct. Moisturizing the skin helps maintain skin barrier function and prevents dryness, especially if acne treatments may cause temporary dryness.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice b indicates a need for further teaching because frequently touching the face can transfer bacteria and oils from the hands to the face, potentially worsening acne symptoms.
Incorrect choices: a. "I will avoid squeezing my acne lesions to prevent scarring." - This statement is correct. Squeezing acne lesions can lead to scarring and should be avoided.
c. "I will avoid using oil-based cosmetics and skincare products." - This statement is correct. Oil-based products can clog pores and contribute to acne breakouts, so it is best to use non-comedogenic products.
d. "I will avoid wearing tight-fitting clothing that may irritate my skin." - This statement is correct. Tight-fitting clothing can trap sweat and irritate the skin, potentially worsening acne. Loose, breathable clothing is recommended.
Explanation
Explanation: Choice d indicates a need for further teaching because staying well-hydrated is essential for overall health, including skin health. While water alone may not directly impact acne, adequate hydration is crucial for maintaining healthy skin.
Incorrect choices: a. "I will reduce my intake of high-glycemic index foods like white bread and sugary snacks." - This statement is correct. High-glycemic index foods can lead to increased insulin levels, which may exacerbate acne.
b. "I will limit my consumption of dairy products, as they may worsen acne." - This statement is correct. Some individuals may experience worsening of acne with the consumption of dairy products.
c. "I will include more fruits and vegetables in my diet to support skin health." - This statement is correct. A balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables provides essential nutrients for skin health.
Explanation
Explanation: Oral retinoids, such as isotretinoin, are beneficial for severe acne vulgaris and can effectively reduce sebum production, skin inflammation, and acne lesions.
Incorrect choices: a. Oral antihistamine - Oral antihistamines are not typically used to treat acne vulgaris. They are used to manage allergy symptoms but do not target the underlying causes of acne.
b. Oral corticosteroid - Oral corticosteroids may be used in some cases of severe inflammation, but they are not a primary treatment for acne vulgaris and have potential side effects with long-term use.
d. Oral antibiotic - Oral antibiotics are used to treat acne when there is bacterial involvement, but they may not be as effective as oral retinoids in severe cases and may contribute to antibiotic resistance over time.
Eczema
Explanation
Explanation: Eczema is characterized by dry, red, and inflamed patches on the skin, which can be itchy and may sometimes appear scaly.
Incorrect choices: a. This choice describes a different skin condition, such as hives or urticaria, not eczema.
b. Painful blisters and pustules are more typical of conditions like impetigo or folliculitis, not eczema.
d. White, scaly patches with well-defined borders are associated with fungal infections like tinea versicolor, not eczema.
Explanation
Explanation: The term "dermatitis" is often used interchangeably with eczema to describe a group of skin conditions characterized by inflammation and irritation.
Incorrect choices: a. Psoriasis is a different skin condition characterized by red, raised, and scaly patches.
b. Acne is a skin condition characterized by clogged pores and pimples, not related to eczema.
d. Rosacea is a skin condition causing redness and visible blood vessels on the face, not related to eczema.
Explanation
Explanation: In infants, eczema often affects the scalp, face, and cheeks. It can cause dry, red, and flaky patches on the baby's skin.
Incorrect choices: b. Elbows and knees are common areas affected by psoriasis, not eczema.
C. The lower back is not a typical location for eczema flare-ups.
d. Buttocks and thighs are not commonly affected by eczema in infants.
Explanation
Explanation: Eczema is often associated with allergies, particularly allergic reactions to certain foods, environmental allergens, or irritants.
Incorrect choices: b. Diabetes, c. Hypothyroidism, and d. Hypertension are not directly linked to the development of eczema.
Explanation
Explanation: Eczema is most commonly seen in young children, particularly infants and toddlers. However, it can affect people of all ages.
Incorrect choices: a. Eczema is less common in elderly adults.
c. While eczema can occur in adolescents, it is more prevalent in younger children.
d. Eczema is not specifically associated with pregnancy.
Explanation
Explanation: Eczema is characterized by red, dry, and inflamed patches on the skin, which can be itchy and may sometimes appear scaly.
Incorrect choices: a. This choice describes a different skin condition, such as hives or urticaria, not eczema.
b. Painful blisters and pustules are more typical of conditions like impetigo or folliculitis, not eczema.
d. White, scaly patches with well-defined borders are associated with fungal infections like tinea versicolor, not eczema.
Explanation
Explanation: Pruritus, or itching, is a hallmark clinical manifestation of atopic dermatitis, which is a common type of eczema.
Incorrect choices: b. Swelling of the face and lips is not a typical manifestation of eczema.
c. Hyperpigmentation may occur in some chronic skin conditions, but it is not specific to eczema.
d. Formation of papules and nodules is more characteristic of conditions like acne or granuloma annulare, not atopic dermatitis.
Explanation
Explanation: In older children and adults, eczema often affects the elbows and knees, as well as other areas with skin folds.
Incorrect choices: a. The scalp is more commonly affected in infants and younger children.
c. The lower back is not a typical location for eczema flare-ups.
d. Buttocks and thighs are not as commonly affected as the elbows and knees.
Which type of eczema is associated with exposure to irritants in the environment?
Explanation
A.Atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition often associated with genetic factors, immune dysfunction, and hypersensitivity. It typically presents in individuals with a history of allergies, asthma, or hay fever.
B.Contact dermatitis occurs due to direct exposure to environmental irritants or allergens, such as soaps, detergents, chemicals, or plants like poison ivy. It can be classified into irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis.
C.Nummular eczema presents as coin-shaped lesions on the skin and is often associated with dry skin or allergens but is not directly linked to environmental irritants.
D.Seborrheic dermatitis affects areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, face, and chest. It is thought to be linked to overgrowth of yeast (e.g., Malassezia) and is influenced by factors like stress and hormones.
Explanation
Explanation: Nummular eczema presents with round or oval-shaped lesions that resemble targets or coins.
Incorrect choices: b. Honey-colored crusts are typical of impetigo, not nummular eczema.
c. Linear streaks may be seen in cases of contact dermatitis due to the pattern of allergen exposure.
d. Spider-like veins on the skin are associated with spider angiomas and are not related to nummular eczema.
Explanation
Explanation: Eczema is characterized by red, inflamed, and itchy skin lesions with well-defined borders.
Incorrect choices: a. Pustules filled with clear fluid are more indicative of conditions like impetigo, not eczema.
c. Eczema can affect multiple body parts and is not confined to just one area.
d. Pruritus or itching is a typical symptom of eczema and is considered a key diagnostic criterion.
Explanation
Explanation: Target-shaped lesions are not typical of eczema but may be seen in other conditions like erythema multiforme.
Incorrect choices: a. Rapidly spreading erythema is a characteristic of cellulitis, not eczema.
c. Honey-colored crusts on the skin are associated with impetigo, not eczema.
d. Relief with exposure to irritants is not a diagnostic feature of eczema.
Explanation
Explanation: Patch testing is a common diagnostic test used to identify potential allergens in cases of allergic contact dermatitis, a type of eczema.
Incorrect choices: b. PCR analysis is a molecular technique used for detecting DNA, and it is not a standard diagnostic test for eczema.
c. Complete blood count (CBC) is a general blood test that may show nonspecific signs of inflammation but is not specific to eczema.
d. Skin biopsy is performed to rule out other skin conditions but is not the primary diagnostic test for eczema.
Explanation
Explanation: Nummular eczema is characterized by the presence of distinct coin-shaped or round lesions on the skin.
Incorrect choices: a. Atopic dermatitis is associated with generalized red, inflamed patches of skin, not coin-shaped lesions.
b. Contact dermatitis is caused by exposure to irritants or allergens and does not typically result in coin-shaped lesions.
d. Seborrheic dermatitis is commonly seen on the scalp and face and presents with red, scaly patches, not coin-shaped lesions.
Explanation
Explanation: Infantile atopic dermatitis often affects areas with skin creases and flexures, such as the folds of the elbows and knees.
Incorrect choices: a. Cradle cap on the scalp is a condition related to seborrheic dermatitis, not infantile atopic dermatitis.
b. Vesicles and bullae on the skin are seen in conditions like pemphigus or bullous impetigo, not infantile atopic dermatitis.
c. Itchy skin may be present in eczema, but it is not limited to the diaper area and can occur in other parts of the body as well.
Explanation
Explanation: Cold weather is a common trigger for exacerbating eczema symptoms, as it can cause the skin to become dry and more prone to irritation and itching.
Incorrect choices: b. Sun exposure can be beneficial for some skin conditions but is not a common trigger for eczema exacerbation.
c. High humidity may actually help improve eczema symptoms for some individuals by keeping the skin moisturized.
d. While some people with eczema may have food sensitivities, consumption of dairy products is not a common trigger for eczema exacerbation in all cases.
Explanation
Explanation: Excessive sweating can worsen eczema symptoms in individuals with sensitive skin, as sweat can irritate the skin and lead to itching and inflammation.
Incorrect choices: a. Frequent moisturization is actually recommended to help manage eczema and keep the skin hydrated.
c. Avoiding allergenic foods may be helpful for individuals with food allergies, but it may not directly impact eczema symptoms for everyone.
d. Regular use of mild soaps is beneficial for individuals with eczema to avoid skin irritation from harsh chemicals and fragrances.
Explanation
Explanation: Air pollution can exacerbate eczema symptoms in some individuals by increasing skin sensitivity and inflammation.
Incorrect choices: a. Low humidity can actually worsen eczema symptoms for some individuals, as dry air can lead to skin dryness and irritation.
b. Exposure to pet dander may trigger allergies in some individuals, but it is not a direct cause of eczema aggravation for everyone.
d. Use of hypoallergenic fabrics is often recommended for individuals with eczema to minimize skin irritation from clothing.
Explanation
Explanation: Stress and anxiety can trigger or worsen eczema symptoms in some individuals due to the skin-brain connection and the release of stress hormones.
Incorrect choices: a. Regular exercise routine is generally beneficial for overall health, including skin health, and is not a common trigger for eczema exacerbation.
c. Adequate sleep is essential for skin health and may actually help improve eczema symptoms for some individuals.
d. Having a strong social support network can help individuals cope with stress, but it is not a direct cause of eczema exacerbation.
Explanation
Explanation: Processed foods with high levels of sugar, artificial additives, and preservatives can trigger inflammation and worsen eczema symptoms in some individuals.
Incorrect choices: a. High intake of omega-3 fatty acids is generally considered beneficial for skin health and may actually help improve eczema symptoms in some individuals.
b. Consuming probiotic-rich foods can promote gut health, which may indirectly benefit some individuals with eczema, but it is not a common trigger for exacerbation.
c. Regular consumption of spicy foods may cause digestive issues for some individuals, but it is not a direct cause of eczema exacerbation.
Explanation
Explanation: Using fragrance-free and mild soaps for cleansing is recommended for individuals with eczema to avoid skin irritation and dryness. Harsh soaps and strong fragrances can exacerbate eczema symptoms.
Incorrect choices: a. Avoiding moisturizers can lead to dry and cracked skin, worsening eczema symptoms. Moisturizers should be used regularly to keep the skin hydrated.
b. Taking hot showers can actually worsen eczema symptoms by stripping the skin of its natural oils and causing further dryness and irritation. Lukewarm showers are preferable.
d. Wearing tight-fitting clothing can irritate the skin and trap moisture, leading to increased itching and inflammation. Loose-fitting and breathable clothing is recommended.
Explanation
Explanation: Keeping the infant's nails short and clean can prevent excessive scratching and reduce the risk of introducing bacteria into the skin, which can lead to secondary skin infections.
Incorrect choices: a. Encouraging the infant to scratch the affected areas can exacerbate eczema symptoms and increase the risk of skin breakdown and infection.
c. Applying topical corticosteroids as prescribed by the healthcare provider can help manage eczema symptoms but does not directly prevent secondary skin infections.
d. Direct sunlight can be beneficial for some skin conditions, but excessive sun exposure can worsen eczema symptoms and increase the risk of skin damage.
Explanation
Explanation: Applying cold compresses can help soothe itching and reduce inflammation in patients with eczema.
Incorrect choices: b. Massaging the affected areas with warm oil can aggravate eczema symptoms by increasing blood flow and potentially irritating the skin further.
c. Using a heating pad can exacerbate itching and inflammation in eczema patients and should be avoided.
d. Over-the-counter hydrocortisone cream may be used with caution for mild eczema, but for severe symptoms, the patient should consult their healthcare provider for appropriate prescription-strength medications.
Explanation
Explanation: Tacrolimus ointment is considered safe for use during pregnancy and can be used to manage eczema symptoms.
Incorrect choices: b. Hydrocortisone cream is a topical corticosteroid that should be used with caution during pregnancy, and its use should be discussed with the healthcare provider.
c. Betamethasone cream is a potent topical corticosteroid that should be avoided during pregnancy unless the benefits outweigh the risks and as advised by the healthcare provider.
d. Coal tar solution may not be recommended during pregnancy due to limited safety data.
Explanation
Explanation: Applying moisturizer to damp skin after bathing helps lock in moisture and prevents dryness in individuals with eczema.
Incorrect choices: a. While avoiding allergenic foods can be helpful for individuals with food allergies, it may not directly impact eczema flare-ups in all cases.
b. Using harsh soaps and fragranced products for cleansing can actually worsen eczema symptoms by irritating the skin.
d. Exposing the affected areas to direct sunlight for prolonged periods can lead to skin damage and exacerbate eczema symptoms. Short periods of sun exposure are recommended, but sunscreen should be used to protect the skin.
Explanation
Explanation: Moisturizers are essential for managing eczema and preventing dryness and skin irritation. Avoiding moisturizers can lead to worsened symptoms.
Incorrect choices: b. Using fragrance-free and mild soaps for bathing is recommended to prevent skin irritation and maintain skin hydration.
c. Keeping the nails short and clean helps prevent excessive scratching and reduces the risk of skin infections.
d. Avoiding triggers like hot showers and harsh detergents can help manage eczema flare-ups and maintain skin health.
Explanation
Explanation: In some cases, shellfish and seafood can be allergenic and may trigger eczema flare-ups in susceptible individuals. It is essential for the patient to identify their specific food triggers through an elimination diet or consultation with a healthcare provider.
Incorrect choices: a. Fresh fruits and vegetables are generally not allergenic and are part of a healthy diet. However, some individuals may be sensitive to specific fruits or vegetables, but this varies from person to person.
c. Whole grains and nuts are nutritious foods and are not typically allergenic for individuals with eczema. However, individual allergies may vary.
d. Dairy products and eggs are common allergens, but not all individuals with eczema have sensitivities to these foods. Again, individual responses to specific foods may vary.
Explanation
Explanation: Applying topical corticosteroids to damp skin enhances absorption and effectiveness. It also helps lock in moisture, which is beneficial for individuals with eczema.
Incorrect choices: b. Topical corticosteroids should not be applied to open wounds or blisters, as it may cause further skin irritation and increase the risk of infection.
c. Topical corticosteroids should be used as prescribed by the healthcare provider. Overuse can lead to skin thinning and other side effects.
d. Applying corticosteroids to unaffected areas is unnecessary and can lead to skin thinning and other side effects.
Explanation
Explanation: Many moisturizers are safe to use during pregnancy and can help manage eczema symptoms by keeping the skin hydrated.
Incorrect choices: a. Avoiding all topical medications during pregnancy may not be necessary. The patient should consult their healthcare provider about the safety of specific medications.
c. Oral corticosteroids are generally not recommended during pregnancy unless the benefits outweigh the risks and as advised by the healthcare provider.
d. Prolonged sun exposure can worsen eczema symptoms and is not recommended. Short periods of sun exposure with proper sunscreen protection may be beneficial for some individuals, but this should be discussed with the healthcare provider.
Explanation
Explanation: Antiseptic creams can cause irritation and further damage to broken skin in individuals with eczema. It is essential to use gentle and soothing products to prevent infection.
Incorrect choices: b. Abrasive exfoliants can exacerbate eczema symptoms by causing skin irritation and should be avoided.
c. Sharing towels and personal items can lead to the spread of bacteria and increase the risk of skin infections. It is essential to use personal items and practice good hygiene habits.
d. Handwashing is crucial for preventing the spread of infections, and using a gentle soap and moisturizing afterward can help prevent drying of the skin.
More questions
Explanation
Explanation: Papules are small, raised, solid skin lesions that are red and inflamed, commonly seen in eczema.
Incorrect choices: a. Bullae are large, fluid-filled blisters.
b. Pustules are small, pus-filled skin lesions.
d. Wheals are raised, red, and itchy skin lesions with irregular borders, commonly seen in hives (urticaria).
Explanation
Explanation: Cold, dry weather is a common trigger for eczema flare-ups, as it can lead to dry and irritated skin.
Incorrect choices: a. Exposure to sunlight can be beneficial for some individuals with eczema, as it provides natural vitamin D and can have anti-inflammatory effects.
c. Consumption of spicy foods may trigger eczema in some individuals with food sensitivities, but it is not a universal trigger.
d. Physical activity is generally not a trigger for eczema, although sweating may exacerbate symptoms in some individuals.
Explanation
Explanation: Topical calcineurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are generally considered safe for use during pregnancy to manage eczema symptoms.
Incorrect choices: a. Topical corticosteroids may be used during pregnancy, but their use should be limited to the lowest effective dose and for the shortest duration possible due to potential risks.
b. Coal tar preparations are not typically recommended during pregnancy due to limited safety data.
d. Topical antihistamines are not commonly used for eczema management, and their safety during pregnancy is not well-established.
Explanation
Explanation: For infants with eczema, using mild, fragrance-free soaps and applying a hypoallergenic moisturizer after bathing helps prevent skin dryness and irritation.
Incorrect choices: a. Bathing the infant daily using hot water can strip the skin of natural oils and worsen eczema symptoms. Infants with eczema may benefit from shorter, lukewarm baths.
b. Moisturizers are essential for managing eczema and preventing dryness and skin irritation. Avoiding moisturizers can lead to worsened symptoms.
c. Tight-fitting clothing made of synthetic fabrics can irritate the skin and worsen eczema symptoms. Infants should be dressed in loose-fitting, breathable clothing.
Explanation
Explanation: A biopsy of the skin lesion is commonly used to confirm the diagnosis of eczema and rule out other skin conditions with similar symptoms.
Incorrect choices: b. Patch testing for allergies is used to identify allergens that may be triggering eczema flare-ups but is not used to confirm the diagnosis of eczema.
c. A complete blood count (CBC) is not typically used to diagnose eczema. It may be ordered to assess for secondary infections or other underlying health conditions.
d. X-ray is not useful for diagnosing eczema, as it primarily provides images of bones and internal structures. It is not commonly used in the evaluation of skin conditions.
The nurse is providing patient education to a client with eczema. Which of the following instructions is correct?
Explanation
Explanation: Moisturizers play a crucial role in managing eczema by hydrating the skin and reducing dryness. Choosing fragrance-free moisturizers helps minimize the risk of skin irritation.
Incorrect choices: a. "Take hot showers to soothe the skin." - Hot water can worsen eczema by stripping the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and increased itching.
b. "Avoid using any moisturizers on the affected areas." - Moisturizers are essential for managing eczema and maintaining skin hydration. Avoiding them can exacerbate the condition.
c. "Wear tight-fitting clothing to prevent scratching." - Tight-fitting clothing can further irritate the skin and worsen itching. Loose-fitting clothing is recommended to reduce friction.
The nurse is teaching a patient with eczema about triggers to avoid. Which of the following should the nurse include as a common trigger for eczema flare-ups?
Explanation
Explanation: Indoor heating can lead to decreased humidity levels, which may cause the skin to dry out and worsen eczema symptoms.
Incorrect choices: a. "Dairy products" - While some individuals with eczema may have food sensitivities, dairy products are not a universal trigger for all individuals with the condition.
b. "Fresh fruits and vegetables" - Fresh fruits and vegetables are generally considered healthy and are not known to be common triggers for eczema flare-ups.
d. "Daily exercise routine" - Regular exercise is beneficial for overall health, and there is no direct association between exercise and eczema flare-ups.
The nurse is providing education to a patient with eczema. Which of the following instructions is important to include in the teaching?
Explanation
Explanation: Keeping the skin well-moisturized is an essential part of eczema management. However, it is important to use fragrance-free moisturizers to avoid potential irritation and exacerbation of symptoms.
Incorrect choices: a. "Take long, hot baths to soothe your skin." - Hot baths can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and increased irritation for individuals with eczema.
b. "Apply scented lotions and perfumes to moisturize your skin." - Scented lotions and perfumes may contain chemicals and fragrances that can trigger allergic reactions and worsen eczema symptoms.
d. "Scratch your itchy areas gently to avoid further irritation." - Scratching can further damage the skin barrier, increase inflammation, and lead to infections. Patients with eczema should be encouraged to avoid scratching and find alternative methods to relieve itching, such as applying cold compresses or using prescribed anti-itch creams.
The nurse is teaching a patient with eczema about potential triggers to avoid. Which of the following statements by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
Explanation
Explanation: Tight-fitting clothing can cause friction and irritation to the skin, which may exacerbate eczema symptoms. It is best to opt for loose-fitting, breathable fabrics to minimize irritation.
Incorrect choices: a. "I will avoid using harsh soaps and detergents on my skin." - This statement is correct. Harsh soaps and detergents can strip the skin of natural oils and disrupt the skin barrier, leading to eczema flare-ups.
b. "I should limit my exposure to pet dander and pollen." - This statement is correct. Pet dander and pollen are common allergens that can trigger eczema exacerbations in susceptible individuals.
d. "I will try to identify and avoid foods that may trigger my eczema flare-ups." - This statement is correct. Identifying and avoiding trigger foods can be helpful for some individuals with eczema, as certain foods may exacerbate their condition.
Scabies
Explanation
Explanation: Scabies is a skin infestation caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. The mite burrows into the skin, laying eggs and causing intense itching and a characteristic rash.
Incorrect choices: a. "Scabies is a bacterial skin infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus." - This statement is incorrect as scabies is caused by a parasitic mite, not a bacterial infection.
c. "Scabies is an autoimmune skin disorder that results in excessive skin shedding." - This statement is incorrect. Scabies is not an autoimmune disorder, and excessive skin shedding is not a characteristic feature of the condition.
d. "Scabies is a fungal infection caused by the fungus Candida albicans." - This statement is incorrect as scabies is caused by a mite, not a fungal infection.
Explanation
Explanation: One of the hallmark clinical manifestations of scabies is the presence of linear burrows on the skin, which are caused by the mite's burrowing activity. The itching is typically more severe at night.
Incorrect choices: a. Pustules and papules with a honey-colored crust - This description is more characteristic of impetigo, a bacterial skin infection, not scabies.
b. Silvery-white plaques with a predilection for extensor surfaces - This description is typical of psoriasis, not scabies.
d. Raised, red welts with severe pruritus triggered by allergens - This description is more characteristic of urticaria (hives), which is an allergic skin reaction, not scabies.
Explanation
Explanation: Scabies is primarily transmitted through direct, prolonged skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual. The mites do not jump or fly through the air to infect others.
Incorrect choices: a. "Scabies can be transmitted through close personal contact with an infected individual." - This statement is correct. Close personal contact, such as hugging or sexual contact, is a common mode of transmission for scabies.
b. "I can contract scabies by using shared clothing or bedding with someone who has it." - This statement is correct. Scabies mites can survive outside the body for a short time and may be transmitted through shared clothing, bedding, or towels.
d. "I should avoid skin-to-skin contact with someone who has scabies to prevent transmission." - This statement is correct. Avoiding skin-to-skin contact can help prevent the spread of scabies to others.
Explanation
Explanation: Scabies infestation can occur on various body parts, but the soles of the feet and palms of the hands are less commonly affected due to the thick skin in these areas.
Incorrect choices: a. Scalp and hairline - Scabies infestation rarely affects the scalp and hairline.
c. Elbows and knees - Scabies infestation can occur in various areas, including the elbows and knees, but the soles of the feet and palms of the hands are less commonly affected.
d. Groin and genital area - Scabies infestation can occur in the groin and genital area, but the soles of the feet and palms of the hands are less commonly affected.
Explanation
Explanation: Scabies mites can be transmitted through shared personal items, such as clothing, towels, and bedding. Avoiding sharing these items can help prevent scabies infestation.
Incorrect choices: a. "Apply topical corticosteroids regularly to the affected areas to prevent scabies." - This statement is incorrect. Topical corticosteroids are used to manage the symptoms of scabies, not to prevent infestation.
b. "Use antibacterial soap for regular handwashing to reduce the risk of scabies." - This statement is incorrect. Scabies is not caused by bacteria, so using antibacterial soap will not prevent infestation.
d. "Keep the skin moisturized with heavy creams or lotions to prevent scabies." - This statement is incorrect. Moisturizing the skin may be beneficial for symptom management but will not prevent scabies infestation.
Explanation
Explanation: One of the hallmark clinical manifestations of scabies is the presence of linear burrows on the skin, which are caused by the mite's burrowing activity. The itching is typically more severe at night.
Incorrect choices: a. Silvery-white plaques with a predilection for extensor surfaces are characteristic of psoriasis, not scabies.
c. Pustules and papules with a honey-colored crust are indicative of impetigo, not scabies.
d. Raised, red welts with severe pruritus triggered by allergens are typical of urticaria or hives, not scabies.
Explanation
Explanation: Scabies infestation can occur on various body parts, but the groin and genital area are commonly affected due to the warm and moist environment.
Incorrect choices: a. The scalp and hairline are not typical sites for scabies infestation, although other conditions like head lice can affect this area.
b. Scabies infestation does not specifically target the soles of the feet and palms of the hands.
c. While scabies can affect the elbows and knees, the groin and genital area are more commonly involved.
Explanation
Explanation: Pediatric scabies presents as excoriated papules and nodules with honey-colored crusts, resulting from intense itching and scratching.
Incorrect choices: a. Petechiae and purpura are indicative of a bleeding disorder or other vascular issues, not scabies.
b. A sandpaper-like rash with "strawberry tongue" is a characteristic finding of scarlet fever, not scabies.
c. Vesicular lesions in a "dewdrop on a rose petal" pattern are typical of chickenpox (varicella), not scabies.
Explanation
Explanation: The hallmark symptom of scabies infestation is intense itching, which is often worse at night and may be severe enough to interfere with sleep.
Incorrect choices: a. Fever and chills are not typically associated with scabies, although they may be present if a secondary infection develops due to scratching.
b. Numbness and tingling sensation are not typical symptoms of scabies; they may suggest another neurological issue.
d. Muscle weakness and fatigue are not characteristic of scabies and may indicate another underlying condition.
Explanation
Explanation: The definitive method for confirming scabies infestation is the microscopic examination of skin scrapings, which can reveal the presence of Sarcoptes scabiei mites, eggs, or fecal pellets.
Incorrect choices: a. Skin biopsy may show hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis, but it is not the definitive method for diagnosing scabies. It can help rule out other skin conditions with similar manifestations.
c. The Mantoux test is used for detecting exposure to tuberculosis, not scabies.
d. Serological testing for antibodies against scabies mites is not typically used for diagnosing scabies and may not provide accurate results.
Explanation
Explanation: Dermoscopy is a non-invasive diagnostic tool commonly used in clinical practice to visualize the mites or burrows on the skin surface, aiding in the diagnosis of scabies.
Incorrect choices: a. Culture of skin scrapings is used to identify fungal infections, not scabies.
b. A complete blood count (CBC) may show elevated white blood cell counts (leukocytosis) in response to infection, but it is not specific for diagnosing scabies.
c. A skin biopsy may be performed in some cases, but it is not the primary diagnostic test for scabies.
Explanation
Explanation: Skin scraping involves applying mineral oil to the skin, followed by scraping off the superficial layer, and then examining the scraped material under a microscope to detect the presence of scabies mites or eggs.
Incorrect choices: a. Tzanck smear is used to examine cells from skin lesions and is not specific for scabies.
b. Patch testing is used to diagnose allergic contact dermatitis and is not specific for scabies.
c. Wood's lamp examination is used to detect certain fungal or bacterial infections, but it is not the primary method for diagnosing scabies.
Explanation
Explanation: Scabies burrows are commonly found in interdigital spaces (between the fingers and toes) and on the wrists, as these areas offer warm and protected environments for the mites to burrow.
Incorrect choices: a. The face and neck are not typical locations for scabies burrows.
b. Extensor surfaces of the arms and legs are less commonly affected by scabies.
c. While scabies burrows can occur on the chest and back, they are more frequently found in the areas mentioned in the correct choice
Explanation
Explanation: Topical corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and itching associated with scabies. They are commonly prescribed to provide relief from symptoms.
Incorrect choices: a. Applying hot packs may provide temporary relief, but it can worsen itching and spread the mites to other areas.
b. Over-the-counter antihistamines may have limited effectiveness in managing the intense itching of scabies.
c. Frequent cool showers may help soothe the skin, but they do not address the underlying cause of itching in scabies.
Explanation
Explanation: During treatment for scabies, it is essential for the client to avoid close personal contact with others to prevent the spread of the mites. This includes avoiding work, school, and other social settings until the treatment is completed and the infestation is resolved.
Incorrect choices: a. Avoiding hugging and shaking hands is appropriate to prevent transmission to others.
b. Avoiding sharing personal items like towels and clothes is important to prevent the spread of scabies to others.
d. Informing sexual partners about the need for treatment is crucial to prevent reinfestation and transmission.
Explanation
Explanation: Washing the child's clothes and bedding in hot water and drying on high heat can effectively kill the scabies mites and prevent transmission to family members.
Incorrect choices: a. Isolating the child in a separate room is not necessary for managing scabies, and it may lead to emotional distress for the child.
c. Applying a topical antifungal cream is not effective for treating scabies, as it is caused by mites, not fungi.
d. Placing the child in contact isolation is not necessary for managing scabies, as it is not highly contagious and can be managed with appropriate hygiene practices.
Explanation
Explanation: Applying the scabicidal medication to wet skin can enhance its effectiveness by helping it to penetrate the skin and reach the mites more effectively.
Incorrect choices: a. Oral antibiotics are not prescribed for scabies unless there is evidence of a secondary bacterial infection.
b. Moisturizing lotion should not be applied immediately after treatment, as it can reduce the absorption of the scabicidal medication.
d. The client should avoid showering immediately after applying the scabicidal medication to allow it to have enough time to work effectively.
Explanation
Explanation: Sharing personal items like towels can spread scabies to others, even if the client has started treatment. It is essential for the client to avoid sharing personal items to prevent transmission.
Incorrect choices: a. Washing clothes and bedding in hot water is a necessary step to kill the mites and prevent reinfestation.
c. Avoiding close contact with family members is important to prevent transmission until the client is treated.
d. Applying the scabicidal cream from head to toe, including under the nails, is a correct application technique to ensure all affected areas are treated.
Explanation
Explanation: Sharing personal items can spread scabies to others, even if they are not experiencing symptoms. It is essential for the client to avoid sharing personal items to prevent transmission.
Incorrect choices: a. Washing clothes, bedding, and towels in hot water and drying them on high heat can effectively kill scabies mites and their eggs, preventing reinfestation.
b. Applying the scabicidal cream to the entire body, including under the nails and between fingers and toes, is necessary to ensure all affected areas are treated.
c. Avoiding close personal contact with others is crucial to prevent transmission until the scabies is completely treated and the infestation is resolved.
Explanation
Explanation: It is essential for the client to complete the full course of prescribed scabicidal treatment, even if itching improves. Stopping the treatment prematurely may lead to incomplete eradication of the mites and possible reinfestation.
Incorrect choices: b. Applying the scabicidal cream again after one week is necessary to ensure all mites are eliminated, including any that may have hatched since the initial treatment.
c. Covering all areas of the body with the scabicidal cream during each application is essential to ensure that all affected areas are treated and the mites are eradicated.
d. Continuing to apply the scabicidal cream even if the rash starts to improve is important to complete the treatment and prevent recurrence.
Explanation
Explanation: Sharing personal items like towels can spread scabies to others, even if they do not have any skin rashes or symptoms. It is essential for the family member to avoid sharing personal items to prevent transmission.
Incorrect choices: a. Washing the client's clothes and bedding in hot water and drying them on high heat can effectively kill scabies mites and their eggs, preventing transmission to other family members.
c. Vacuuming and cleaning the client's living areas and furniture can help remove any mites that may be present, reducing the risk of reinfestation.
d. Avoiding close contact with the client until the scabies is completely treated is crucial to prevent transmission and spread of the infestation.
Explanation
Explanation: It is essential for the client to avoid sharing bedding with others during a scabies infestation. Washing the bedding alone may not be sufficient to eliminate the mites and prevent transmission.
Incorrect choices: a. Avoiding sharing personal items like towels and clothing is crucial to prevent the spread of scabies to others.
b. Washing hands frequently can help reduce the risk of transmitting scabies to other parts of the body or to others.
c. Avoiding close contact with anyone who has a skin rash or itching is necessary to prevent transmission and spread of the infestation.
Explanation
Explanation: It is essential for the child to avoid close contact with other children until the scabies is completely treated to prevent transmission.
Incorrect choices: a. Washing the child's stuffed toys and belongings in hot water and drying them on high heat can help eliminate any mites that may be present and prevent reinfestation.
b. Applying the scabicidal cream to the child's entire body, including the scalp and neck, is necessary to ensure all affected areas are treated.
c. Keeping the child home from school and other activities until the scabies is treated is crucial to prevent transmission to others and reduce the risk of spreading the infestation.
Explanation
Explanation: Sharing personal items can spread scabies to others, even if they don't have any skin rashes or symptoms. It is essential for the client to avoid sharing personal items to prevent transmission.
Incorrect choices: a. Avoiding close contact with anyone who has scabies or is experiencing itching is necessary to prevent transmission and spread of the infestation.
b. Washing clothes and bedding in hot water and drying them on high heat can effectively kill scabies mites and their eggs, preventing reinfestation.
c. Applying scabicidal cream to itchy or irritated areas of the skin is necessary to treat the infestation and prevent further spread.
Explanation
Explanation: Wearing gloves and a gown when providing direct care to the client is essential to prevent transmission of scabies to the nurse and other clients. This helps to maintain infection control and prevent further spread of the infestation.
Incorrect choices: b. Sharing personal items with the client is not appropriate as it can spread scabies to others.
c. Allowing the client to use the same restroom facilities as other clients may increase the risk of transmission.
d. Placing the client in a room with another client who also has scabies is not appropriate as it can lead to cross-contamination.
Explanation
Explanation: Sharing personal items can spread scabies to others, even if they don't have any itching or symptoms. It is essential for the client to avoid sharing personal items to prevent transmission.
Incorrect choices: a. Washing clothing and bedding in hot water and drying them on high heat can effectively kill scabies mites and their eggs, preventing reinfestation.
b. Vacuuming and cleaning living areas and furniture can help remove any mites that may be present, reducing the risk of reinfestation.
c. Continuing to apply scabicidal cream even after symptoms improve is necessary to ensure all mites are eliminated and prevent recurrence.
Explanation
Explanation: Providing each client with their own set of personal care items and linens helps to prevent cross-contamination and transmission of scabies between clients. This ensures infection control measures are maintained and reduces the risk of spreading the infestation.
Incorrect choices: a. Placing the clients in a common room to socialize and interact with each other may increase the risk of transmission and spread of scabies.
c. Encouraging clients to share personal items is not appropriate as it can spread scabies to others.
d. Allowing clients to use the same bathing facilities without using personal protective equipment may increase the risk of transmission and spread of scabies.
Explanation
Explanation: Sharing personal items can spread scabies to others, even if they don't have any rashes or symptoms. It is essential for the client to avoid sharing personal items to prevent transmission.
Incorrect choices: a. Washing clothing and bedding in hot water and drying them on high heat can effectively kill scabies mites and their eggs, preventing reinfestation.
b. Applying scabicidal cream to all areas of the skin that are itchy or rashy is necessary to treat the infestation and prevent further spread.
c. Avoiding close contact with family members until the scabies is treated is necessary to prevent transmission and spread of the infestation.
The nurse is discussing the prognosis of scabies with a client. Which statement made by the client indicates a need for further clarification?
Explanation
Explanation: This statement is incorrect. Scabies is not a chronic condition that requires lifelong management. With proper treatment, scabies can be cured, and symptoms usually improve within a few days. There is no need for lifelong management unless the client is reinfected or exposed to scabies again.
Incorrect choices: a. This statement is incorrect. Scabies infestation does not typically clear up on its own without treatment. It requires specific medications to eliminate the mites and eggs.
b. This statement is correct. With appropriate treatment, scabies symptoms should improve within a few days.
c. This statement is correct. Once scabies is successfully treated, there should be no reinfestation if the client avoids contact with infested individuals or contaminated items.
Explanation
Explanation: This statement is incorrect because scabies is not a chronic condition that requires long-term management. With proper treatment, scabies can be completely cured, and symptoms typically resolve within a few weeks. There is no need for ongoing, long-term management and regular use of scabicidal creams.
Incorrect choices: a. This statement is correct. Once treated, scabies is usually completely cured, and symptoms resolve within a few weeks.
c. This statement is correct. Proper treatment for scabies can result in symptom relief within a few days of starting the medications.
d. This statement is incorrect. Scabies is not a self-limiting condition, and it requires specific treatment to eliminate the infestation and relieve symptoms. Without treatment, scabies can persist and spread to others.
More questions
Scabies is caused by:
Explanation
Explanation: Scabies is caused by the infestation of the skin by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. The mite burrows into the skin, laying eggs and causing an allergic reaction, which leads to the characteristic symptoms of scabies.
Incorrect choices:
a. Bacteria: Scabies is not caused by bacteria. It is a parasitic infestation caused by a mite.
b. Fungus: Scabies is not caused by a fungus. It is caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite.
d. Virus: Scabies is not caused by a virus. It is caused by the infestation of the skin by the scabies mite.
Which of the following is a common symptom of scabies infestation?
Explanation
Explanation: Intense itching, especially at night, is a common symptom of scabies infestation. The itching is a result of the body's allergic reaction to the mite and its eggs.
Incorrect choices:
a. High fever: Fever is not a typical symptom of scabies. Itching is the primary symptom.
c. Yellow discoloration of the skin: Yellow discoloration of the skin is not a symptom of scabies. Itching is the main characteristic.
d. Rapid breathing: Rapid breathing is not a symptom of scabies. Itching is the primary complaint.
How is scabies transmitted from person to person?
Explanation
Scabies is primarily transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person. The mite can also be transmitted through infested clothing, bedding, and furniture.
Incorrect choices:
a. Through respiratory droplets: Scabies is not transmitted through respiratory droplets. It requires direct skin contact.
c. By consuming contaminated food or water: Scabies is not transmitted through contaminated food or water. It is a skin infestation caused by a mite.
d. Through mosquito bites: Scabies is not transmitted through mosquito bites. It requires direct contact with an infected person or infested items.
Which area of the body is commonly affected by scabies infestation?
Explanation
Explanation: Scabies can affect various areas of the body, but the genital area is a common site of infestation, especially in adults.
Incorrect choices:
a. Scalp: While scabies can occur on the scalp, it is less common than other areas of the body.
b. Elbows: Scabies can occur on the elbows, but it is not a common site of infestation.
d. Sole of the feet: Scabies can occur on the sole of the feet, but it is not a common site of infestation, especially in adults.
How is scabies diagnosed?
Explanation
Explanation: Scabies is diagnosed by taking a skin scraping from the affected area and examining it under a microscope to identify the presence of the scabies mite or its eggs.
Incorrect choices:
a. Blood test: Scabies is not diagnosed through a blood test. Skin scraping is the preferred method.
b. X-ray: X-ray is not used to diagnose scabies. It is not a suitable method for identifying the mite.
d. Urine analysis: Urine analysis is not used to diagnose scabies. Skin scraping is the standard method for diagnosis.
Which of the following is a primary intervention for treating scabies?
Explanation
Explanation: The primary intervention for treating scabies is the use of topical scabicide medications. These medications kill the scabies mites and their eggs, effectively treating the infestation.
Incorrect choices:
a. Applying corticosteroid creams: Corticosteroid creams are used to relieve inflammation and itching but do not treat the underlying scabies infestation.
b. Warm compresses: Warm compresses may temporarily relieve itching but do not eliminate the scabies mites.
c. Over-the-counter antifungal creams: Over-the-counter antifungal creams are not effective in treating scabies, as scabies is caused by a mite, not a fungus.
Which precaution is important for individuals diagnosed with scabies infestation?
Explanation
Explanation: Contact precautions are important for individuals diagnosed with scabies infestation. These precautions involve the use of gloves and gowns to prevent the spread of the mites through direct contact with the person or infested items.
Incorrect choices:
a. Isolation precautions: Isolation precautions are not necessary for scabies infestation. Contact precautions are sufficient.
b. Droplet precautions: Droplet precautions are used for diseases spread by respiratory droplets, not scabies.
d. Airborne precautions: Airborne precautions are used for diseases spread by small particles suspended in the air, not scabies.
Scabies infestation can be treated with:
Explanation
Explanation: Scabies infestation can be treated with permethrin cream, which is a topical scabicide that kills the scabies mites and their eggs.
Incorrect choices:
a. Oral antibiotics: Oral antibiotics are not effective in treating scabies, as it is not caused by bacteria.
b. Topical antifungal creams: Topical antifungal creams are not effective in treating scabies, as
scabies is caused by a mite, not a fungus.
c. Bed rest and hydration: Bed rest and hydration are essential for overall health but do not directly treat the scabies infestation.
How can individuals prevent scabies infestation?
Explanation
Explanation: Frequent handwashing is an essential preventive measure for scabies infestation. It helps reduce the risk of acquiring the mites through indirect contact with infested items.
Incorrect choices:
a. Avoiding contact with animals: Scabies is not typically transmitted from animals to humans. It is primarily spread through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person.
b. Using insect repellent: Insect repellent is not effective in preventing scabies infestation, as it is caused by a mite, not insects.
d. Avoiding crowded places: While avoiding crowded places may reduce the risk of some infections, it does not specifically prevent scabies infestation. Direct contact with an infected person or infested items is the primary mode of transmission.
If one member of a household is diagnosed with scabies, what action should be taken for other household members?
Explanation
Explanation: If one member of a household is diagnosed with scabies, all household members should be treated with scabicide medications to prevent the spread of the infestation.
Incorrect choices:
a. Isolate the infected individual in a separate room: While contact precautions are recommended for the infected individual, isolating them in a separate room is not necessary.
c. Wash all household linens in hot water: Washing linens in hot water is recommended to reduce the risk of mites surviving on infested items, but treatment with scabicide medications is the primary preventive measure.
d. Wear personal protective equipment around the infected individual: Contact precautions, including wearing gloves and gowns, are recommended for healthcare providers but not necessarily for household members. Treating all household members is the most effective preventive measure.
Psoriasis
Explanation
Explanation: Psoriasis is an autoimmune skin disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to the rapid buildup of skin cells and the formation of red, scaly patches on the skin's surface.
Incorrect choices: a. A contagious bacterial skin infection - Psoriasis is not caused by bacteria, and it is not contagious.
c. A fungal infection causing itching and rash - Psoriasis is not caused by a fungus; it is an autoimmune condition.
d. A viral skin condition resulting in fluid-filled blisters - Psoriasis does not result in fluid-filled blisters; it presents as red, scaly patches instead.
Explanation
Explanation: Psoriasis commonly presents as red, scaly, and thickened patches on the skin. These patches can be itchy, painful, and sometimes crack and bleed.
Incorrect choices: a. Smooth and pink patches on the skin - This is not characteristic of psoriasis, which typically involves scaling and thickening of the skin.
b. Flaky, white patches on the skin - This is not typical of psoriasis; the patches are usually red and scaly.
d. Raised, flesh-colored bumps on the skin - This description does not match the typical appearance of psoriasis patches.
Explanation
Explanation: Psoriasis is believed to have a genetic component, and it is considered an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to the characteristic skin changes.
Incorrect choices: a. Poor hygiene and lack of skin care - Psoriasis is not caused by poor hygiene or lack of skin care.
b. Exposure to environmental toxins - While environmental factors may trigger or worsen psoriasis in some individuals, they are not the primary cause of the condition.
d. Excessive sun exposure - Sun exposure may improve psoriasis symptoms in some people, but it is not the underlying cause of the condition.
Explanation
Explanation: Psoriasis commonly affects the scalp, leading to the formation of red, scaly patches on the scalp's surface. It can also extend to the hairline and behind the ears.
Incorrect choices: b. Soles of the feet - Psoriasis can affect the soles of the feet, but it is less common than scalp involvement.
c. Abdomen - Psoriasis can occur on the abdomen, but it is not as frequently affected as the scalp.
d. Neck - Psoriasis can involve the neck area, but it is not the most common site of involvement.
Explanation
Explanation: The primary etiological factor in psoriasis is a genetic predisposition. Psoriasis has a strong hereditary component, and individuals with a family history of the condition are at a higher risk of developing it. While environmental triggers can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms, the condition itself is primarily influenced by genetic factors.
Incorrect choices: a. Bacterial infection: Psoriasis is not caused by a bacterial infection. It is an autoimmune condition characterized by an overactive immune response, leading to inflammation and skin cell overproduction.
b. Fungal overgrowth: Fungal overgrowth is not a cause of psoriasis. Psoriasis is not related to fungal infections and has a different underlying mechanism.
d. Allergic reaction: While certain allergens may exacerbate psoriasis symptoms in some individuals, an allergic reaction is not the primary cause of psoriasis. The condition's pathophysiology is rooted in immune system dysfunction rather than allergic responses.
Explanation
Explanation: Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder in which T-cells, a type of white blood cell, become overactive and trigger an inflammatory response. These T-cells promote the rapid growth of skin cells, leading to the characteristic plaques seen in psoriasis.
Incorrect choices: b. B-cells: While B-cells are important components of the immune system, they are not primarily involved in the etiology of psoriasis. T-cells are the central players in the autoimmune response seen in psoriasis.
c. Platelets: Platelets are primarily responsible for blood clotting and are not directly related to the development of psoriasis.
d. Eosinophils: Eosinophils are a type of white blood cell involved in immune responses against parasitic infections and allergic reactions. While they are important in certain immune processes, they are not the main players in psoriasis etiology.
Explanation
Explanation: Environmental factors such as stress, trauma, infections, and certain medications are considered triggers that can worsen psoriasis symptoms in individuals who are already genetically predisposed to the condition. These triggers can lead to psoriasis flare-ups or worsen existing plaques.
Incorrect choices: a. Primary cause of psoriasis: Environmental factors are not the primary cause of psoriasis. While they can influence the severity of symptoms, the condition itself is primarily driven by genetic factors and immune system dysfunction.
b. Minor role with no significant impact: Environmental triggers are not minor in psoriasis etiology. They can have a significant impact on symptom severity and recurrence in susceptible individuals.
d. Protective factors against developing psoriasis: Environmental factors are not protective against developing psoriasis. As an autoimmune condition, psoriasis is primarily influenced by genetic predisposition and immune system dysfunction, not by protective environmental factors.
Explanation
Explanation: Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder characterized by an overactive immune system. In psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly triggers inflammation, leading to the rapid growth of skin cells and the formation of plaques.
Incorrect choices: a. Immune system suppresses inflammation and skin cell proliferation: This statement is incorrect. In psoriasis, the immune system does not suppress inflammation but rather promotes it.
b. Immune system responds normally to environmental triggers: This statement is incorrect. In psoriasis, the immune system's response to triggers is abnormal, leading to the characteristic inflammation and skin cell overgrowth.
d. Immune system functions independently of psoriasis development: This statement is incorrect. The immune system plays a central role in psoriasis etiology. The abnormal immune response is the driving force behind the development and progression of psoriasis.
Explanation
Explanation: Genetic predisposition in psoriasis contributes to the development of the condition by causing abnormal functioning of the immune system. Certain genes involved in the immune response are associated with psoriasis, leading to an overactive immune system that triggers inflammation and skin cell overproduction.
Incorrect choices: a. Genetic factors increase skin sensitivity to environmental irritants: While some environmental triggers can worsen psoriasis symptoms, genetic predisposition primarily influences the immune system's response, not skin sensitivity to irritants.
b. Genetic factors cause an allergic reaction to certain foods: Psoriasis is not primarily an allergic reaction, and genetic factors do not cause allergic reactions to specific foods in this context.
d. Genetic factors impair the skin's barrier function: Psoriasis is not caused by a skin barrier dysfunction. The condition is characterized by immune system dysregulation and the subsequent inflammation and rapid skin cell turnover.
Explanation
Explanation: Psoriasis is characterized by the presence of itchy, raised, red patches on the skin with silvery scales. These patches are known as plaques and are a hallmark feature of psoriasis.
Incorrect choices: a. Painful, deep ulcers on the skin: This description does not align with psoriasis. Psoriasis plaques are not typically painful or ulcerated.
c. Small, fluid-filled blisters on the palms and soles: This description is more characteristic of a condition called palmoplantar pustulosis, not psoriasis.
d. Thickened, hardened skin with deep cracks: This description is more typical of a condition called lichenified eczema or chronic contact dermatitis, not psoriasis.
Explanation
Explanation: Psoriasis commonly affects the scalp and nails in addition to other areas of the body. Scalp psoriasis can cause flaking and scale buildup on the scalp, while nail psoriasis can lead to pitting, discoloration, and thickening of the nails.
Incorrect choices: b. Buttocks and thighs: While psoriasis can occur in these areas, it is not one of the most common areas affected.
c. Lower back and shoulders: These areas can be affected by psoriasis, but they are not the most commonly affected regions.
d. Upper arms and neck: Psoriasis can occur on the upper arms and neck, but it is not the most frequently affected area.
Explanation
Explanation: Fatigue and malaise are common symptoms experienced by individuals with psoriasis. The chronic inflammation and immune system dysregulation in psoriasis can lead to feelings of tiredness and general discomfort.
Incorrect choices: a. Persistent fever and chills: Fever and chills are not typical symptoms of psoriasis. They may indicate an infection or other underlying health condition.
b. Frequent nosebleeds: Nosebleeds are not directly associated with psoriasis. They may be caused by other factors such as nasal dryness or irritation.
d. Excessive thirst and frequent urination: These symptoms are not typically related to psoriasis. They may be indicative of diabetes or other medical conditions.
Explanation
Explanation: Psoriasis lesions commonly appear in a symmetrical pattern, affecting similar areas on both sides of the body. For example, if a plaque is present on the right elbow, there is a high likelihood of a corresponding plaque on the left elbow.
Incorrect choices: a. Psoriasis lesions are evenly distributed across the body: Psoriasis lesions are not evenly distributed and tend to cluster in certain areas, such as elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
b. Psoriasis lesions are typically limited to the face and neck: While psoriasis can occur on the face and neck, it is more commonly found on extensor surfaces (elbows and knees) and the scalp.
c. Psoriasis lesions are more commonly found on the left side of the body: There is no evidence to support a preference for the left side of the body in psoriasis distribution. The symmetrical pattern is a more characteristic feature.
Explanation
Explanation: Chronic psoriasis is characterized by thickened, scaly plaques with silvery-white scales. These plaques result from the excessive growth and turnover of skin cells in psoriasis.
Incorrect choices: a. Generalized redness with no scaling: This description does not align with chronic psoriasis. Psoriasis plaques are typically scaly and have a characteristic appearance.
b. Pustules and fluid-filled blisters: Pustular psoriasis is a specific subtype of psoriasis characterized by pustules, but it is not a hallmark of chronic psoriasis.
c. Hyperpigmented patches with rough texture: Hyperpigmentation and rough texture are not typical features of chronic psoriasis. The characteristic feature is the presence of silvery-white scales on thickened plaques.
Explanation
Explanation: The presence of at least 3 typical psoriasis plaques on the body is one of the essential diagnostic criteria for confirming psoriasis. These plaques are characterized by well-defined, erythematous (red), raised lesions with silvery-white scales.
Incorrect choices: a. Positive skin biopsy showing eosinophils infiltration: While a skin biopsy may be performed to support the diagnosis of psoriasis, the presence of eosinophils is not specific to psoriasis and can be found in various skin conditions.
b. Family history of autoimmune diseases: A family history of autoimmune diseases may increase the risk of developing psoriasis, but it is not a definitive diagnostic criterion for the condition.
d. Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) on blood test: An elevated ESR can indicate inflammation in the body, but it is not specific to psoriasis and may be present in other inflammatory conditions as well.
Explanation
Explanation: The Auspitz sign refers to the appearance of tiny bleeding points when the scales on psoriatic plaques are removed or scraped. This sign is a characteristic feature of psoriasis and helps differentiate it from other skin conditions.
Incorrect choices: a. Moist, oozing skin lesions: Moist, oozing lesions are not typical of psoriasis. Psoriasis plaques are dry and scaly in nature.
b. Dark, hyperpigmented patches: Hyperpigmentation is not a characteristic feature of psoriasis. Psoriatic plaques are typically erythematous (red) with silvery-white scales.
d. Translucent, fluid-filled blisters: Translucent, fluid-filled blisters are not typically associated with psoriasis. This description is more consistent with a condition called pemphigus, not psoriasis.
Explanation
Explanation: A skin biopsy is commonly performed to confirm the diagnosis of psoriasis. It involves taking a small sample of skin tissue from a psoriatic plaque and examining it under a microscope to identify the characteristic histological changes, such as hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and elongation of the rete ridges.
Incorrect choices: a. Skin patch testing for allergens: Patch testing is used to diagnose allergic contact dermatitis, not psoriasis.
b. Chest X-ray to assess lung involvement: Chest X-rays are not necessary for the diagnosis of psoriasis, as it primarily affects the skin and joints, not the lungs.
c. Complete blood count (CBC) to assess white blood cell count: While a CBC may be performed to assess inflammation, it is not specific to psoriasis and cannot confirm the diagnosis. A skin biopsy is needed for definitive diagnosis.
Explanation
Explanation: The development of wheals and hives is not characteristic of psoriasis. Wheals and hives are associated with urticaria (hives), which is a separate skin condition caused by histamine release.
Incorrect choices: a. Pitting and ridging of the nails: Pitting and ridging of the nails are common nail changes seen in psoriasis and can aid in its diagnosis.
b. Koebner phenomenon upon skin trauma: The Koebner phenomenon, where new psoriatic lesions form at sites of skin trauma or injury, is a characteristic feature of psoriasis.
d. Silvery-white scales on erythematous plaques: Silvery-white scales on erythematous (red) plaques are a classic feature of psoriasis and help differentiate it from other skin conditions.
Explanation
Explanation: Plaque psoriasis is the most common type of psoriasis, accounting for approximately 80-90% of all cases. It is characterized by the presence of raised, well-defined, erythematous (red) plaques with silvery-white scales.
Incorrect choices: a. Guttate psoriasis: Guttate psoriasis is characterized by small, teardrop-shaped lesions scattered on the skin, often following a streptococcal infection. It is less common than plaque psoriasis.
b. Inverse psoriasis: Inverse psoriasis affects skin folds, such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts. It appears as smooth, red patches and is less common than plaque psoriasis.
d. Pustular psoriasis: Pustular psoriasis is a specific subtype characterized by pustules on the skin, but it is less common than plaque psoriasis.
Explanation
Explanation: Applying topical corticosteroids to affected areas can help reduce inflammation, itching, and discomfort associated with psoriasis. However, the nurse should ensure that the patient follows the prescribed dosage and instructions for the use of corticosteroids.
Incorrect choices: b. Encouraging the patient to scratch the affected areas gently is not appropriate, as scratching can exacerbate psoriasis and lead to skin damage and infection.
c. NSAIDs are not typically used to manage itching and discomfort in psoriasis. They may be prescribed for joint pain associated with psoriatic arthritis, but they do not target the skin symptoms of psoriasis.
d. While warm baths can be soothing, frequent baths may actually dry out the skin and worsen psoriasis. Additionally, the water should be lukewarm rather than hot to avoid triggering flare-ups.
Explanation
Explanation: Taking long, hot baths can actually worsen psoriasis by drying out the skin and triggering flare-ups. Instead, patients with psoriasis should take short, lukewarm baths or showers to avoid exacerbating the condition.
Incorrect choices: a. Moisturizing the skin regularly is an essential part of psoriasis management to prevent dryness and scaling.
b. Avoiding fragranced soaps and lotions can help minimize skin irritation and sensitivity, which is beneficial for patients with psoriasis.
c. Applying sunscreen before going outside is important, as exposure to UV rays can trigger or worsen psoriasis. Sun protection helps prevent further skin damage.
Explanation
Explanation: Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to UV light to treat psoriasis. During phototherapy sessions, patients should wear special shields to protect their eyes and genitals from potential UV damage.
Incorrect choices: a. Patients undergoing phototherapy are actually exposed to controlled amounts of UV light, which is different from uncontrolled sun exposure. Phototherapy is a prescribed treatment and should be done under healthcare professional supervision.
b. While phototherapy may cause temporary skin darkening or tanning, it is not associated with permanent changes in skin color.
d. Phototherapy does not increase the risk of skin infections. However, patients with psoriasis should practice good hygiene to prevent infections related to their condition and skin care routine.
Explanation
Explanation: Topical retinoids can increase the skin's sensitivity to sunlight and may cause sunburn. Patients should avoid excessive sun exposure and use sunscreen to protect their skin when using topical retinoids.
Incorrect choices: a. Topical retinoids should be applied to dry skin, not wet skin, to ensure proper absorption and effectiveness.
b. Topical retinoids are typically applied to the entire affected area, not just individual psoriasis plaques. They work best when applied consistently to the entire affected area.
c. Topical retinoids may take several weeks to show significant improvement in psoriasis symptoms, and immediate relief is not typical.
Explanation
Explanation: Immunosuppressive medications can weaken the immune system, making the patient more susceptible to infections. It is important for the patient to promptly report any signs of infection or illness to their healthcare provider for appropriate management.
Incorrect choices: b. The administration of immunosuppressive medications is often specific to each medication and should be taken as prescribed by the healthcare provider, with or without food, as indicated.
c. Immunosuppressive medications can increase the risk of infections, but they do not directly increase the risk of sunburn. Patients should, however, be cautious about sun exposure due to potential skin sensitivity.
d. Discontinuing immunosuppressive medications abruptly can be dangerous and should only be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider. Sudden discontinuation can lead to worsening of psoriasis and potential rebound effects.
Explanation
Explanation: Keeping the skin well-hydrated is essential in managing psoriasis. Patients should use fragrance-free moisturizers to prevent skin dryness and irritation, which can trigger flare-ups.
Incorrect choices: a. "Avoid using moisturizers, as they can worsen psoriasis flare-ups." - This statement is incorrect. Moisturizers are important for managing psoriasis symptoms and preventing dryness and irritation.
b. "Take hot baths with scented soaps to soothe the skin." - Hot baths and scented soaps can actually worsen psoriasis symptoms and should be avoided.
d. "Expose your skin to direct sunlight for prolonged periods to improve symptoms." - While some sunlight exposure may benefit psoriasis, prolonged and direct exposure can lead to skin damage and increase the risk of skin cancer. Sun exposure should be limited and done with caution.
Explanation
Explanation: Stress is a known trigger for psoriasis flare-ups. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing, can help reduce the risk of exacerbations.
Incorrect choices: a. "Maintain a healthy diet, including foods high in sugar and saturated fats." - While a healthy diet is beneficial for overall health, there is no specific evidence that links certain foods to psoriasis flare-ups.
c. "Exposure to cold weather can help improve psoriasis symptoms." - Cold weather may actually exacerbate psoriasis symptoms, as dry and cold conditions can lead to skin dryness and irritation.
d. "Regularly use alcohol-based hand sanitizers to prevent infections." - Alcohol-based hand sanitizers can dry out the skin and may irritate psoriasis lesions. It is better to use gentle, non-irritating handwashing techniques.
Explanation
Explanation: Adherence to prescribed treatment plans and attending follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are crucial for effectively managing psoriasis and preventing complications.
Incorrect choices: a. "Regularly scrubbing the affected areas to remove scaling." - Vigorous scrubbing can irritate the skin and worsen psoriasis symptoms. Gentle cleansing is recommended.
b. "Avoiding all forms of physical activity to prevent skin irritation." - Engaging in light physical activity is generally encouraged, as long as it does not exacerbate psoriasis symptoms.
c. "Using topical corticosteroids as needed without healthcare provider consultation." - It is essential for patients to follow their healthcare provider's instructions regarding the use of topical corticosteroids, as inappropriate or excessive use can lead to adverse effects.
Explanation
Explanation: Petroleum-based ointments can help seal in moisture and soothe the skin, reducing itchiness and discomfort associated with psoriasis.
Incorrect choices: a. "Take long, hot showers to soothe the skin." - Hot showers can actually worsen psoriasis symptoms by drying out the skin. Patients should take short, lukewarm showers instead.
c. "Wear tight-fitting clothing to prevent skin irritation." - Tight-fitting clothing can rub against the skin and worsen psoriasis symptoms. Patients should wear loose, breathable clothing.
d. "Use scented moisturizers for a pleasant fragrance." - Scented moisturizers may contain ingredients that can irritate the skin and trigger flare-ups. Unscented or fragrance-free moisturizers are recommended.
Explanation
Explanation: While sunlight can improve psoriasis symptoms in some individuals, direct exposure for extended periods can lead to skin damage and increase the risk of skin cancer. Sunscreen and limited sun exposure are advised.
Incorrect choices: b. "Applying emollients or moisturizers regularly." - Regular application of emollients or moisturizers is important for keeping the skin hydrated and preventing dryness and irritation, which can exacerbate psoriasis.
c. "Engaging in outdoor physical activities." - Engaging in light physical activities is generally encouraged, as long as it does not worsen psoriasis symptoms.
d. "Frequent application of alcohol-based hand sanitizers." - Alcohol-based hand sanitizers can dry out the skin and may irritate psoriasis lesions. It is better to use gentle, non-irritating handwashing techniques.
More questions
Explanation
Explanation: Psoriasis is not contagious and cannot be spread through direct contact with affected individuals. It is an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to the characteristic red, scaly patches on the skin.
Incorrect choices: a. This statement is correct. Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that causes red, scaly patches on the skin.
b. This statement is correct. Psoriasis is indeed an autoimmune disease where the body's immune system attacks healthy skin cells.
d. This statement is correct. Treatment for psoriasis aims to reduce inflammation and slow down the rapid skin cell growth to manage the symptoms of the condition.
Explanation
Explanation: Auspitz sign is a characteristic finding in psoriasis where pinpoint bleeding occurs when scales on the skin are removed. It is caused by the rapid growth and shedding of skin cells, which leads to the formation of delicate blood vessels that bleed easily.
Incorrect choices: a. Auspitz sign is not related to increased bleeding tendency in the patient; it is specific to psoriasis and its characteristic skin changes.
b. Presence of skin pustules and blisters is not associated with Auspitz sign and may indicate other skin conditions.
c. Formation of deep fissures in the skin is not directly related to Auspitz sign, which focuses on the bleeding after scale removal.
Explanation
Explanation: The primary assessment technique used to diagnose psoriasis is a physical examination of the skin. The characteristic red, raised patches with silver scales are indicative of psoriasis. While additional tests like skin biopsy may be used to confirm the diagnosis, the initial diagnosis is based on the visual appearance of the skin lesions.
Incorrect choices: a. A skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis of psoriasis, but it is not the primary assessment technique used to diagnose the condition.
b. Blood tests may be conducted to rule out other conditions or assess for systemic involvement, but they are not the primary method of diagnosing psoriasis.
d. MRI is not a diagnostic tool for psoriasis. It may be used in certain cases to assess joint involvement in psoriatic arthritis, but it does not diagnose psoriasis itself.
Explanation
Explanation: Psoriasis is a chronic skin disorder that results from an overactive immune response, leading to the rapid growth of skin cells. This causes red, raised, and scaly patches to form on the skin, which can be itchy and painful.
Incorrect choices: a. Psoriasis is not primarily an autoimmune disease affecting the respiratory system. It is primarily a skin condition, although it may be associated with certain autoimmune factors.
b. Psoriasis is not caused by a bacterial infection. It is a non-infectious skin disorder with an underlying immune-mediated mechanism.
d. Psoriasis is not a type of skin cancer. It is a benign skin condition that does not involve the malignant transformation of melanocytes.
Explanation
Explanation: The typical clinical manifestations of psoriasis include red, raised, and scaly patches on the skin. These patches are often itchy and may be associated with discomfort.
Incorrect choices: a. Purulent discharge is not a characteristic feature of psoriasis. Psoriasis lesions typically do not contain pus.
b. Psoriasis lesions are not smooth and painless. They are raised and may be painful or itchy.
d. Ulcerated and bleeding skin sores are not typical of psoriasis. Psoriasis lesions are characterized by dry, scaly plaques rather than open sores.
Explanation
Explanation: Psoriasis has a strong genetic component, and individuals with a family history of the condition are more likely to develop it. Specific genetic factors are involved in the immune response and skin cell growth regulation, leading to psoriasis.
Incorrect choices: b. While exposure to certain chemicals and irritants can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms, they are not the primary factor contributing to its development.
c. Psoriasis is not caused by a bacterial infection. It is a non-infectious inflammatory skin disorder.
d. Sun exposure can affect psoriasis, but it is not the primary factor contributing to its development. In some cases, moderate sunlight exposure may even improve psoriasis symptoms.
Which nursing intervention is appropriate for a patient with psoriasis?
Explanation
Explanation: Moisturizing the skin is essential for managing psoriasis and preventing dryness and scaling. Regular use of moisturizers helps maintain skin hydration and reduce the discomfort associated with psoriasis.
Incorrect choices: a. Encouraging the patient to pick or scratch the affected areas can worsen psoriasis and lead to skin damage and infection.
b. Applying hot packs to the skin lesions can exacerbate psoriasis and should be avoided. Lukewarm or cool packs may provide relief for some patients.
c. A diet high in spicy and acidic foods is not recommended for psoriasis patients, as certain foods may trigger flare-ups or exacerbate symptoms. A well-balanced, anti-inflammatory diet is more appropriate for psoriasis management.
How is psoriasis typically diagnosed?
Explanation
Explanation: A definitive diagnosis of psoriasis is often made through a skin biopsy, where a small sample of the affected skin is taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of psoriasis-related changes.
Incorrect choices: a. Blood tests are not used to diagnose psoriasis, as it is not caused by a bacterial infection.
c. Chest X-rays are not part of the diagnostic process for psoriasis, as it primarily affects the skin and not the lungs.
d. Urinalysis is not used to diagnose psoriasis, as it does not provide relevant information about the skin condition.
The nurse is providing education to a patient with psoriasis about potential triggers that can worsen the condition. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further education?
Explanation
Explanation: Moisturizers are beneficial in managing psoriasis symptoms as they help keep the skin hydrated and reduce dryness and itching. Avoiding moisturizers can worsen psoriasis symptoms and is not recommended.
Incorrect choices: a. Stress is a known trigger for psoriasis flare-ups, and avoiding stress can help manage the condition.
b. Limiting alcohol consumption is important as alcohol can trigger or exacerbate psoriasis symptoms.
d. Smoking is associated with increased severity and risk of psoriasis, and quitting smoking can help improve symptoms.
The nurse is caring for a patient with psoriasis. Which assessment finding is consistent with psoriasis?
Explanation
Explanation: Psoriasis is characterized by red and raised skin patches covered with silver or white scales. These patches are often itchy and can be found on various parts of the body, such as the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back.
Incorrect choices: a. Clear and smooth skin without any changes is not consistent with psoriasis, which is marked by visible skin changes like red, raised patches.
c. Skin rash with fluid-filled blisters may indicate conditions such as contact dermatitis or eczema but is not typical of psoriasis.
d. Purple or red lumps under the skin are more suggestive of other conditions, such as nodules or hematomas, rather than psoriasis.
What is the typical age of onset for psoriasis?
Explanation
Explanation: Psoriasis can develop at any age, but the most common age of onset is during adolescence and young adulthood. However, it can also appear for the first time later in life.
Incorrect choices: a. Infancy and early childhood - Psoriasis can occur in children, but it is less common in infancy and early childhood.
c. Middle age and older adulthood - While psoriasis can develop at any age, it is less common to have an onset in middle age and older adulthood.
d. Any age, as it is random - Although psoriasis can appear at any age, there is a higher prevalence of onset during adolescence and young adulthood.
Exams on Integumentary System
Custom Exams
Login to Create a Quiz
Click here to loginLessons
 Naxlex
Just Now
Naxlex
Just Now
Notes Highlighting is available once you sign in. Login Here.
Acne Vulgaris
Objectives
- Identify the etiology and contributing factors of acne vulgaris, including hormonal influences, genetics, and environmental triggers, to understand the multifactorial nature of the condition.
- Differentiate between the various types of acne lesions, such as comedones, papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts, to accurately assess and categorize the severity of acne in patients.
- Analyze the appropriate pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions for acne vulgaris, including topical agents, oral medications, lifestyle modifications, and skin care regimens, to develop individualized treatment plans for patients.
- Recognize potential complications of acne vulgaris, such as scarring, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, and psychosocial effects, to implement preventive measures and provide comprehensive patient education.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of acne management strategies through ongoing patient assessment and outcome measurement, to modify treatment plans as necessary and optimize patient outcomes.
Introduction
- Acne vulgaris is a chronic and common skin condition that primarily affects adolescents and young adults, but it can also occur in individuals of any age. It is characterized by the formation of various lesions, including comedones, papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts, predominantly on the face, chest, and back.
- Understanding the etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic criteria, and management strategies for acne is essential for healthcare professionals to provide effective care and support for patients affected by this often bothersome and distressing skin disorder.
Definition and Background
- Acne vulgaris is a multifactorial skin disorder that involves the pilosebaceous units of the skin. These units consist of hair follicles and sebaceous glands, which produce sebum—an oily substance that lubricates and protects the skin.
- The pathogenesis of acne is complex, encompassing several interrelated factors:
- Excessive Sebum Production: Hormonal changes, particularly during adolescence, stimulate sebum production, leading to an increase in skin oiliness.
- Follicular Hyperkeratinization: Abnormal shedding of skin cells within the hair follicles can block the sebaceous ducts, leading to the formation of comedones.
- Bacterial Colonization: The bacterium Propionibacterium acnes, which resides on the skin, proliferates in the blocked follicles, contributing to inflammation and lesion development.
- Inflammation: The immune system's response to bacterial colonization and the trapped sebum initiates an inflammatory cascade, leading to the formation of papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts.
II. Clinical Manifestations
- Acne vulgaris presents with a range of lesions that can vary in appearance and severity:
- Comedones: These are the hallmark lesions of acne and can be either open (blackheads) or closed (whiteheads).
- Open comedones occur when the follicular opening remains open, allowing the trapped sebum and skin cells to oxidize, resulting in a dark color.
- Closed comedones form when the follicular opening is partially blocked, leading to a white or flesh-colored bump.
- Inflammatory Lesions: Papules are small, red, raised bumps resulting from inflamed comedones.
- Pustules are similar but contain pus, giving them a yellow or white appearance. Nodules are deeper, larger, and more painful bumps that extend into the dermis, and cysts are closed, painful, pus-filled lesions that can cause scarring.
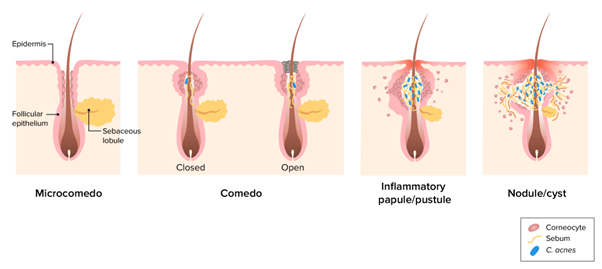
III. Diagnostic Criteria
- The diagnosis of acne vulgaris is primarily clinical and based on the presence of characteristic lesions on the skin.
- Healthcare professionals typically assess the patient's skin, taking note of the type and severity of the acne lesions.
- In some cases, grading systems, such as the Global Acne Grading System or the Leeds Revised Acne Grading System, may be used to categorize the severity of acne and track treatment progress.
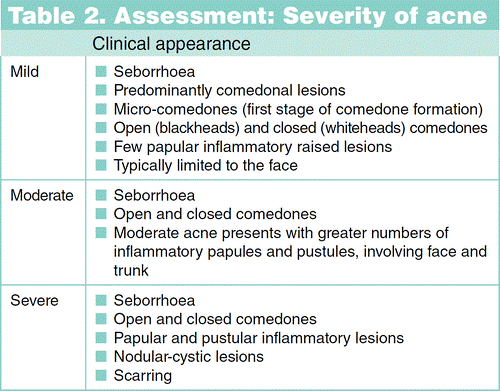
IV. Nursing Management
- Assessment: Comprehensive skin assessments are essential to identify the type and extent of acne lesions, as well as any potential exacerbating factors or triggers.
- Patient Education: Providing clear and detailed education to patients and their families about acne vulgaris is crucial. This education should include information about the etiology, exacerbating factors (e.g., stress, diet, cosmetics), proper skin care techniques, and the importance of medication adherence.
- Skin Care: Instructing patients on the appropriate skin care routine can help minimize acne breakouts. This includes gentle cleansing with non-comedogenic products, avoiding scrubbing or excessive touching of the face, and applying oil-free, non-comedogenic moisturizers.
- Medication Administration: Healthcare professionals may administer or prescribe various topical and oral medications to manage acne.
- Topical treatments commonly include benzoyl peroxide, retinoids, and topical antibiotics.
- Oral medications may include antibiotics, oral contraceptives, hormonal therapies, or isotretinoin, which is reserved for severe, treatment-resistant acne.
V. Patient Education
- Skin Care Routine: Educate patients on the importance of developing and maintaining a personalized skin care routine tailored to their skin type and the severity of their acne.
- Medication Adherence: Emphasize the significance of adhering to prescribed medications consistently to achieve the most optimal treatment outcomes.
- Acne Triggers: Help patients identify potential triggers and lifestyle factors that may exacerbate acne, such as stress, diet, and certain cosmetics, to promote proactive management and prevention of flare-ups.
VI. Prevention and Self-Care
- Encourage patients to avoid squeezing or picking at acne lesions, as this can lead to scarring and secondary infections.
- Promote lifestyle modifications, including maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and practicing stress management, to support overall skin health and minimize acne-related exacerbations.
VII. Prognosis
- The prognosis for acne vulgaris is generally favorable with appropriate management and adherence to the prescribed treatment regimen.
- The duration of treatment and response to therapy may vary based on the severity of acne, individual response to treatments, and the patient's compliance with the treatment plan.
- Patients should be informed that while some acne lesions may improve within a few weeks, others may take several months to resolve fully.
Conclusion
- In conclusion, acne vulgaris is a complex skin disorder with a multifaceted pathogenesis involving excess sebum production, follicular hyperkeratinization, bacterial colonization, and inflammation.
- It manifests through various lesions, including comedones, papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts, and its severity can range from mild to severe.
- Patient education and adherence to a comprehensive skin care and medication regimen are pivotal in managing acne and achieving optimal treatment outcomes.
- By understanding the etiology and clinical manifestations of acne, healthcare professionals can effectively support patients in managing this prevalent and sometimes emotionally distressing skin condition.
Eczema
Objectives
- Define eczema and differentiate it from other skin conditions, identifying the characteristic clinical manifestations, such as redness, itching, dryness, and skin lesions.
- Recognize common triggers and aggravating factors that may exacerbate eczema symptoms, such as irritants, allergens, weather changes, stress, and hormonal fluctuations.
- Explain the pathophysiology of eczema, including the role of immune system dysregulation and genetic predisposition in its development, as well as its chronic and relapsing nature.
- Demonstrate proper skin care practices for eczema management, including gentle cleansing techniques, regular moisturization, and the use of wet wraps to soothe severe eczema and enhance the absorption of topical medications.
- Develop an individualized care plan for a patient with eczema, incorporating strategies to avoid triggers, lifestyle modifications, appropriate use of prescribed medications (e.g., corticosteroid creams), and self-monitoring techniques to achieve long-term symptom relief and prevent complications.
- Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
- It is crucial for healthcare professionals to understand the etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic criteria, and management of eczema to provide effective care for patients suffering from this condition.
I. Definition and Background
- Eczema is a chronic skin disorder characterized by inflammation, redness, itching, and dryness.
- It is classified as a type of atopic dermatitis, which is the most common form of eczema.
- The exact cause of eczema is not fully understood but is believed to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors.
- It often presents in childhood and may persist into adulthood, although some individuals may experience resolution as they grow older.
II. Clinical Manifestations
- Intense itching (pruritus): Itching is a hallmark symptom of eczema and can be severe, leading to scratching and skin damage.
- Rash: The affected skin appears red, and inflamed, and may develop small fluid-filled blisters that can ooze and crust over.
- Dryness and scaling: The skin becomes dry, and scaly, and may crack, leading to increased susceptibility to infection.
- Lichenification: In chronic cases, the skin may thicken and develop a leathery appearance due to persistent scratching.
III. Diagnostic Criteria
- Diagnosis of eczema is primarily clinical, based on the characteristic appearance and distribution of the rash.
- A detailed patient history, including a family history of atopic diseases, can support the diagnosis.
- The absence of specific laboratory or diagnostic tests for eczema makes it crucial to differentiate it from other skin conditions that may present similarly.
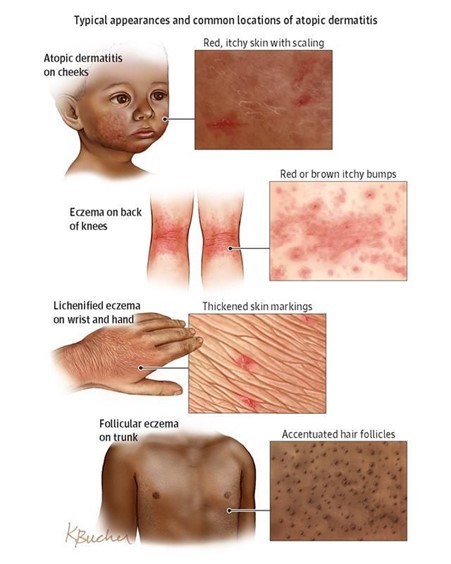
IV. Triggers and Aggravating Factors
- Allergens: Pollen, pet dander, dust mites, certain foods, and environmental allergens can trigger or worsen eczema symptoms.
- Irritants: Harsh soaps, detergents, fragrances, and chemicals may irritate the skin and exacerbate eczema.
- Climate and Weather: Dry, cold weather can lead to increased skin dryness, while heat and sweat may aggravate itching.
- Stress: Emotional stress can exacerbate eczema symptoms in some individuals.
Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels, especially during pregnancy, can influence eczema symptoms.
V. Nursing Management
- Skin Care: Promote good skin hygiene and moisturize regularly to prevent dryness and minimize irritation.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and advise patients to avoid known triggers and irritants that worsen their eczema.
- Topical Medications: Apply corticosteroid creams or ointments as prescribed by a healthcare provider to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Antihistamines: These may be recommended to help relieve itching and improve sleep.
- Wet Dressings: Use wet wraps or wet dressings to soothe severe eczema and enhance the absorption of topical medications.
- Education: Provide patient and family education on eczema management, including proper skin care, medication use, and lifestyle modifications.
VI. Patient Education
- Importance of Moisturization: Emphasize the need for regular moisturization to keep the skin hydrated and reduce itching.
- Avoid Scratching: Educate patients on the risks of scratching and strategies to avoid it, such as using distraction techniques or wearing soft gloves at night.
- Trigger Identification: Encourage patients to identify and avoid triggers that exacerbate their eczema symptoms.
- Medication Adherence: Stress the importance of using prescribed medications as directed and attending follow-up appointments with healthcare providers.
VII. Prognosis
- Eczema is a chronic condition that can be managed with proper care and lifestyle modifications.
- While there is no cure for eczema, many individuals experience periods of remission and milder symptoms over time.
- Early and effective management can significantly improve the quality of life for patients with eczema.
Scabies
Objectives
- Identify the etiology and pathophysiology of scabies, including the role of the Sarcoptes scabiei mite in infestation, to understand the basis of the disease process.
- Differentiate between the clinical manifestations of scabies and other skin conditions to accurately assess and diagnose scabies in patients.
- Analyze the appropriate pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment modalities for scabies, including topical scabicides, oral medications, and environmental decontamination, to develop effective management plans for patients.
- Recognize the importance of infection control measures in preventing scabies transmission, particularly in healthcare and communal settings, to implement appropriate measures for outbreak prevention and containment.
- Educate patients and families about scabies transmission, treatment, and prevention, including the significance of compliance with prescribed medications and preventive measures to promote successful treatment outcomes and minimize the risk of reinfection.
- Scabies is a contagious parasitic infestation of the skin caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis.
- It is an important topic for healthcare professionals to understand, as it can cause significant discomfort and has the potential for rapid transmission.
I. Definition and Background
- Scabies is caused by the burrowing of the female mite Sarcoptes scabiei into the upper layer of the skin to lay eggs, leading to an inflammatory response and intense itching.
- The mite's life cycle includes egg, larva, nymph, and adult stages.
- Scabies is highly contagious and is usually spread through prolonged skin-to-skin contact or sharing of personal items like clothing or bedding.
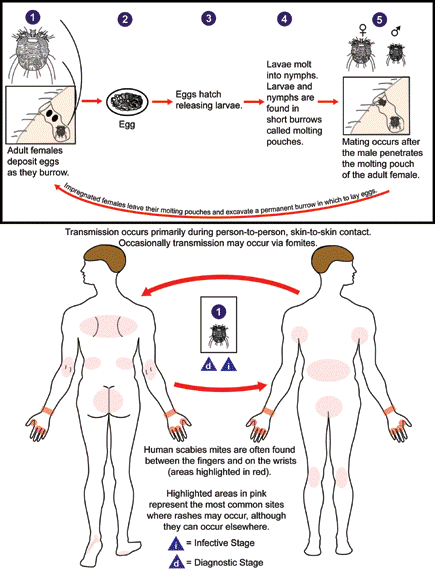
II. Clinical Manifestations
- Intense Pruritus: The primary symptom of scabies is severe itching, which often worsens at night and can be particularly bothersome for patients.
- Burrows: The mites create burrows that appear as red, raised, and serpiginous (snake-like) lines or tracks on the skin, usually measuring a few millimeters in length.
- Rash and Secondary Lesions: The burrowing activity causes an inflammatory response leading to a rash with red papules, pustules, and vesicles.
- Common locations for burrows include interdigital spaces, wrists, elbows, axillae, areolae, and genital area.
- Scratching may result in secondary lesions, such as excoriated papules, nodules, or blisters.
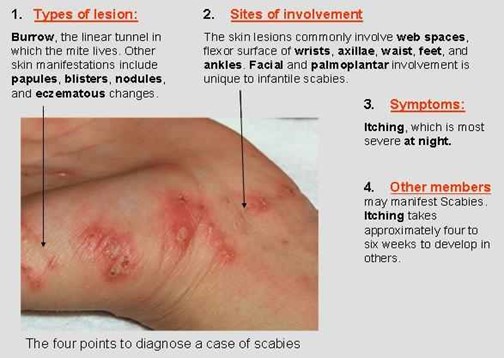
III. Diagnostic Criteria
- Clinical Presentation: Diagnosis is primarily based on the characteristic appearance of burrows, rash, and intense pruritus, especially when found in multiple household members or close contacts.
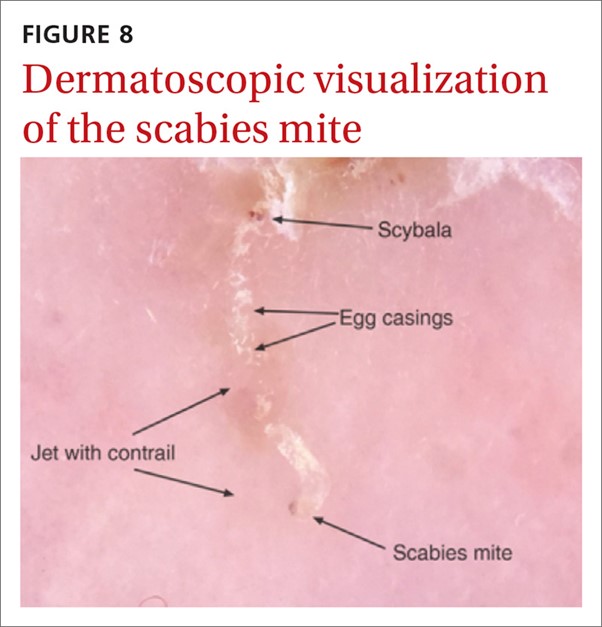
- Skin Scraping: A skin scraping is performed by removing a small portion of the affected skin and examining it under a microscope to identify the mites, eggs, or fecal pellets.
IV. Nursing Management
- Assessment: Conduct a thorough skin assessment to identify the presence of burrows, rashes, and secondary skin lesions.
- Patient Education: Provide comprehensive education to patients and their families about scabies transmission, prevention, and treatment measures.
- Medication Administration: Administer prescribed scabicide medications, which are the mainstay of treatment.
- Topical permethrin is commonly used, and oral ivermectin may be considered for severe cases or when topical treatment is not feasible.
- Family and Household Management: Instruct family members and close contacts to receive treatment simultaneously, even if they are asymptomatic, to prevent reinfection.
V. Patient Education
- Transmission Prevention: Educate patients on the importance of avoiding close physical contact with infested individuals, sharing personal items, and practicing good hygiene to prevent the spread of scabies.
- Treatment Adherence: Emphasize the necessity of completing the full course of scabicide treatment to ensure complete eradication of the mites.
- Itch Management: Teach patients techniques to relieve itching, such as cool compresses and antihistamines, and emphasize the importance of avoiding scratching to prevent skin damage and secondary infections.
VI. Infection Control Measures
- Isolation Precautions: Place patients with suspected or confirmed scabies on contact precautions to prevent direct skin-to-skin contact with others.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Healthcare personnel should wear disposable gloves and gowns when providing care to scabies-infested patients.
- Environmental Cleaning: Thoroughly clean and disinfect surfaces and equipment that may have come into contact with the patient or their belongings.
- Linen and Clothing Handling: Handle contaminated linen and clothing as potentially infectious material, placing them in leak-proof bags for transport.
- Patient and Family Education: Educate patients and families about scabies transmission, prevention, and the importance of completing the prescribed treatment.
- Contact Tracing: Identify and notify individuals who may have had close contact with the infested patient and provide appropriate guidance and follow-up.
- Hand Hygiene: Emphasize proper handwashing with soap and water, especially after contact with infested skin or contaminated items.
- Treatment Compliance: Ensure all affected patients receive prompt and appropriate treatment for scabies and monitor treatment compliance.
- Healthcare Personnel Education: Educate healthcare personnel about scabies, its transmission, and infection control measures to prevent further spread.
- Monitoring and Surveillance: Implement monitoring and surveillance measures to identify and respond promptly to suspected or confirmed scabies cases.
VII. Prognosis
- Scabies is generally a curable condition with appropriate treatment.
- Symptoms typically improve within a few days after starting treatment, but itching may persist for a few weeks.
- Patients should be educated on the possibility of reinfection if exposed to scabies again.
Psoriasis
Objectives
- Identify the clinical manifestations of psoriasis, including the characteristic appearance of raised, red plaques with silvery scales, and differentiate between the different types of psoriasis (plaque, guttate, inverse, pustular, and erythrodermic).
- Understand the pathophysiology of psoriasis, including the autoimmune nature of the condition, the role of immune system dysregulation, and the accelerated turnover of epidermal cells leading to the formation of skin lesions.
- Recognize common triggers and exacerbating factors for psoriasis, such as stress, infections, skin injuries, certain medications, and environmental factors, to provide appropriate patient education on managing these triggers to minimize flare-ups.
- Demonstrate competence in the administration of topical treatments for psoriasis, including corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and retinoids, ensuring correct application techniques and educating patients on potential side effects and proper usage.
- Develop a comprehensive nursing care plan for patients with psoriasis, incorporating strategies to promote skin health, manage symptoms, provide emotional support, and collaborate with the interdisciplinary team to optimize treatment outcomes and enhance the patient's quality of life.
- Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the etiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic criteria, and management of psoriasis is essential for healthcare professionals to provide effective care for patients suffering from this condition.
I. Definition and Background
- Psoriasis is a chronic, non-contagious skin disorder characterized by red, raised, and scaly patches on the skin surface.
- It is considered an autoimmune condition, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to rapid skin cell turnover.
- Psoriasis can affect various parts of the body, including the scalp, elbows, knees, and trunk.
- The severity and presentation of psoriasis can vary widely among individuals.
II. Etiology and Pathophysiology
- The exact cause of psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, immunological, and environmental factors.
- Immune system dysregulation triggers an abnormal immune response, leading to the overproduction of skin cells and the rapid turnover of epidermal cells.
- Inflammation and the release of cytokines further contribute to the characteristic plaques seen in psoriasis.
III. Clinical Manifestations
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most common type, characterized by well-defined, red, raised plaques covered with silvery scales.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Presents as small, drop-like lesions scattered over the body, often triggered by bacterial infections (e.g., streptococcal throat infection).
- Inverse Psoriasis: Affects skin folds, such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts, and appears as smooth, red, and inflamed patches.
- Pustular Psoriasis: Presents with pustules filled with non-infectious pus, and may be localized or generalized.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A severe and rare form, characterized by widespread redness and scaling of the skin, often leading to medical emergencies.
IV. Diagnostic Criteria
- Diagnosis of psoriasis is primarily clinical, based on the characteristic appearance and distribution of skin lesions.
- Biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other skin conditions.
V. Nursing Management
- Assessment: Conduct a comprehensive assessment of the patient's skin condition, including the type, severity, and distribution of psoriasis lesions.
- Education: Provide patient and family education about psoriasis, including the chronic nature of the condition, triggers, and available treatment options.
- Skin Care: Promote good skin hygiene and moisturize regularly to reduce dryness and scaling.
- Topical Medications: Apply prescribed topical treatments, such as corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, or retinoids, to reduce inflammation and slow down skin cell turnover.
- Phototherapy: Collaborate with the healthcare team to administer phototherapy, such as UVB or PUVA therapy, as a treatment option for moderate to severe psoriasis.
- Biologic and Systemic Therapies: Support patients receiving biologic agents or systemic medications for severe psoriasis, ensuring proper administration and monitoring for side effects.
VI. Patient Education
- Stress Management: Educate patients on stress reduction techniques, as stress can exacerbate psoriasis symptoms.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Advise patients on lifestyle changes, such as avoiding triggers and maintaining a healthy diet, to support overall skin health.
- Medication Adherence: Emphasize the importance of adhering to prescribed medications and attending follow-up appointments for effective psoriasis management.
VII. Prognosis
- Psoriasis is a chronic condition without a cure, but it can often be managed effectively with appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications.
- Long-term management can help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups, improving the patient's quality of life.
Naxlex
Videos
Login to View Video
Click here to loginTake Notes on Integumentary System
This filled cannot be empty
Join Naxlex Nursing for nursing questions & guides! Sign Up Now


