Pathophysiology Proctored Exam
Total Questions : 39
Showing 10 questions, Sign in for moreThe risk of developing coronary artery disease is increased up to threefold by
What is the usual source of pulmonary emboli
A patient is diagnosed with pulmonary disease and elevated pulmonary valvular resistance. Which of the following heart failures may result from this condition?
What is the major effect of calcium channel blockers on cardiac contractions
The mitral and tricuspid valves close after the ventricles are filled with blood because the
Explanation
Clubbing is a medical condition characterized by bulbous enlargement of the distal portion of a digit (usually a finger, but sometimes a toe) due to soft tissue proliferation and increased bone deposition. The affected digit takes on a rounded or "club-like" appearance, and the angle between the nail and nail bed (known as the Lovibond angle) increases to greater than 180 degrees.
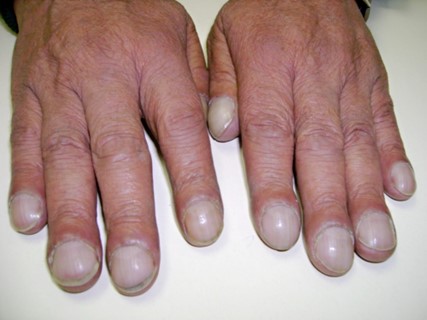
Clubbing is commonly associated with a variety of medical conditions that interfere with oxygenation of the blood, including lung diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), interstitial lung disease, and bronchiectasis; heart diseases such as congenital heart defects and cyanotic heart disease; and gastrointestinal diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease and cirrhosis.
The exact mechanism underlying clubbing is not fully understood, but it is thought to involve a combination of vascular, inflammatory, and neurogenic factors. Hypoxia (low oxygen levels) is believed to play a central role in the development
of clubbing, leading to the release of growth factors and cytokines that promote soft tissue and bone proliferation.
Clubbing is typically diagnosed based on physical examination findings, including the Lovibond angle and the presence of nail bed fluctuation (when the nail bed feels spongy or compressible). It is important to identify and treat any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to clubbing, as these can have significant implications for the patient's health and quality of life.
Which elevated value may be protective of the development of atherosclerosis
Which of the following type of croup is most common
Patient wants to know what causes atherosclerosis. How should the nurse respond? In general, atherosclerosis is caused by
The progression of chronic bronchitis is best halted by?
Sign Up or Login to view all the 39 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Naxlex’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now


