Med Surg Exam 8
ATI Med Surg Exam 8
Total Questions : 46
Showing 10 questions Sign up for moreA client with a history of Addison's disease and flu-like symptoms accompanied by nausea and vomiting over the past week is brought to the facility. His wife reports that he acted confused and was extremely weak when he awoke that morning. The client's blood pressure is 90/58 mm Hg, his pulse is 116 beats/minute, and his temperature is 101° F (38.3° C). A diagnosis of acute adrenal insufficiency is made. What should the nurse expect to administer by I.V. infusion?
Explanation
A. Methylprednisolone (Solu-medrol):
Explanation: Acute adrenal insufficiency is a life-threatening condition characterized by a sudden deficiency of adrenal hormones. In this situation, intravenous glucocorticoids such as methylprednisolone are administered to replace the deficient hormones and stabilize the patient. This is the appropriate intervention to address the acute adrenal crisis.
B. Hypotonic saline:
Explanation: Hypotonic saline is not the first-line treatment for acute adrenal insufficiency. The priority is to replace glucocorticoids to address the adrenal hormone deficiency.
C. Potassium (K-dur):
Explanation: While electrolyte imbalances can occur in adrenal insufficiency, potassium replacement alone does not address the primary issue of glucocorticoid deficiency in acute adrenal insufficiency.
D. Regular Insulin:
Explanation: Regular insulin is not the primary treatment for acute adrenal insufficiency. Glucocorticoid replacement, such as methylprednisolone, is the key intervention.
The nurse is caring for a patient with Addison's disease who is scheduled for discharge. When teaching the patient about hormone replacement therapy, the nurse should address what topic?
Explanation
A. The need to match the daily steroid dose to immediate symptoms:
Explanation: Adjusting the steroid dose based on immediate symptoms is not a recommended approach. Patients should follow the prescribed regimen provided by their healthcare provider.
B. The importance of monitoring liver function:
Explanation: While monitoring liver function is important for some medications, it is not the primary focus when teaching about hormone replacement therapy in Addison's disease. The emphasis is on the need for life-long steroid replacement.
C. The need for life-long steroid replacement:
Explanation: Patients with Addison's disease require life-long steroid replacement therapy to compensate for the deficiency in adrenal hormones. It's important for the patient to understand that adherence to the prescribed steroid regimen is essential for maintaining health and preventing adrenal crisis.
D. The possibility extreme weight loss from the use of corticosteroids:
Explanation: While corticosteroids can have various side effects, extreme weight loss is not a typical or desired outcome of steroid therapy for Addison's disease. Weight changes and potential side effects should be discussed, but the emphasis should be on the importance of long-term steroid replacement.
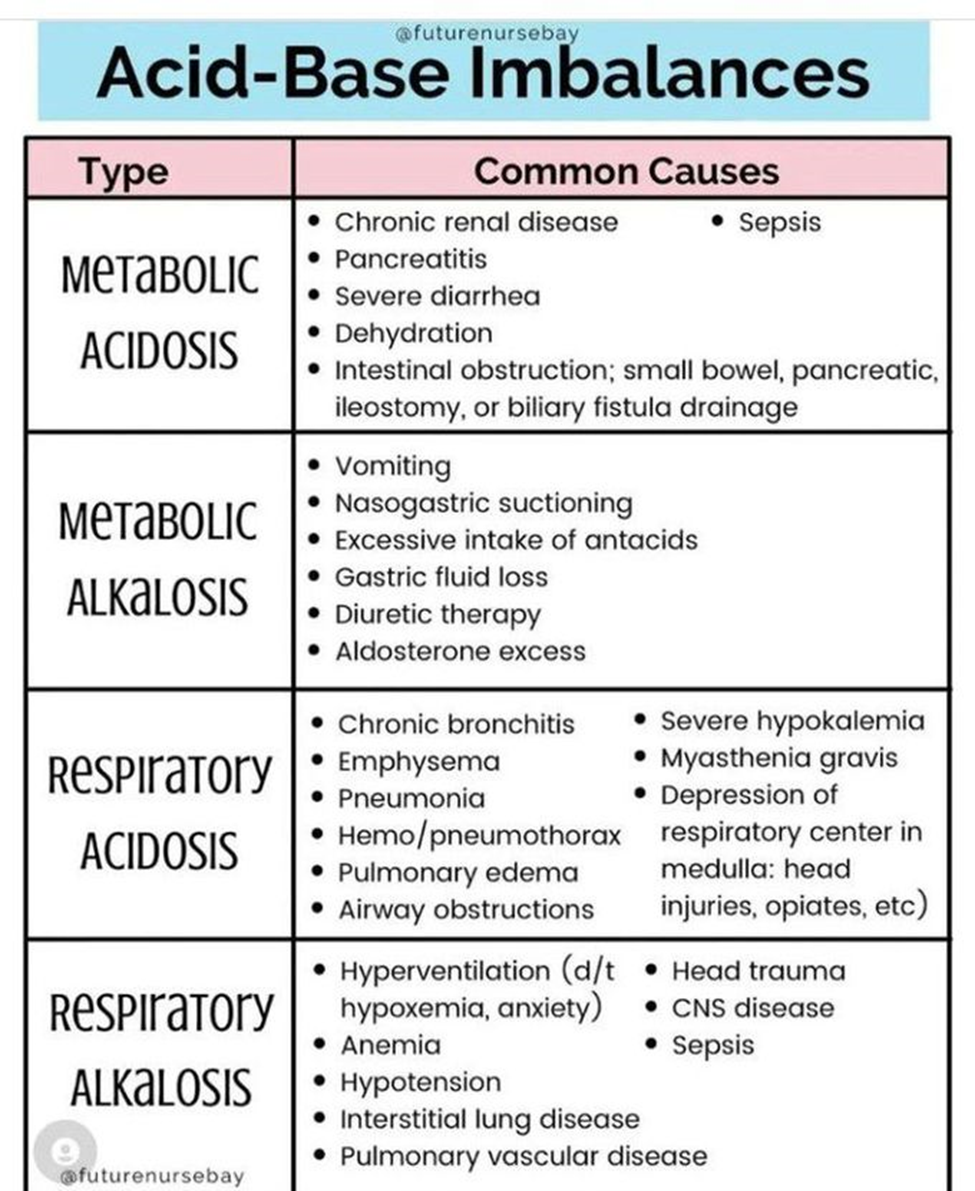
A patient with a longstanding diagnosis of generalized anxiety disorder presents to the emergency room. The triage nurse notes upon an assessment that the patient is hyperventilating. The triage nurse is aware that hyperventilation is the MOST common cause of which acid-base imbalance?
Explanation
A. Respiratory Acidosis:
Explanation: Respiratory acidosis occurs when there is inadequate elimination of carbon dioxide, leading to an increase in PaCO2 and a decrease in blood pH. This is typically associated with conditions that impair ventilation.
B. Metabolic Alkalosis:
Explanation: Metabolic alkalosis is characterized by an elevated blood pH and bicarbonate (HCO3-) concentration. It is not directly caused by hyperventilation but is often associated with conditions such as excessive vomiting or excessive bicarbonate intake.
C. Metabolic Acidosis:
Explanation: Metabolic acidosis is characterized by a decrease in blood pH and bicarbonate concentration. It is not directly caused by hyperventilation but may result from conditions such as diabetic ketoacidosis or lactic acidosis.
D. Respiratory Alkalosis:
Explanation: Hyperventilation is the most common cause of respiratory alkalosis. During hyperventilation, there is an excessive loss of carbon dioxide (CO2) through rapid breathing, leading to a decrease in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) in the blood. This results in an increase in blood pH, causing an alkalotic state.
A client is being treated on the medical unit for a sickle cell crisis. The nurse's most recent assessment reveals an oral temperature of 100.5°F and a new onset of fine crackles on lung auscultation. What is the nurse's most appropriate action?
Explanation
A. Inform the primary care provider that the patient may have an infection:
Explanation: The presence of an elevated oral temperature and new onset of fine crackles on lung auscultation suggests a potential respiratory infection, which is a significant concern in a patient with sickle cell disease. Notifying the primary care provider allows for further evaluation and appropriate management of the infection.
B. Liaise with the respiratory therapist and consider high-flow oxygen:
Explanation: While oxygenation may be necessary, especially if the patient is experiencing respiratory distress, addressing the potential infection is the priority. Consulting with the respiratory therapist and considering high-flow oxygen can be part of the overall plan based on the primary care provider's recommendations.
C. Apply supplementary oxygen by nasal cannula:
Explanation: Providing oxygen support may be necessary, but it should be done in consultation with the primary care provider, who can guide the appropriate level of oxygen therapy based on the patient's condition.
D. Administer bronchodilators by nebulizer:
Explanation: Bronchodilators are typically used for conditions like asthma or COPD, and their use might not be the primary intervention in the context of a sickle cell crisis with signs of a potential respiratory infection. Addressing the infection takes precedence, and the primary care provider's input is essential in determining the appropriate course of action.
A client with chronic kidney disease has chronic anemia. What pharmacologic alternative to blood transfusion may be used for this patient?
Explanation
A. Erythropoietin (Epogen):
Explanation: Erythropoietin is a hormone that stimulates the production of red blood cells. In chronic kidney disease, especially when associated with anemia, the production of erythropoietin by the kidneys may be reduced. Erythropoietin (Epogen) is commonly used to stimulate the production of red blood cells and manage anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease.
B. Eltrombopag (Promacta):
Explanation: Eltrombopag is a medication used to stimulate the production of platelets and is primarily indicated for conditions associated with thrombocytopenia (low platelet count). It is not used to treat anemia associated with chronic kidney disease.
C. GM-CSF (Leukine):
Explanation: Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF or Leukine) is a medication that stimulates the production of white blood cells and is used in certain conditions to address decreased white blood cell counts. It is not typically used for managing anemia.
D. Thrombopoietin (TPO):
Explanation: Thrombopoietin is a hormone that stimulates the production of platelets. Medications that mimic the action of thrombopoietin, such as romiplostim and eltrombopag, are used to treat thrombocytopenia. Thrombopoietin is not used for the treatment of anemia.
A client with Cushing's syndrome is receiving education about dietary changes from the nurse. Which statement by the patient demonstrates the need for further teaching?
Explanation
A. "I can eat a salad with oil and vinegar dressing":
Explanation: This statement is correct. A salad with oil and vinegar dressing is a healthy option, and the patient does not need to avoid this.
B. "I can cook soup using canned vegetables":
Explanation: This statement is generally acceptable. However, the patient should be aware of the sodium content in canned vegetables and choose low-sodium options to manage fluid retention, which can be a concern in Cushing's syndrome.
C. "I can eat dried fruit for breakfast with my oatmeal":
Explanation: This statement is questionable. Dried fruits may have higher sugar content and can contribute to an increase in calorie intake. In Cushing's syndrome, where there may be weight gain, it's advisable to choose fresh fruits over dried ones.
D. "I can eat baked chicken with green beans for dinner":
Explanation: This statement is correct. Baked chicken with green beans is a healthy and balanced option.
A client comes into the clinic complaining of fatigue. Blood work shows an increased bilirubin concentration and an increased reticulocyte count. What would the nurse suspect the patient has?
Explanation
A. Leukemia:
Explanation: Leukemia is a cancer of the blood-forming tissues, including the bone marrow and lymphatic system. It typically presents with an abnormal increase in white blood cells. While fatigue can be a symptom, increased bilirubin concentration and an increased reticulocyte count are not typical findings in leukemia.
B. Hemolytic Anemia:
Explanation: Hemolytic anemia is characterized by the premature destruction of red blood cells, leading to an increased release of bilirubin (from the breakdown of hemoglobin) and an increased reticulocyte count (as the body attempts to compensate by producing more red blood cells). This is a likely possibility given the presented symptoms.
C. Hypoproliferative Anemia:
Explanation: Hypoproliferative anemia is characterized by a decreased production of red blood cells. It is unlikely in this scenario, as an increased reticulocyte count suggests an attempt by the bone marrow to increase red blood cell production.
D. Thrombocytopenia:
Explanation: Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by a low platelet count. It does not typically present with an increased bilirubin concentration or an increased reticulocyte count.
A nurse is providing education to a client with iron deficiency anemia who has been prescribed iron supplements. What should the nurse include in health education?
Explanation
A. Increase the intake of vitamin E to enhance absorption:
Explanation: Iron absorption can be enhanced by taking vitamin C, not vitamin E. Therefore, this statement is not accurate.
B. Iron will cause the stools to darken in color:
Explanation: This statement is accurate. Iron supplements can cause stools to become darker in color. This is a common and harmless side effect.
C. Take the iron with dairy products to enhance absorption:
Explanation: Calcium-containing foods and supplements can inhibit the absorption of iron. Therefore, it is recommended to avoid taking iron supplements with dairy products.
D. Limit foods high in fiber due to the risk for diarrhea:
Explanation: Iron supplements can cause constipation, not diarrhea. Therefore, limiting foods high in fiber is not necessary.
The nurse is collecting data for a client who has been diagnosed with iron-deficiency anemia. What subjective findings does the nurse recognize as symptoms related to this type of anemia?
Explanation
A. "I have difficulty breathing when walking 30 feet":
Explanation: Difficulty breathing on exertion (dyspnea) is a common symptom of iron-deficiency anemia. This is because iron is a crucial component of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen to body tissues. In the absence of sufficient iron, the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood is reduced, leading to symptoms such as shortness of breath.
B. "I feel hot all of the time":
Explanation: Feeling hot all the time is not a typical symptom of iron-deficiency anemia. Anemia is more likely to cause symptoms related to poor oxygen delivery, such as fatigue and shortness of breath.
C. "I have a difficult time falling asleep at night":
Explanation: Difficulty falling asleep is not a classic symptom of iron-deficiency anemia. Symptoms are more likely to be related to fatigue and weakness.
D. "I have an increase in my appetite":
Explanation: An increase in appetite is not a typical symptom of iron-deficiency anemia. In fact, individuals with anemia may experience a decrease in appetite.
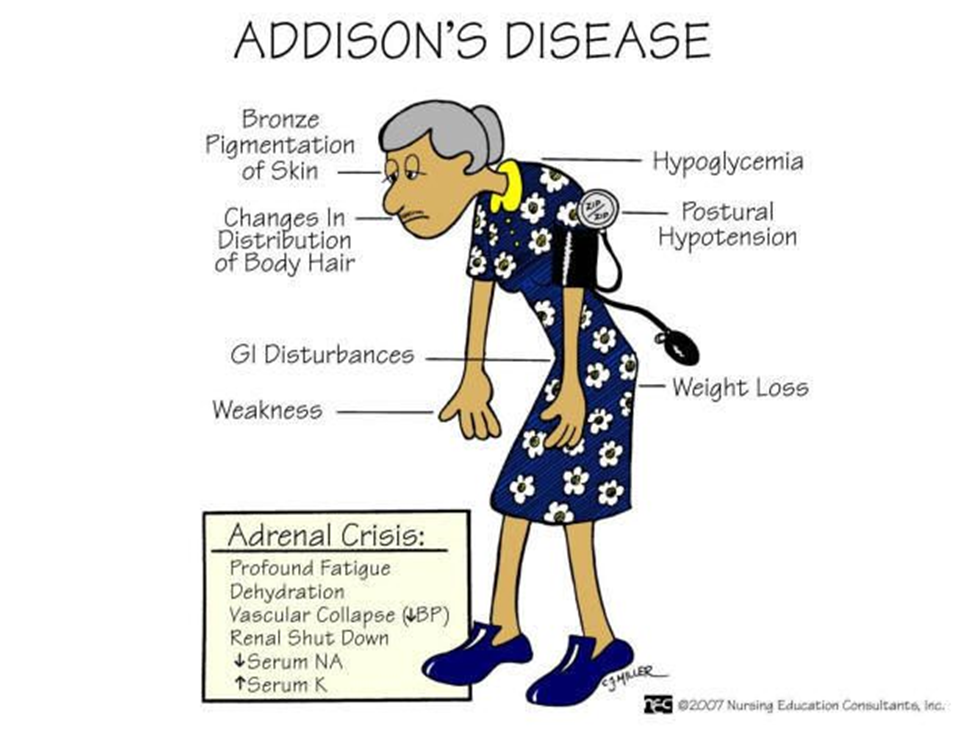
A nurse is caring for a patient with Addison's Disease. Which of the following clinical manifestations should the nurse expect to observe? (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY)
Explanation
A. Buffalo hump:
Explanation: A buffalo hump is associated with excess cortisol, which is not a typical manifestation of Addison's disease. Instead, patients with Addison's disease may experience weight loss and muscle wasting.
B. Hyponatremia:
Explanation: Correct. Hyponatremia (low sodium levels) can occur in Addison's disease due to the loss of aldosterone, which plays a role in sodium and water balance.
C. Decreased glucose level:
Explanation: Correct. Addison's disease can lead to hypoglycemia (low blood glucose levels) because cortisol, which is important for maintaining blood glucose, is deficient.
D. Weight gain:
Explanation: Weight gain is not a typical manifestation of Addison's disease. Instead, weight loss and muscle wasting may occur.
E. Craving for salt:
Explanation: Correct. Addison's disease can lead to salt craving, as aldosterone deficiency results in increased sodium loss and potassium retention.
You just viewed 10 questions out of the 46 questions on the ATI Med Surg Exam 8 Exam. Subscribe to our Premium Package to obtain access on all the questions and have unlimited access on all Exams. Subscribe Now



