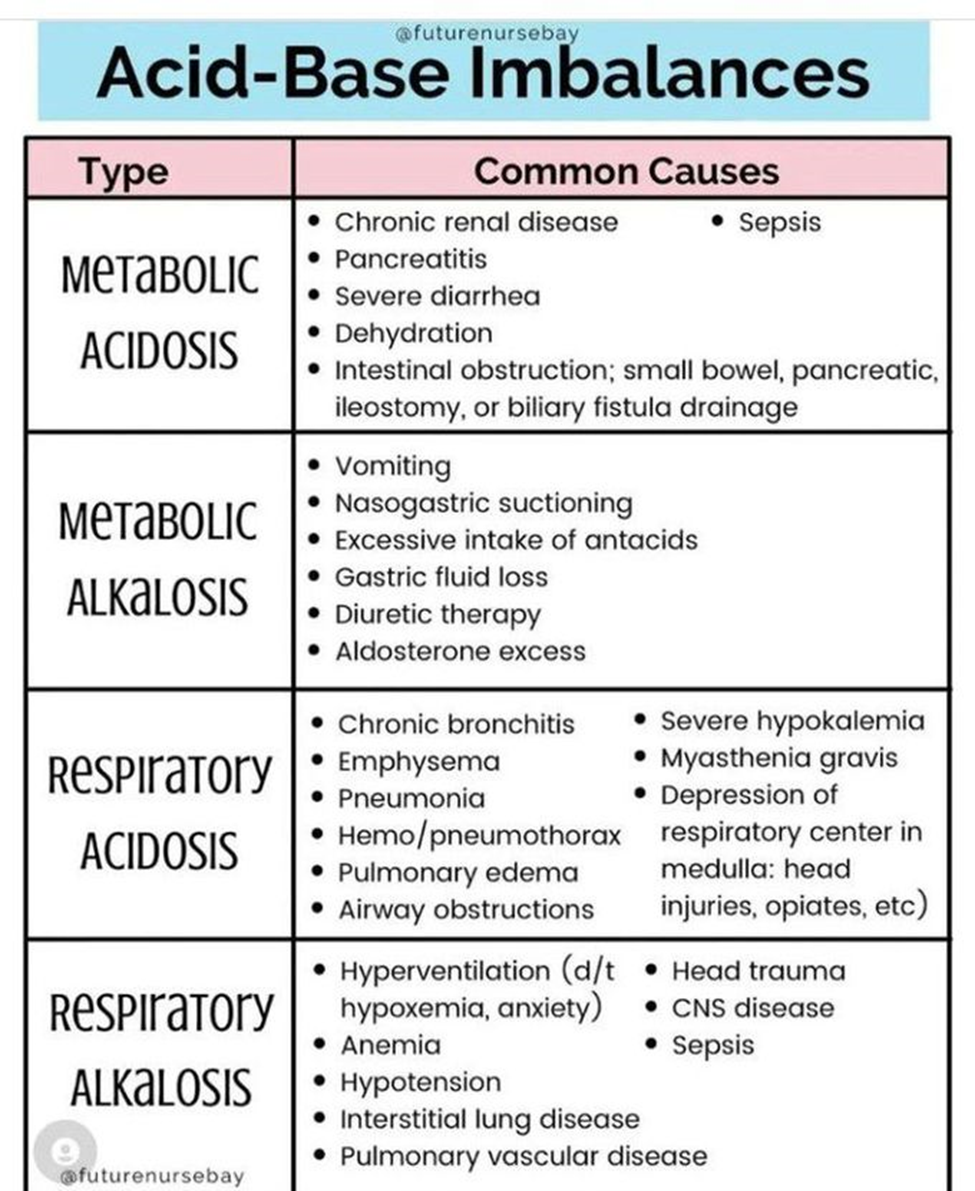
A patient with a longstanding diagnosis of generalized anxiety disorder presents to the emergency room. The triage nurse notes upon an assessment that the patient is hyperventilating. The triage nurse is aware that hyperventilation is the MOST common cause of which acid-base imbalance?
Respiratory Acidosis
Metabolic Alkalosis
Metabolic Acidosis
Respiratory Alkalosis
The Correct Answer is D
A. Respiratory Acidosis:
Explanation: Respiratory acidosis occurs when there is inadequate elimination of carbon dioxide, leading to an increase in PaCO2 and a decrease in blood pH. This is typically associated with conditions that impair ventilation.
B. Metabolic Alkalosis:
Explanation: Metabolic alkalosis is characterized by an elevated blood pH and bicarbonate (HCO3-) concentration. It is not directly caused by hyperventilation but is often associated with conditions such as excessive vomiting or excessive bicarbonate intake.
C. Metabolic Acidosis:
Explanation: Metabolic acidosis is characterized by a decrease in blood pH and bicarbonate concentration. It is not directly caused by hyperventilation but may result from conditions such as diabetic ketoacidosis or lactic acidosis.
D. Respiratory Alkalosis:
Explanation: Hyperventilation is the most common cause of respiratory alkalosis. During hyperventilation, there is an excessive loss of carbon dioxide (CO2) through rapid breathing, leading to a decrease in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) in the blood. This results in an increase in blood pH, causing an alkalotic state.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Increase the intake of vitamin E to enhance absorption:
Explanation: Iron absorption can be enhanced by taking vitamin C, not vitamin E. Therefore, this statement is not accurate.
B. Iron will cause the stools to darken in color:
Explanation: This statement is accurate. Iron supplements can cause stools to become darker in color. This is a common and harmless side effect.
C. Take the iron with dairy products to enhance absorption:
Explanation: Calcium-containing foods and supplements can inhibit the absorption of iron. Therefore, it is recommended to avoid taking iron supplements with dairy products.
D. Limit foods high in fiber due to the risk for diarrhea:
Explanation: Iron supplements can cause constipation, not diarrhea. Therefore, limiting foods high in fiber is not necessary.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. "If a vial of insulin will be used up within 21 days, it may be kept at room temperature."
This statement suggests a duration of up to 21 days for room temperature storage after the vial is in use. However, most insulins can typically be stored at room temperature for up to 28 days after initial use. This recommendation might be more conservative than necessary for many types of insulin.
B. "If a vial of insulin will be used up within 2 weeks, it may be kept at room temperature."
This choice suggests a timeframe of 14 days for room temperature storage after opening the vial. However, for many insulins, the recommended duration for room temperature storage after opening is up to 28 days.
C. "If you are going to use up the vial within 1 month, it can be kept at room temperature."
This option extends the timeframe to 1 month for room temperature storage after the vial is in use. However, the generally recommended duration for many insulins is up to 28 days after opening.
D. "If a vial of insulin will be used up within 1 week, it may be kept at room temperature."
This choice suggests a very short duration of 7 days for room temperature storage after opening the vial. Most insulins can typically be stored at room temperature for a longer duration after initial use.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
