The nurse is preparing to administer Insulin Lispro (Humalog) to a client with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus for carbohydrate coverage. The nurse understands the injection should be administered:
with the meal
post-prandial
pre-prandial
AC/HS
The Correct Answer is A
A. With the meal:
Insulin Lispro is a rapid-acting insulin that is designed to be taken just before or with meals.
It helps control the rise in blood sugar that occurs after eating.
B. Post-prandial:
"Post-prandial" refers to after a meal. Insulin Lispro is usually administered before or with a meal to cover the increase in blood glucose that happens after eating.
C. Pre-prandial:
"Pre-prandial" refers to before a meal. This is accurate for Insulin Lispro, as it is given shortly before or with meals.
D. AC/HS:
"AC" stands for "ante cibum," which means before meals, and "HS" stands for "hora somni," which means at bedtime. This terminology is more commonly associated with the timing of oral medications rather than insulin.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. "I will make sure I call the diabetes educator each time I adjust my insulin dose."
This statement suggests a reliance on insulin adjustment and implies frequent contact with the diabetes educator. However, it doesn't address the primary treatment for type 2 diabetes.
B. "I read that a pancreas transplant will provide a cure for my diabetes."
This statement mentions a pancreas transplant, which is a significant and rare intervention typically reserved for severe cases of diabetes. However, it's not considered the primary treatment for type 2 diabetes.
C. "I will make sure to follow the weight loss plan designed by the dietitian."
This statement aligns with a key aspect of managing type 2 diabetes, as weight management, along with diet and exercise, is a primary approach. Lifestyle modifications, including weight loss, are often part of the primary treatment plan.
D. "I will take my oral anti-diabetic agents when my morning blood sugar is high."
This statement indicates an understanding of the importance of oral anti-diabetic agents, which are commonly used in the management of type 2 diabetes. Timing medication based on blood sugar levels is a key aspect of treatment.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
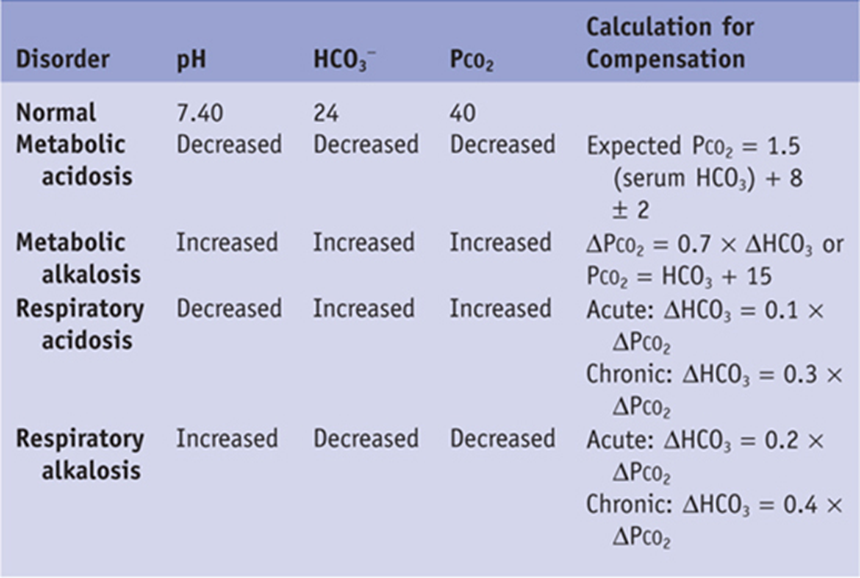
A. pH 7.28, pCO2 36, HCO3 23:
Explanation: The pH is low, indicating acidosis. However, the pCO2 is within the normal range, which is not consistent with respiratory acidosis. The HCO3 is slightly low but not significantly, and this doesn't align with typical findings in respiratory acidosis.
B. pH 7.52, pCO2 28, HCO3 25:
Explanation: The pH is high, indicating alkalosis. The pCO2 is below the normal range, which is not consistent with respiratory acidosis. The HCO3 is within the normal range, and these values are not typical for respiratory acidosis.
C. pH 7.25, pCO2 50, HCO3 22:
Explanation: The pH is low, indicating acidosis. The pCO2 is elevated, which is typical in respiratory acidosis. The HCO3 is within the normal range, suggesting uncompensated respiratory acidosis.
D. pH 7.35, pCO2 40, HCO3 24:
Explanation: The pH is within the normal range, and both pCO2 and HCO3 are normal. These values do not indicate acidosis.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
