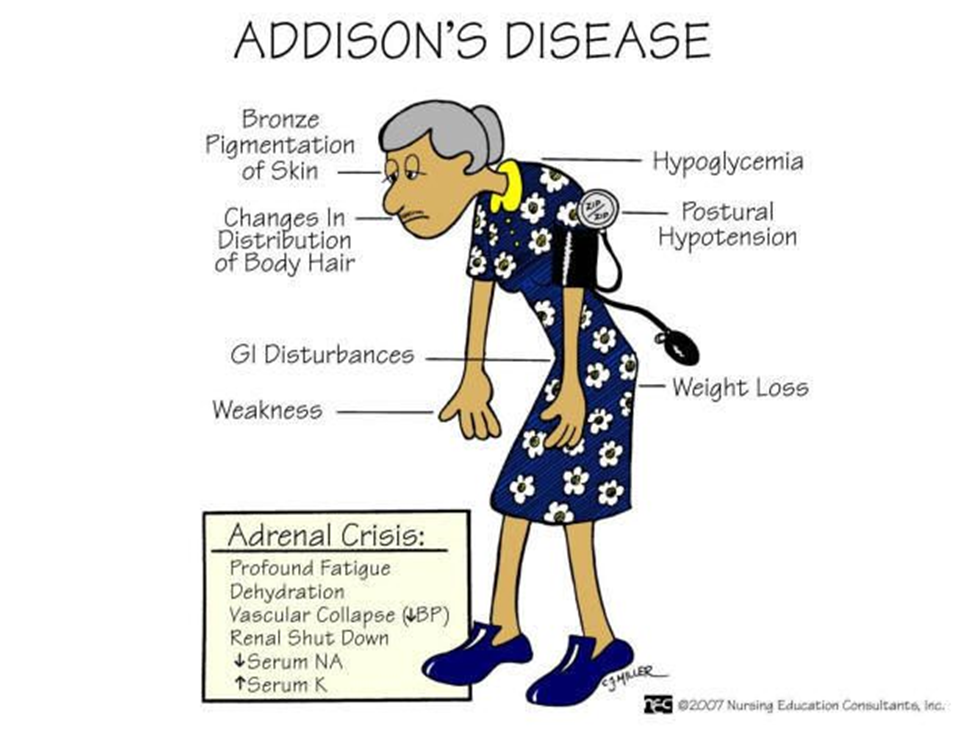
A nurse is caring for a patient with Addison's Disease. Which of the following clinical manifestations should the nurse expect to observe? (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY)
buffalo hump
hyponatremia
decreased glucose level
weight gain
Craving for salt
Correct Answer : B,C,E
A. Buffalo hump:
Explanation: A buffalo hump is associated with excess cortisol, which is not a typical manifestation of Addison's disease. Instead, patients with Addison's disease may experience weight loss and muscle wasting.
B. Hyponatremia:
Explanation: Correct. Hyponatremia (low sodium levels) can occur in Addison's disease due to the loss of aldosterone, which plays a role in sodium and water balance.
C. Decreased glucose level:
Explanation: Correct. Addison's disease can lead to hypoglycemia (low blood glucose levels) because cortisol, which is important for maintaining blood glucose, is deficient.
D. Weight gain:
Explanation: Weight gain is not a typical manifestation of Addison's disease. Instead, weight loss and muscle wasting may occur.
E. Craving for salt:
Explanation: Correct. Addison's disease can lead to salt craving, as aldosterone deficiency results in increased sodium loss and potassium retention.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. Methylprednisolone (Solu-medrol):
Explanation: Acute adrenal insufficiency is a life-threatening condition characterized by a sudden deficiency of adrenal hormones. In this situation, intravenous glucocorticoids such as methylprednisolone are administered to replace the deficient hormones and stabilize the patient. This is the appropriate intervention to address the acute adrenal crisis.
B. Hypotonic saline:
Explanation: Hypotonic saline is not the first-line treatment for acute adrenal insufficiency. The priority is to replace glucocorticoids to address the adrenal hormone deficiency.
C. Potassium (K-dur):
Explanation: While electrolyte imbalances can occur in adrenal insufficiency, potassium replacement alone does not address the primary issue of glucocorticoid deficiency in acute adrenal insufficiency.
D. Regular Insulin:
Explanation: Regular insulin is not the primary treatment for acute adrenal insufficiency. Glucocorticoid replacement, such as methylprednisolone, is the key intervention.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. IV administration of 50% dextrose in water:
This is the correct answer. The client is severely hypoglycemic, and IV administration of 50% dextrose in water is the most rapid way to raise the blood glucose level in an emergency situation.
B. IV bolus of 5% dextrose in 0.45% NaCl:
While this solution contains dextrose, it is not as concentrated as 50% dextrose. In an emergency, a more concentrated solution is needed to rapidly correct severe hypoglycemia.
C. Administer 4 oz. clear juice:
Oral intake may be too slow in this critical situation. IV administration is more appropriate for rapidly raising the blood glucose level.
D. Subcutaneous administration of 12 to 15 units of regular insulin:
This would further lower the blood glucose level and is not appropriate for treating severe hypoglycemia.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
