A nurse is instructing a client with newly diagnosed hypo-parathyroidism about this disorder. The nurse explains to the patient that the physician has prescribed daily supplements of calcium and vitamin D. Which education by the nurse is appropriate for this patient?
"The parathyroid has no effect on calcium levels in the body, this will just help prevent osteoporosis"
"The reason you have hypo-parathyroidism is because you were diagnosed with hypothyroidism, and when the thyroid doesn't work, neither does the parathyroid, so you need these supplements."
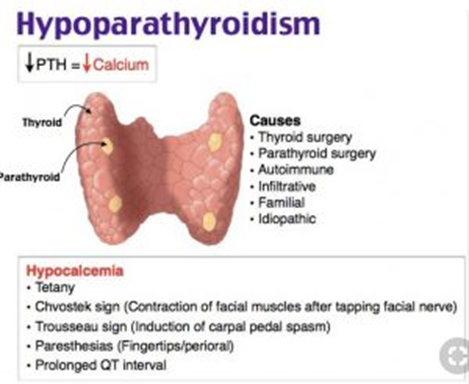
"A decrease in parathyroid hormone causes low calcium levels, so your body to break down bones in order to maintain normal calcium levels, and this will prevent that from happening."
"An increase in parathyroid hormone causes your body to move calcium into the cells to reduce blood calcium levels, so you have to replace the levels in the blood."
The Correct Answer is C
A. "The parathyroid has no effect on calcium levels in the body; this will just help prevent osteoporosis":
Explanation: This statement is incorrect. The parathyroid gland plays a crucial role in calcium homeostasis. Hypoparathyroidism, characterized by decreased parathyroid hormone (PTH) production, leads to low blood calcium levels, not high levels.
B. "The reason you have hypoparathyroidism is that you were diagnosed with hypothyroidism, and when the thyroid doesn't work, neither does the parathyroid, so you need these supplements."
Explanation: This statement is incorrect. The parathyroid and thyroid are separate glands with distinct functions. Hypoparathyroidism is not a result of hypothyroidism.
C. "A decrease in parathyroid hormone causes low calcium levels, so your body to break down bones to maintain normal calcium levels, and this will prevent that from happening."
Explanation: This is the correct statement. Hypoparathyroidism leads to a decrease in PTH, resulting in low blood calcium levels. Without sufficient PTH, the body may resort to breaking down bones to maintain calcium levels.
D. "An increase in parathyroid hormone causes your body to move calcium into the cells to reduce blood calcium levels, so you have to replace the levels in the blood."
Explanation: This statement is incorrect. An increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH) typically leads to increased blood calcium levels by promoting the release of calcium from bones and reducing calcium excretion by the kidneys. This describes hyperparathyroidism, not hypoparathyroidism.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
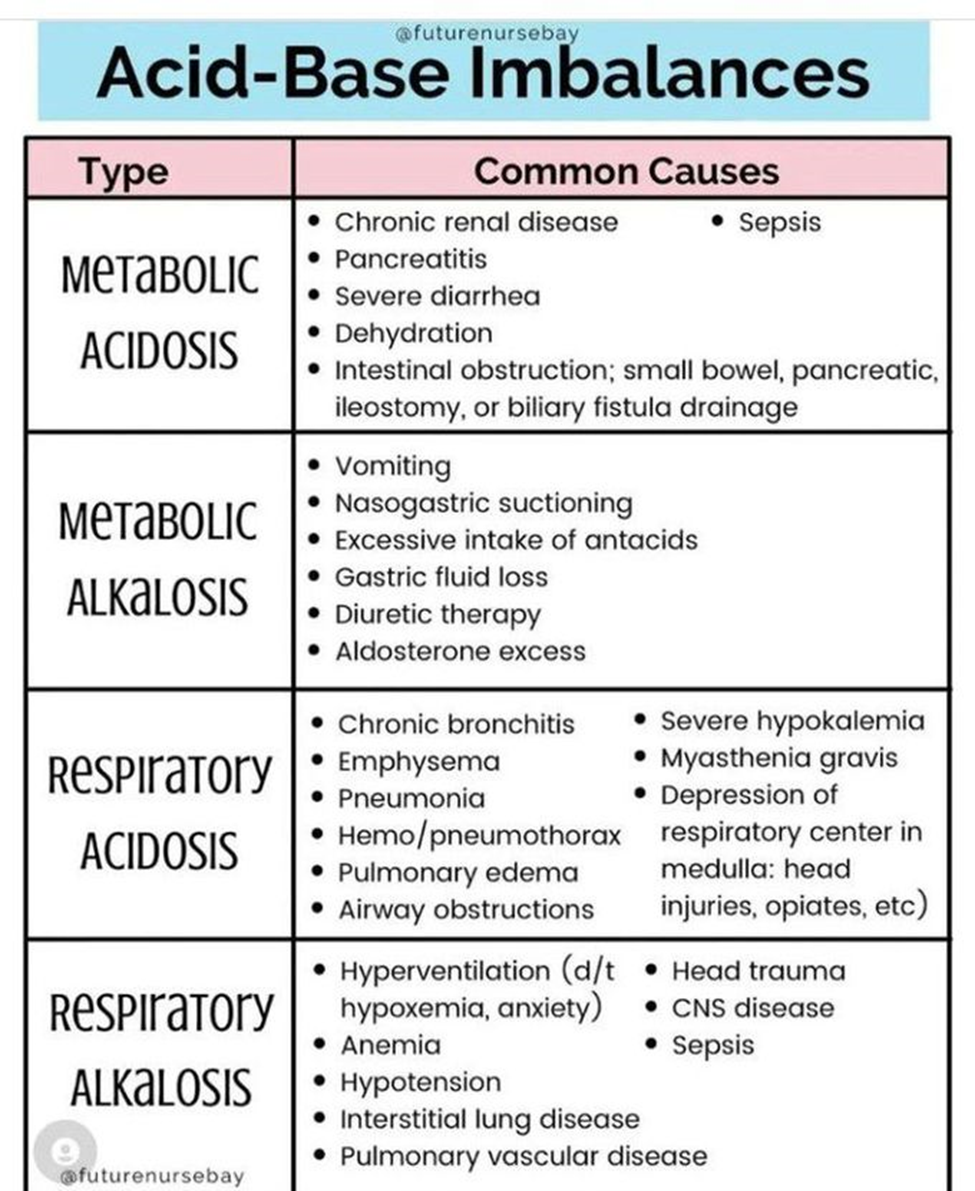
A. Respiratory Acidosis:
Explanation: Respiratory acidosis occurs when there is inadequate elimination of carbon dioxide, leading to an increase in PaCO2 and a decrease in blood pH. This is typically associated with conditions that impair ventilation.
B. Metabolic Alkalosis:
Explanation: Metabolic alkalosis is characterized by an elevated blood pH and bicarbonate (HCO3-) concentration. It is not directly caused by hyperventilation but is often associated with conditions such as excessive vomiting or excessive bicarbonate intake.
C. Metabolic Acidosis:
Explanation: Metabolic acidosis is characterized by a decrease in blood pH and bicarbonate concentration. It is not directly caused by hyperventilation but may result from conditions such as diabetic ketoacidosis or lactic acidosis.
D. Respiratory Alkalosis:
Explanation: Hyperventilation is the most common cause of respiratory alkalosis. During hyperventilation, there is an excessive loss of carbon dioxide (CO2) through rapid breathing, leading to a decrease in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2) in the blood. This results in an increase in blood pH, causing an alkalotic state.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. 30 minute onset; 2-hour duration: This does not accurately represent the onset and peak action time of Insulin Lispro.
B. 15 minute onset; 30-60 minutes peak: This is correct. Insulin Lispro has a rapid onset (starts working within 15 minutes) and a peak action time of 30-60 minutes after administration.
C. 2-hour onset; 12-hour duration: This is not accurate for rapid-acting insulin. Rapid-acting insulin has a much quicker onset and shorter duration compared to this option.
D. 15 minute onset; no peak (continuous): While the onset time is correct, stating "no peak" is not entirely accurate. Rapid-acting insulin does have a peak, but it's relatively short, occurring within the first hour after administration.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
