The nurse is monitoring a client who was diagnosed with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and is being treated with NPH and regular insulin. Which manifestations alert the nurse to the presence of a possible hypoglycemic reaction? (SELECT ALL THAT APPLY)
Nervousness
Tremors
Irritability
Anorexia
Hot, dry skin
Muscle cramps
Correct Answer : A,B,C
A. Nervousness:
Explanation: Correct. Nervousness is a common symptom of hypoglycemia.
B. Tremors:
Explanation: Correct. Tremors or shakiness can occur with hypoglycemia.
C. Irritability:
Explanation: Correct. Irritability is one of the signs of hypoglycemia.
D. Anorexia:
Explanation: Anorexia or loss of appetite is a possible symptom of hypoglycemia but not as commonly observed as other symptoms.
E. Hot, dry skin:
Explanation: Hot, dry skin is not typically associated with hypoglycemia. Diaphoresis or sweating is more common.
F. Muscle cramps:
Explanation: Muscle cramps are not typical symptoms of hypoglycemia.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Increase the intake of vitamin E to enhance absorption:
While vitamin C can enhance iron absorption, vitamin E does not play a significant role in iron absorption. Vitamin C-rich foods can be advised to enhance iron absorption.
B. Iron will cause the stools to darken in color:
This statement is accurate. Iron supplements can cause stools to appear darker in color, often black or greenish-black. This change in stool color is normal and expected when taking iron supplements.
C. Take the iron with dairy products to enhance absorption:
Dairy products can inhibit iron absorption. It's better to take iron supplements with vitamin C-rich foods or orange juice to enhance absorption.
D. Limit foods high in fiber due to the risk for diarrhea:
Fiber-rich foods do not necessarily need to be limited when taking iron supplements. However, some individuals may experience constipation when taking iron supplements, in which case increasing fluid intake and dietary fiber can help alleviate constipation.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
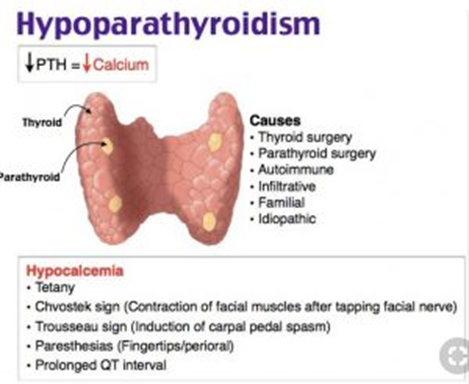
A. "The parathyroid has no effect on calcium levels in the body; this will just help prevent osteoporosis":
Explanation: This statement is incorrect. The parathyroid gland plays a crucial role in calcium homeostasis. Hypoparathyroidism, characterized by decreased parathyroid hormone (PTH) production, leads to low blood calcium levels, not high levels.
B. "The reason you have hypoparathyroidism is that you were diagnosed with hypothyroidism, and when the thyroid doesn't work, neither does the parathyroid, so you need these supplements."
Explanation: This statement is incorrect. The parathyroid and thyroid are separate glands with distinct functions. Hypoparathyroidism is not a result of hypothyroidism.
C. "A decrease in parathyroid hormone causes low calcium levels, so your body to break down bones to maintain normal calcium levels, and this will prevent that from happening."
Explanation: This is the correct statement. Hypoparathyroidism leads to a decrease in PTH, resulting in low blood calcium levels. Without sufficient PTH, the body may resort to breaking down bones to maintain calcium levels.
D. "An increase in parathyroid hormone causes your body to move calcium into the cells to reduce blood calcium levels, so you have to replace the levels in the blood."
Explanation: This statement is incorrect. An increase in parathyroid hormone (PTH) typically leads to increased blood calcium levels by promoting the release of calcium from bones and reducing calcium excretion by the kidneys. This describes hyperparathyroidism, not hypoparathyroidism.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
