A client is being treated on the medical unit for a sickle cell crisis. The nurse's most recent assessment reveals an oral temperature of 100.5°F and a new onset of fine crackles on lung auscultation. What is the nurse's most appropriate action?
Liaise with the respiratory therapist and consider high flow oxygen.
Inform the primary care provider that the patient may have an infection.
Apply supplementary oxygen by nasal cannula.
Administer bronchodilators by nebulizer.
The Correct Answer is B
A. Inform the primary care provider that the patient may have an infection:
Explanation: The presence of an elevated oral temperature and new onset of fine crackles on lung auscultation suggests a potential respiratory infection, which is a significant concern in a patient with sickle cell disease. Notifying the primary care provider allows for further evaluation and appropriate management of the infection.
B. Liaise with the respiratory therapist and consider high-flow oxygen:
Explanation: While oxygenation may be necessary, especially if the patient is experiencing respiratory distress, addressing the potential infection is the priority. Consulting with the respiratory therapist and considering high-flow oxygen can be part of the overall plan based on the primary care provider's recommendations.
C. Apply supplementary oxygen by nasal cannula:
Explanation: Providing oxygen support may be necessary, but it should be done in consultation with the primary care provider, who can guide the appropriate level of oxygen therapy based on the patient's condition.
D. Administer bronchodilators by nebulizer:
Explanation: Bronchodilators are typically used for conditions like asthma or COPD, and their use might not be the primary intervention in the context of a sickle cell crisis with signs of a potential respiratory infection. Addressing the infection takes precedence, and the primary care provider's input is essential in determining the appropriate course of action.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Leukemia:
Explanation: Leukemia is a cancer of the blood-forming tissues, including the bone marrow and lymphatic system. It typically presents with an abnormal increase in white blood cells. While fatigue can be a symptom, increased bilirubin concentration and an increased reticulocyte count are not typical findings in leukemia.
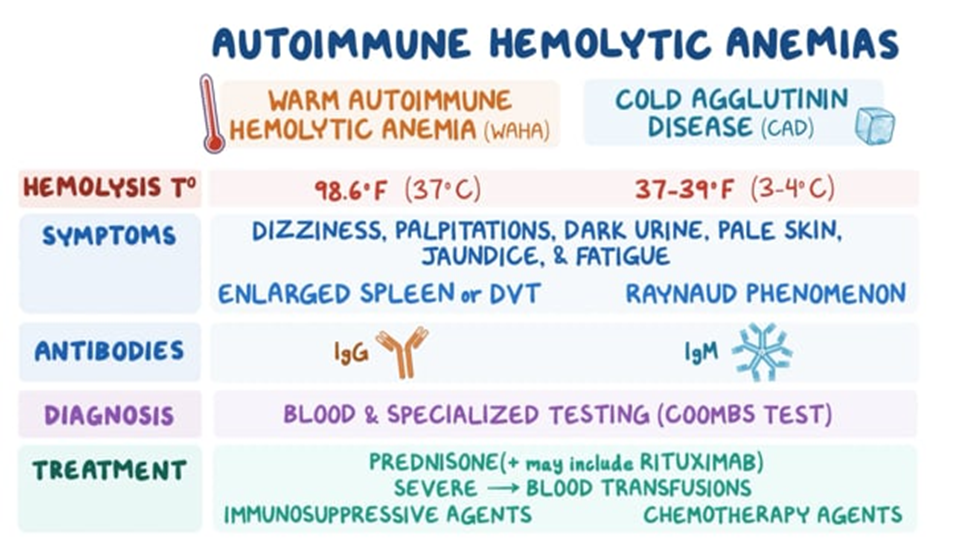
B. Hemolytic Anemia:
Explanation: Hemolytic anemia is characterized by the premature destruction of red blood cells, leading to an increased release of bilirubin (from the breakdown of hemoglobin) and an increased reticulocyte count (as the body attempts to compensate by producing more red blood cells). This is a likely possibility given the presented symptoms.
C. Hypoproliferative Anemia:
Explanation: Hypoproliferative anemia is characterized by a decreased production of red blood cells. It is unlikely in this scenario, as an increased reticulocyte count suggests an attempt by the bone marrow to increase red blood cell production.
D. Thrombocytopenia:
Explanation: Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by a low platelet count. It does not typically present with an increased bilirubin concentration or an increased reticulocyte count.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Management of diabetic ketoacidosis:
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a severe complication of diabetes characterized by high blood sugar, ketones in the urine, and metabolic acidosis. While it's crucial to understand how to manage DKA, this may be considered more advanced knowledge and may not be categorized as a basic survival skill for someone newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes.
B. Signs and symptoms of diabetic neuropathy:
Diabetic neuropathy is a long-term complication that involves damage to the nerves due to prolonged high blood sugar levels. While understanding neuropathy is important for long-term health, it may not be the first topic addressed as a basic survival skill for someone newly diagnosed.
C. Effects of surgery and pregnancy on blood sugar levels:
Understanding how surgery and pregnancy can affect blood sugar levels is important for managing diabetes in specific situations. However, this knowledge might be considered more advanced and may not be the initial focus for someone just starting to learn about diabetes self-care.
D. Recognition of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia:
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of both low and high blood sugar is essential for immediate self-care. This includes understanding when blood sugar is too low (hypoglycemia) and requires prompt treatment, as well as recognizing the symptoms of high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) and knowing how to address them. This knowledge is fundamental for the daily management and well-being of someone with diabetes.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
