med Surg Nursing 102 Exam 4
ATI med Surg Nursing 102 Exam 4
Total Questions : 52
Showing 10 questions Sign up for moreA nurse is assessing a client who is experiencing hypervolemia. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is not a correct finding for hypervolemia. Hypotension is a low blood pressure, which can be caused by hypovolemia (low blood volume) or other factors. Hypervolemia is an excess of fluid in the body, which can increase the blood pressure.
Choice B reason: This is not a correct finding for hypervolemia. Bradycardia is a slow heart rate, which can be caused by heart block, medication, or other factors. Hypervolemia can cause tachycardia (fast heart rate) as the heart tries to pump the excess fluid.
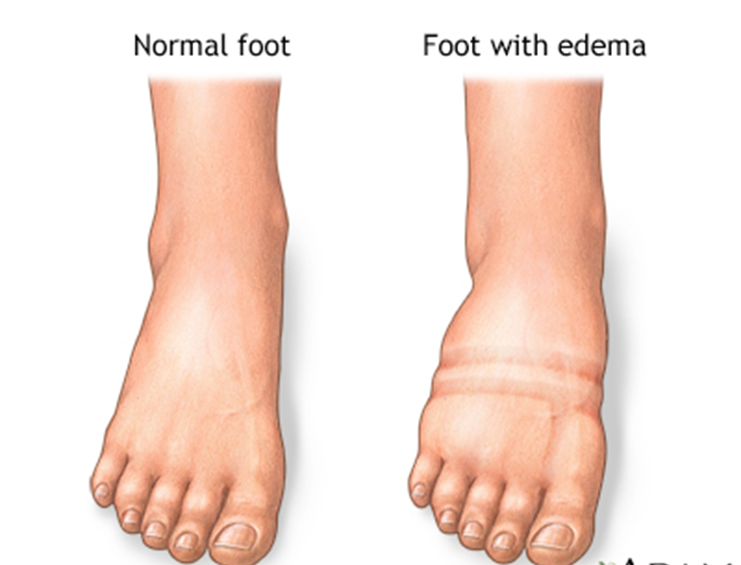
Choice C reason: This is a correct finding for hypervolemia. Peripheral edema is a swelling of the extremities due to fluid accumulation in the tissues. Hypervolemia can cause peripheral edema as the fluid leaks from the blood vessels into the interstitial spaces.
Choice D reason: This is not a correct finding for hypervolemia. Weight loss is a decrease in body weight, which can be caused by dehydration, malnutrition, or other factors. Hypervolemia can cause weight gain as the body retains more fluid.
A nurse is assessing a client who has an obstruction of the common bile duct resulting from chronic cholelithiasis. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is a correct finding for a client with an obstruction of the common bile duct. Fatty stools are caused by the reduced or absent flow of bile into the intestine, which impairs the digestion and absorption of fats.
Choice B reason: This is not a correct finding for a client with an obstruction of the common bile duct. Tenderness in the left upper abdomen may indicate a problem with the spleen, the stomach, or the pancreas, but not the bile duct.
Choice C reason: This is not a correct finding for a client with an obstruction of the common bile duct. Ecchymosis of the extremities is a bruising of the skin due to bleeding under the surface. It may be caused by trauma, medication, or bleeding disorders, but not by bile duct obstruction.
Choice D reason: This is not a correct finding for a client with an obstruction of the common bile duct. Pale-colored urine is a sign of dilute or low concentration of urine, which may be caused by excessive fluid intake, diabetes insipidus, or kidney failure, but not by bile duct obstruction.
A nurse is assessing a client with suspected fluid volume overload. Which finding requires further action?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Pyuria, or pus in the urine, is not a direct sign of fluid volume overload. It may indicate a urinary tract infection, kidney stones, or other renal problems.
Choice B reason: Weight loss is not a typical finding of fluid volume overload. In fact, weight gain is a common symptom of fluid retention, as the body holds more fluid than it excretes.
Choice C reason: Jugular vein distention, or the bulging of the neck veins, is a serious indicator of fluid volume overload. It reflects increased pressure in the right side of the heart and the systemic circulation. It may also signal heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, or pericardial tamponade.
Choice D reason: Muscle contractions are not directly related to fluid volume overload. They may be caused by electrolyte imbalances, dehydration, muscle fatigue, or nerve disorders.
A client with ongoing back pain, nausea, and abdominal bloating has been diagnosed with cholecystitis secondary to gallstones. The nurse should anticipate that the client will undergo which preferred treatment?
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is not a correct answer because intracorporeal lithotripsy is a procedure that uses a laser or an ultrasonic probe to break up gallstones inside the gallbladder or the bile ducts. It is not a preferred treatment for cholecystitis, as it does not remove the inflamed gallbladder.
Choice B reason: This is a correct answer because laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a surgery that removes the gallbladder through small incisions in the abdomen. It is the preferred treatment for cholecystitis, as it eliminates the source of inflammation and prevents further complications.
Choice C reason: This is not a correct answer because extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) is a procedure that uses shock waves to break up gallstones outside the body. It is not a preferred treatment for cholecystitis, as it does not remove the inflamed gallbladder and may not be effective for all types of gallstones.
Choice D reason: This is not a correct answer because methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE) infusion is a procedure that uses a chemical solvent to dissolve gallstones inside the gallbladder. It is not a preferred treatment for cholecystitis, as it does not remove the inflamed gallbladder and may cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and liver damage.
A nurse is discussing early signs of hypervolemia with a patient admitted with congestive heart failure. Which signs should the nurse include in their teaching?
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is not a correct sign of hypervolemia. Increased thirst and dry mucous membranes are signs of dehydration or fluid volume deficit, which can occur due to excessive fluid loss or inadequate fluid intake.
Choice B reason: This is not a correct sign of hypervolemia. Low blood pressure and increased heart rate are signs of hypovolemic shock, which can occur due to severe fluid loss or hemorrhage.
Choice C reason: This is a correct sign of hypervolemia. Difficulty breathing and weight gain are signs of fluid overload, which can occur due to excessive fluid retention or impaired cardiac function. Difficulty breathing can be caused by pulmonary edema, which is the accumulation of fluid in the lungs. Weight gain can be caused by the increase in total body fluid.
Choice D reason: This is not a correct sign of hypervolemia. Dry cough and poor skin turgor are signs of dehydration or fluid volume deficit, which can occur due to excessive fluid loss or inadequate fluid intake.
The nurse is providing discharge instructions for a slightly overweight client seen in the Emergency Department with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Which instruction should the nurse give for management of this disease process?
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is not a correct instruction because drinking a carbonated beverage before bed can worsen the reflux symptoms by increasing the gastric pressure and the production of gas.
Choice B reason: This is not a correct instruction because increasing fatty foods can worsen the reflux symptoms by delaying the gastric emptying and relaxing the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which allows the stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus.
Choice C reason: This is a correct instruction because elevating the head of the bed when sleeping can help prevent the reflux symptoms by using gravity to keep the stomach contents from flowing back into the esophagus.
Choice D reason: This is not a correct instruction because eating dinner late in the evening can worsen the reflux symptoms by increasing the amount and acidity of the stomach contents, which can easily flow back into the esophagus when lying down. The client should avoid eating within 3 hours of bedtime.
A nurse is caring for a child who has acute appendicitis. Which of the following results should the nurse anticipate when reviewing this client's laboratory values?
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is not a correct result that the nurse should anticipate. RBC stands for red blood cells, which carry oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. The normal range for RBC is 4-5.5 /mm^3^, so a value of 4.2 /mm^3^ is within the normal range and does not indicate any abnormality.
Choice B reason: This is a correct result that the nurse should anticipate. WBC stands for white blood cells, which fight infections and inflammation in the body. The normal range for WBC is 5-10 /mm^3^, so a value of 17 /mm^3^ is above the normal range and indicates leukocytosis, which is an increase in the number of white blood cells. Leukocytosis can be caused by acute appendicitis, as the body tries to fight the infection and inflammation in the appendix.
Choice C reason: This is not a correct result that the nurse should anticipate. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell that are the first to respond to bacterial infections. The normal range for neutrophils is 3-5.8 /mm^3^, so a value of 3.2 /mm^3^ is within the normal range and does not indicate any abnormality.
Choice D reason: This is not a correct result that the nurse should anticipate. Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that are involved in the immune response and the production of antibodies. The normal range for lymphocytes is 1-4 /mm^3^, so a value of 3 /mm^3^ is within the normal range and does not indicate any abnormality.
A nurse is to administer a hypotonic solution to a patient with a critically high sodium. Which solution is hypotonic?
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is not a correct answer because 0.9% Sodium Chloride is an isotonic solution, which means it has the same osmolarity as the blood plasma. It does not cause any fluid shifts between the intracellular and extracellular compartments.
Choice B reason: This is not a correct answer because Lactated Ringer's is an isotonic solution, which means it has the same osmolarity as the blood plasma. It does not cause any fluid shifts between the intracellular and extracellular compartments.
Choice C reason: This is not a correct answer because D5W (5% Dextrose in Water) is an isotonic solution when it is in the IV bag, but it becomes hypotonic once it enters the body, as the dextrose is rapidly metabolized and only water remains. However, it is not a preferred solution for a patient with critically high sodium, as it can cause cerebral edema and worsen the neurological status.
Choice D reason: This is a correct answer because 0.45% Sodium Chloride is a hypotonic solution, which means it has a lower osmolarity than the blood plasma. It causes fluid to shift from the extracellular to the intracellular compartment, which can help lower the sodium level and correct the fluid imbalance.
A severely dehydrated client has come in for rapid administration of IV fluids. Which of the following solutions is the best solution for rapid infusion?
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is a correct answer because normal saline is an isotonic solution, which means it has the same osmolarity as the blood plasma. It does not cause any fluid shifts between the intracellular and extracellular compartments, and it can help restore the fluid balance and the blood pressure of the dehydrated client.
Choice B reason: This is not a correct answer because 1/2 normal saline is a hypotonic solution, which means it has a lower osmolarity than the blood plasma. It causes fluid to shift from the extracellular to the intracellular compartment, which can lead to cellular swelling and edema. It is not suitable for rapid infusion, as it can cause hemolysis and hypotension.
Choice C reason: This is not a correct answer because D5W (5% Dextrose in Water) is an isotonic solution when it is in the IV bag, but it becomes hypotonic once it enters the body, as the dextrose is rapidly metabolized and only water remains. It causes fluid to shift from the extracellular to the intracellular compartment, which can lead to cellular swelling and edema. It is not suitable for rapid infusion, as it can cause hemolysis and hypotension.
Choice D reason: This is not a correct answer because D5 1/2 normal saline is a hypertonic solution, which means it has a higher osmolarity than the blood plasma. It causes fluid to shift from the intracellular to the extracellular compartment, which can lead to cellular shrinkage and dehydration. It is not suitable for rapid infusion, as it can cause hypernatremia and fluid overload.
A client with a peptic ulcer is diagnosed with Helicobacter pylori infection. The nurse is teaching the client about the medications prescribed, including two antibiotics metronidazole and clarithromycin and a PPI omeprazole. Which statement by the client indicates the best understanding of the medication regimen?
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is not a correct statement because these medications do not coat the ulcer. They are not antacids or mucosal protectants, which can form a protective layer over the ulcer and neutralize the stomach acid.
Choice B reason: This is not a correct statement because these medications do not stop the acid production. They only reduce it by inhibiting the proton pump, which is responsible for secreting acid into the stomach.
Choice C reason: This is not a correct statement because these medications should be taken as prescribed, not as needed. They are not analgesics or anti-inflammatory drugs, which can relieve the pain and inflammation of the ulcer.
Choice D reason: This is a correct statement because these medications have two effects: they kill the bacteria that cause the infection and inflammation of the ulcer, and they reduce the acid production that aggravates the ulcer. This can help heal the ulcer and prevent complications.
You just viewed 10 questions out of the 52 questions on the ATI med Surg Nursing 102 Exam 4 Exam. Subscribe to our Premium Package to obtain access on all the questions and have unlimited access on all Exams. Subscribe Now



