The nurse is providing discharge instructions for a slightly overweight client seen in the Emergency Department with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Which instruction should the nurse give for management of this disease process?
Drink a carbonated beverage before bed
Increase fatty foods one at a time
Elevate the head of the bed when sleeping
Eat dinner late in the evening
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A reason: This is not a correct instruction because drinking a carbonated beverage before bed can worsen the reflux symptoms by increasing the gastric pressure and the production of gas.
Choice B reason: This is not a correct instruction because increasing fatty foods can worsen the reflux symptoms by delaying the gastric emptying and relaxing the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which allows the stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus.
Choice C reason: This is a correct instruction because elevating the head of the bed when sleeping can help prevent the reflux symptoms by using gravity to keep the stomach contents from flowing back into the esophagus.
Choice D reason: This is not a correct instruction because eating dinner late in the evening can worsen the reflux symptoms by increasing the amount and acidity of the stomach contents, which can easily flow back into the esophagus when lying down. The client should avoid eating within 3 hours of bedtime.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["A","B","D"]
Explanation
Choice A reason: Oily stools are common, especially when excessive fat is consumed, because orlistat blocks the absorption of fat in the intestines. The undigested fat is then eliminated in the stool, making it oily, greasy, or foul-smelling.
Choice B reason: Many patients note having an increase of gas and flatus, because orlistat can also interfere with the digestion of carbohydrates and proteins, causing fermentation and gas production in the colon.
Choice C reason: Constipation is not a common side effect with this medication. In fact, orlistat may cause the opposite effect of diarrhea, as the unabsorbed fat can irritate the bowel and increase the motility.
Choice D reason: Some patients report the development of fecal incontinence, because orlistat can cause unpredictable bowel movements and difficulty in controlling the passage of stool, especially if the patient consumes a high-fat diet.
Choice E reason: This medication does have side effects, even though it can be bought over the counter. Orlistat is a prescription-strength drug that can cause serious adverse reactions, such as liver damage, kidney stones, gallbladder problems, and vitamin deficiencies. The over-the-counter version is a lower dose than the prescription one, but it still requires medical supervision and lifestyle changes.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
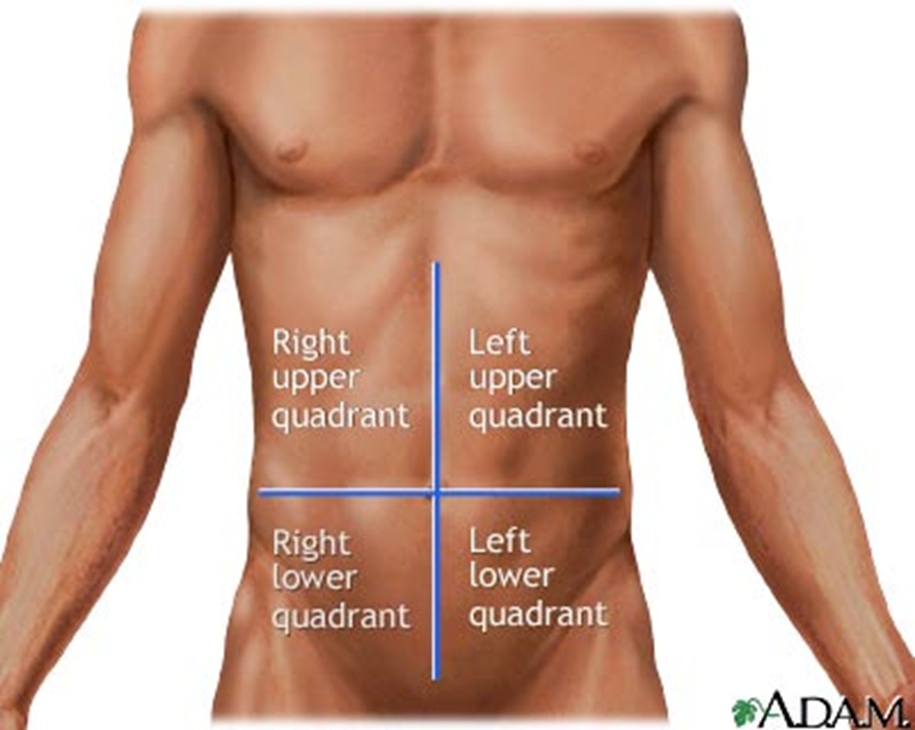
Choice A reason: The upper right quadrant is not the correct location for McBurney's point. This quadrant contains the liver, gallbladder, right kidney, and part of the colon. Pain in this area may indicate problems with these organs, such as hepatitis, gallstones, or kidney infection.
Choice B reason: The upper left quadrant is not the correct location for McBurney's point. This quadrant contains the stomach, spleen, left kidney, and part of the colon. Pain in this area may indicate problems with these organs, such as gastritis, splenomegaly, or kidney stones.
Choice C reason: The lower right quadrant is the correct location for McBurney's point. This quadrant contains the appendix, right ovary, and right fallopian tube. McBurney's point is a point on the abdomen that is one-third of the distance from the right anterior superior iliac spine to the umbilicus. Pain in this area may indicate appendicitis, ovarian cyst, or ectopic pregnancy.
Choice D reason: The lower left quadrant is not the correct location for McBurney's point. This quadrant contains the sigmoid colon, left ovary, and left fallopian tube. Pain in this area may indicate problems with these organs, such as diverticulitis, ovarian torsion, or pelvic inflammatory disease.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
