A client with ongoing back pain, nausea, and abdominal bloating has been diagnosed with cholecystitis secondary to gallstones. The nurse should anticipate that the client will undergo which preferred treatment?
Intracorporeal lithotripsy
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL)
Methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE) infusion
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A reason: This is not a correct answer because intracorporeal lithotripsy is a procedure that uses a laser or an ultrasonic probe to break up gallstones inside the gallbladder or the bile ducts. It is not a preferred treatment for cholecystitis, as it does not remove the inflamed gallbladder.
Choice B reason: This is a correct answer because laparoscopic cholecystectomy is a surgery that removes the gallbladder through small incisions in the abdomen. It is the preferred treatment for cholecystitis, as it eliminates the source of inflammation and prevents further complications.
Choice C reason: This is not a correct answer because extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) is a procedure that uses shock waves to break up gallstones outside the body. It is not a preferred treatment for cholecystitis, as it does not remove the inflamed gallbladder and may not be effective for all types of gallstones.
Choice D reason: This is not a correct answer because methyl tertiary butyl ether (MTBE) infusion is a procedure that uses a chemical solvent to dissolve gallstones inside the gallbladder. It is not a preferred treatment for cholecystitis, as it does not remove the inflamed gallbladder and may cause side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and liver damage.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason: Ulcerative colitis is not a complication of diverticulitis. Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that causes ulcers and inflammation in the colon and rectum. Diverticulitis is an acute condition that occurs when small pouches called diverticula in the colon become infected or inflamed.
Choice B reason: Dysphagia is not a complication of diverticulitis. Dysphagia is a term for difficulty swallowing, which can have many causes, such as stroke, nerve damage, or esophageal cancer. Diverticulitis affects the lower part of the digestive tract, not the upper part.
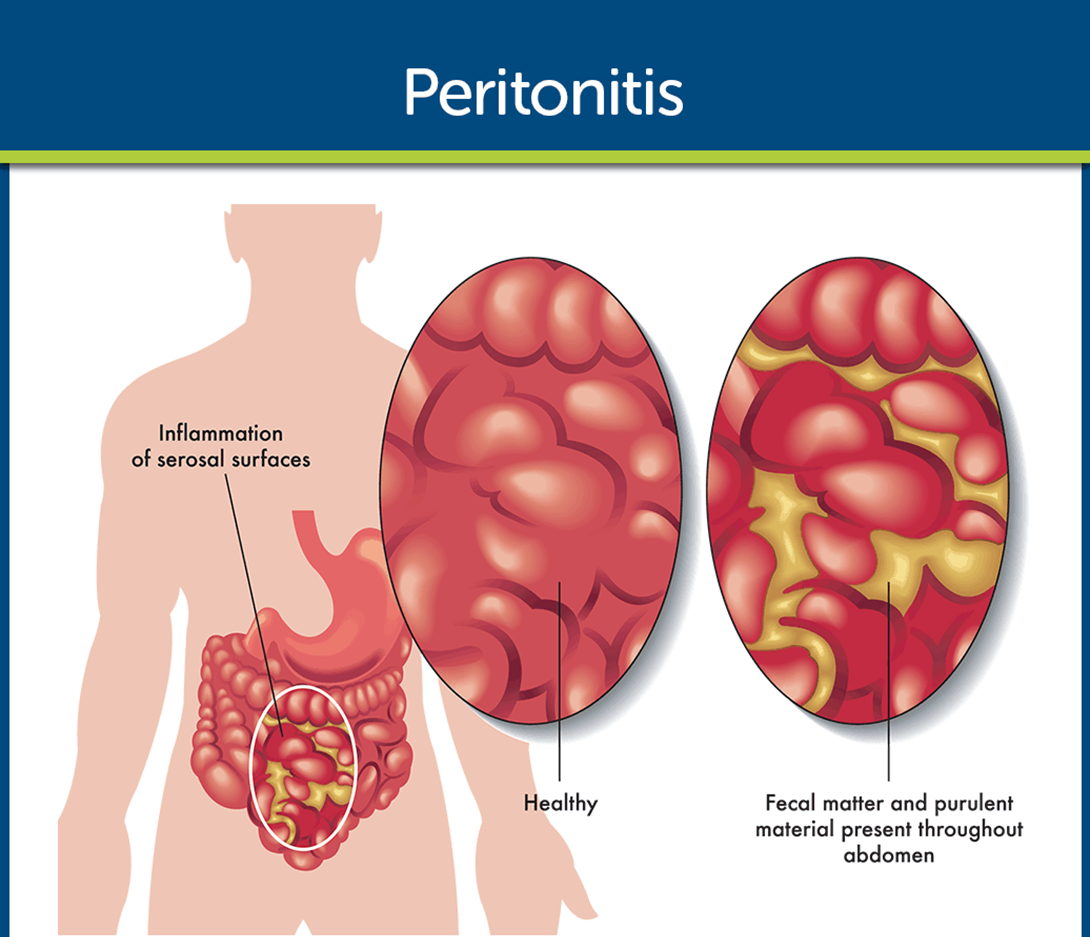
Choice C reason: Peritonitis is a complication of diverticulitis. Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, the membrane that lines the abdominal cavity. It can be caused by a perforation or rupture of a diverticulum, which allows bacteria and fecal matter to enter the peritoneal space. Peritonitis is a serious and life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Choice D reason: Crohn's disease is not a complication of diverticulitis. Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease that can affect any part of the digestive tract, causing ulcers, fistulas, and strictures. Diverticulitis is an acute condition that affects only the colon, not the entire digestive tract.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is a correct answer because normal saline is an isotonic solution, which means it has the same osmolarity as the blood plasma. It does not cause any fluid shifts between the intracellular and extracellular compartments, and it can help restore the fluid balance and the blood pressure of the dehydrated client.
Choice B reason: This is not a correct answer because 1/2 normal saline is a hypotonic solution, which means it has a lower osmolarity than the blood plasma. It causes fluid to shift from the extracellular to the intracellular compartment, which can lead to cellular swelling and edema. It is not suitable for rapid infusion, as it can cause hemolysis and hypotension.
Choice C reason: This is not a correct answer because D5W (5% Dextrose in Water) is an isotonic solution when it is in the IV bag, but it becomes hypotonic once it enters the body, as the dextrose is rapidly metabolized and only water remains. It causes fluid to shift from the extracellular to the intracellular compartment, which can lead to cellular swelling and edema. It is not suitable for rapid infusion, as it can cause hemolysis and hypotension.
Choice D reason: This is not a correct answer because D5 1/2 normal saline is a hypertonic solution, which means it has a higher osmolarity than the blood plasma. It causes fluid to shift from the intracellular to the extracellular compartment, which can lead to cellular shrinkage and dehydration. It is not suitable for rapid infusion, as it can cause hypernatremia and fluid overload.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
