Hesi Med Surg Exam 1
Hesi Med Surg Exam 1
Total Questions : 53
Showing 10 questions Sign up for moreA client with a seizure disorder is seen at the clinic for a follow-up visit and a prescription renewal for phenytoin. Which assessment finding warrants immediate intervention by the nurse?
Explanation
C. Double vision.Double vision, or diplopia, can indicatephenytoin toxicity, which is a serious condition that may lead to impaired vision and increased risk of falls or injuries. This side effect suggests that the patient may be experiencing adverse reactions to the medication, necessitating prompt evaluation and intervention, such as checking serum phenytoin levels and possibly adjusting the medication regimen
.The other options do not require immediate intervention:
- A. Chronic insomniais not a critical side effect of phenytoin and may be managed with lifestyle modifications or further assessment.
- B. Puffy, bleeding gumsare common side effects associated with phenytoin (gingival hyperplasia) but are not immediately life-threatening.
- D. Blood pressure 100/78 mm Hgis within normal limits and does not indicate a need for urgent action
A young adult client with osteoarthritis of both knees expresses the desire to continue daily walks in the park with friends. How should the nurse respond?
Explanation
Choice A rationale
Encouraging the client to continue their walking routine is a supportive and positive response. This acknowledges the client’s desire to stay active and engage in activities they enjoy despite their osteoarthritis. It promotes a sense of empowerment and independence, which can be important for overall well-being.
Choice B rationale
Advising less weight-bearing to prevent joint destruction may seem logical, but it is not the best advice. Regular exercise, including walking, can actually help manage osteoarthritis by strengthening the muscles around the joints, improving flexibility, and reducing pain.
Choice C rationale
Recommending walking indoors for improved stability and safety might be helpful in some cases, but it is not necessarily the best response. The client has expressed a desire to continue walking in the park with friends, which also has social and mental health benefits.
Choice D rationale
Suggesting a calcium supplement along with continued walking is not the best advice. While calcium is important for bone health, osteoarthritis is not caused by a lack of calcium. It’s a degenerative joint disease that involves the breakdown of cartilage in the joints.
The nurse is preparing a client for surgery who was admitted to the emergency center following a motor vehicle collision.
The client has a fracture of the femur and is bleeding at the bone protrusion site.
During the preoperative assessment, the nurse determines that the client currently receives heparin subcutaneously daily.
Which is the priority nursing action?
Explanation
Notifying the healthcare provider of the client’s medication history is the priority nursing action. Heparin is an anticoagulant, which increases the risk of bleeding. The healthcare provider needs this information to make appropriate decisions about the client’s surgical plan and postoperative care.
A client experiences an ABO incompatibility reaction after multiple blood transfusions. Which finding should the nurse report immediately to the healthcare provider?
Explanation
Lower back pain and hypotension are symptoms of an ABO incompatibility reaction, which is a serious complication of blood transfusion. This reaction occurs when the client receives a blood type that is incompatible with their own. It can cause a rapid and severe response, including back pain, hypotension, fever, and chills. This should be reported immediately to the healthcare provider.
A client experiences an ABO incompatibility reaction after multiple blood transfusions. Which finding should the nurse report immediately to the healthcare provider?
Explanation
Choice A rationale
An ABO incompatibility reaction can occur if a patient receives the wrong type of blood during a blood transfusion. Symptoms of an ABO incompatibility reaction include lower back pain and hypotension, which are serious and should be reported immediately to the healthcare provider.
Choice B rationale
A delayed painful rash with urticaria is not typically a symptom of an ABO incompatibility reaction. While it could indicate an allergic reaction, it is not as immediate or potentially life-threatening as the symptoms in Choice A1.
Choice C rationale
Acute rhinitis and nasal stuffiness are more commonly associated with respiratory infections, not ABO incompatibility reactions. These symptoms are not typically a direct result of a blood transfusion.
Choice D rationale
Arthritic joint changes and chronic pain are not associated with ABO incompatibility reactions. These symptoms are more likely related to long-term conditions like arthritis.
The nurse is caring for a client admitted to the hospital with a tentative diagnosis of bacterial meningitis. Which diagnostic procedure should the nurse prepare the client for the healthcare provider?
Explanation
Choice A rationale
A lumbar puncture is a key diagnostic procedure for suspected bacterial meningitis. It allows for the collection of cerebrospinal fluid, which can be analyzed for signs of bacterial infection.
Choice B rationale
Skull radiography is not typically used to diagnose bacterial meningitis. While it can help identify abnormalities in the structure of the skull or brain, it cannot detect the presence of bacteria.
Choice C rationale
While an MRI can provide detailed images of the brain and surrounding tissues, it is not the primary tool for diagnosing bacterial meningitis. It may be used in conjunction with other tests, but a lumbar puncture is more definitive.
Choice D rationale
A CT scan can be used to detect abnormalities in the brain, such as swelling or inflammation, which could be indicative of meningitis. However, it cannot definitively diagnose bacterial meningitis.
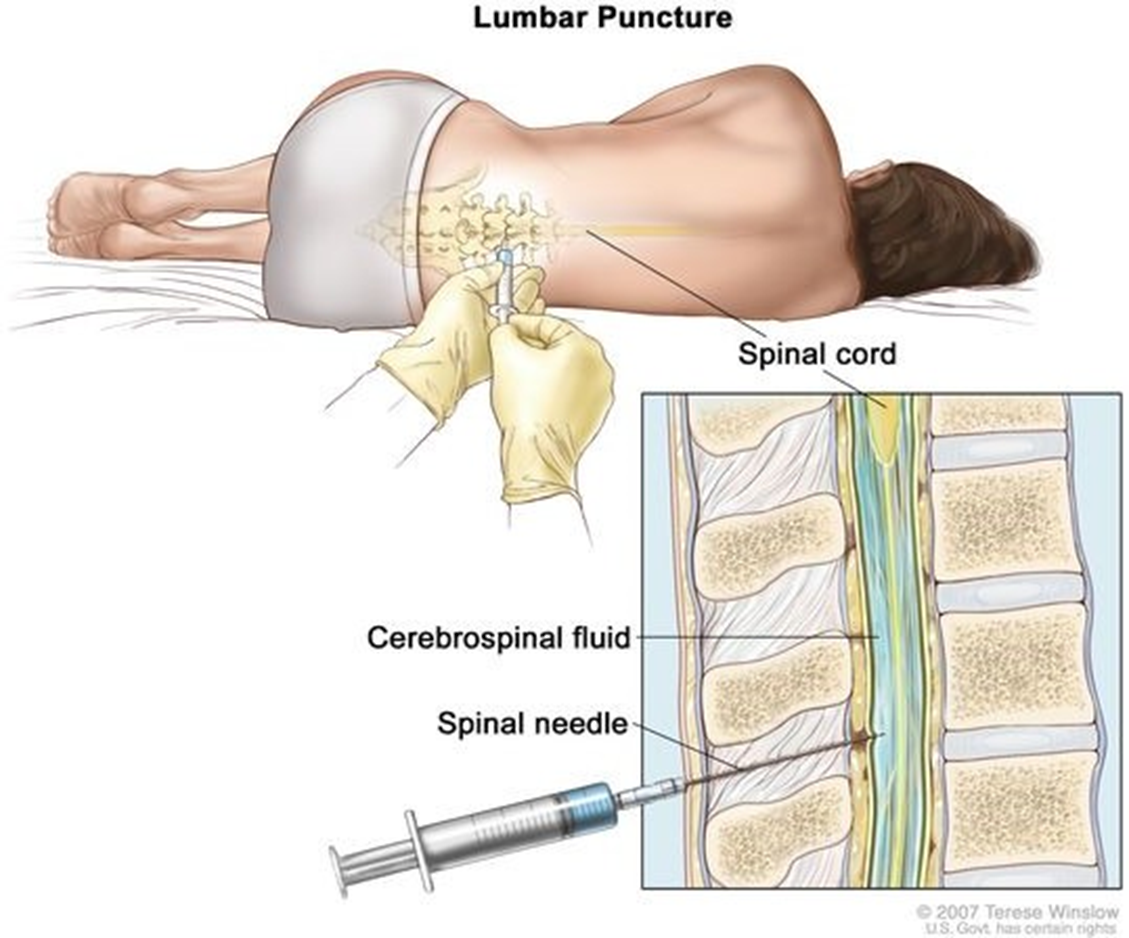
A nurse is caring for a patient who has been admitted to the hospital with a suspected diagnosis of bacterial meningitis. Which diagnostic procedure should the nurse prepare the patient for?
Explanation
Choice A rationale
As with, a lumbar puncture is the primary diagnostic procedure for suspected bacterial meningitis. The other choices, while useful for detecting other conditions, are not as definitive for diagnosing bacterial meningitis.
Choice B rationale
As mentioned in the rationale for, Choice B, skull radiography is not typically used to diagnose bacterial meningitis.
Choice C rationale
As mentioned in the rationale for, Choice C, an MRI can provide detailed images of the brain and surrounding tissues, but it is not the primary tool for diagnosing bacterial meningitis.
Choice D rationale
As mentioned in the rationale for, Choice D, a CT scan can detect abnormalities in the brain, but it cannot definitively diagnose bacterial meningitis.
A nurse is educating a patient with Type 2 diabetes mellitus and peripheral neuropathy. What advice should the nurse give?
Explanation
Choice A rationale
While it’s important for patients with peripheral neuropathy to protect their feet, it’s recommended that they wear shoes at all times to prevent injury. Being barefoot, even inside the house, can increase the risk of foot injuries.
Choice B rationale
Regular foot exams are crucial for patients with peripheral neuropathy. Family members can assist with these exams, helping to identify any changes or injuries that may require medical attention.
Choice C rationale
Heating pads are not typically recommended for patients with peripheral neuropathy. Due to the loss of sensation in their feet, they may not realize if the pad is too hot, which could lead to burns.
Choice D rationale
Soaking feet in lukewarm water for extended periods is not typically recommended for patients with peripheral neuropathy. Prolonged exposure to water can dry out the skin and increase the risk of injury.
An overweight young adult diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus is admitted for a hernia repair.
The patient reports feeling very weak and jittery.
What actions should the nurse take? (Select all that apply)
Explanation
Choice A rationale
Checking the fingerstick glucose level is an immediate action that the nurse should take when a patient with type 2 diabetes reports feeling weak and jittery. These symptoms could indicate hypoglycemia, a condition characterized by low blood sugar levels.
Choice B rationale
Assessing skin temperature and moisture can help the nurse determine if the patient is sweating, a common symptom of hypoglycemia.
Choice C rationale
Administering a PRN dose of regular insulin is not the appropriate action if the patient is experiencing symptoms of hypoglycemia. Insulin would further lower the patient’s blood sugar levels, potentially worsening their condition.
Choice D rationale
Documenting anxiety on the surgical checklist may not be immediately helpful in addressing the patient’s current symptoms. While it’s important to document all relevant information, the nurse’s immediate focus should be on assessing and managing the patient’s symptoms.
Choice E rationale
Measuring pulse and blood pressure can provide important information about the patient’s cardiovascular status. Hypoglycemia can cause tachycardia and potentially hypotension, so these vital signs should be monitored.

The nurse is providing discharge teaching to an older adult patient hospitalized for treatment of venous leg ulcers. Which instructions should the nurse include in the teaching plan? (Select all that apply.)
Explanation
Choice A rationale
Eating a diet that is high in protein and vitamins A and C is beneficial for wound healing. Protein is essential for tissue repair, while vitamins A and C play a crucial role in collagen synthesis, which is vital for wound healing.
Choice B rationale
Maintaining bed rest as much as possible is not the best advice for a patient with venous leg ulcers. Mobility improves blood circulation, which can aid in the healing of the ulcers.
Choice C rationale
Keeping legs elevated when sitting or lying down can help reduce swelling and improve blood flow, which can promote healing of the ulcers.
Choice D rationale
Inspecting ankles daily for areas of darkening skin is important as it can help in early detection of any potential complications or worsening of the condition.
Choice E rationale
Applying intermittent cold compresses four times daily is not typically recommended for venous leg ulcers. The standard treatment involves cleaning and dressing the wound, using compression therapy, and in some cases, taking prescribed medications.
You just viewed 10 questions out of the 53 questions on the Hesi Med Surg Exam 1 Exam. Subscribe to our Premium Package to obtain access on all the questions and have unlimited access on all Exams. Subscribe Now



