Ati Med Surg n241 exam
Ati Med Surg n241 exam
Total Questions : 41
Showing 10 questions Sign up for moreWhich intervention is appropriate to include in the plan of care for a patient with Parkinson's disease?
Explanation
Choice A reason: A soft diet with thin liquids may be recommended for patients with Parkinson's disease who have difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), but it is not the most appropriate intervention for all patients. Dysphagia is common in Parkinson's disease due to impaired muscle movement, and a soft diet can help prevent choking and aspiration.
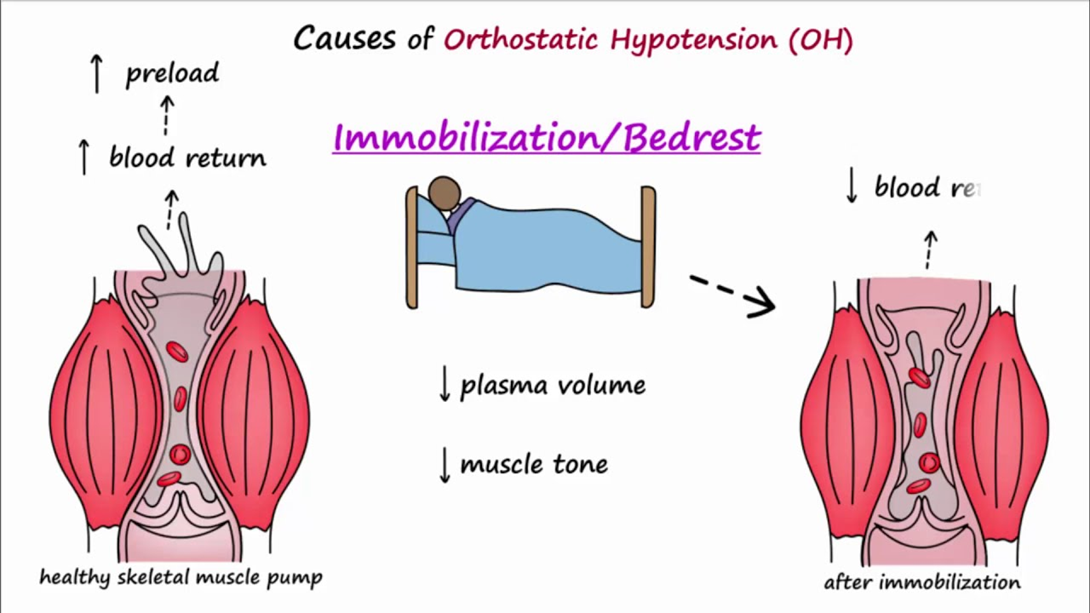
Choice B reason: Assessing for orthostatic hypotension is crucial in the care of patients with Parkinson's disease. Orthostatic hypotension is a common non-motor symptom where there is a significant drop in blood pressure upon standing. Normal blood pressure should not drop more than 20 mm Hg systolic or 10 mm Hg diastolic within 2 to 5 minutes of standing². This condition can increase the risk of falls, which is a significant concern in this population.
Choice C reason: Exophthalmos, the bulging of the eyes, is not associated with Parkinson's disease. It is typically related to thyroid eye disease, such as Graves' disease, and would not be a relevant assessment for a Parkinson's patient unless there is a known co-existing thyroid condition.
Choice D reason: Limiting fluids to prevent urinary incontinence is not an appropriate intervention for Parkinson's disease. Adequate hydration is essential, and urinary incontinence should be managed with other strategies, such as bladder training, scheduled toileting, and possibly medication, depending on the cause.
The nurse is assessing a client admitted for treatment of pneumonia and possible sepsis. Which information is most important for the nurse to report?
Explanation
Choice A reason: The serum lactate level of 3.9 mmol/L is significantly higher than the normal range of 0.5-2 mmol/L. This is a critical value to report as it indicates a high likelihood of sepsis, which is a life-threatening condition requiring immediate intervention. Elevated lactate levels suggest that the tissues are not adequately oxygenated, a state known as tissue hypoxia, which is a hallmark of sepsis.
Choice B reason: While the vital signs show a slight fever (100°F), the heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood pressure are within normal limits for an adult and do not indicate an immediate life-threatening condition.
Choice C reason: A pulse oximetry reading of 96% on supplemental oxygen is within the acceptable range, indicating adequate oxygen saturation and not a direct sign of sepsis.
Choice D reason: The presence of rhonchi bilaterally suggests airway obstruction due to mucus, which can be associated with pneumonia. However, this finding alone does not carry the same immediate risk of morbidity and mortality as an elevated lactate level indicative of sepsis.
The nurse is planning discharge teaching for a client with Parkinson's disease. What information regarding levodopa/carbidopa therapy should the nurse include in this session?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Levodopa/carbidopa therapy is often recommended to be taken with food to prevent nausea, which is a common side effect. Therefore, advising not to take it with food is incorrect.
Choice B reason: While levodopa/carbidopa can cause insomnia, it is not the most critical piece of information for discharge teaching. Managing insomnia can be part of ongoing treatment discussions.
Choice C reason: Checking for signs of infection is a general safety measure but is not specific to levodopa/carbidopa therapy. It is important for all medications and health conditions.
Choice D reason: It is crucial to take levodopa/carbidopa at the same time each day to maintain steady levels of the medication in the body, which helps to control the symptoms of Parkinson's disease effectively. Consistency in medication timing is key to managing the disease's symptoms.
The nurse caring for a client with thyroid disease notes a current T4 level of 2.9 mcg/dL (normal range: 5-11.5 mcg/dL). Which findings are consistent with this result?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Tachycardia and weight gain are not typically associated with low T4 levels. Tachycardia and weight loss are more commonly seen in hyperthyroidism, where T4 levels would be elevated.
Choice B reason: Diarrhea and hypoglycemia are not directly related to low T4 levels. Diarrhea can be a symptom of hyperthyroidism, while hypoglycemia is not commonly associated with thyroid function.
Choice C reason: Hypotension and periorbital edema are findings that can be associated with hypothyroidism, which is consistent with the low T4 level of 2.9 mcg/dL. Hypothyroidism can lead to reduced cardiac output and systemic vascular resistance, causing hypotension. Periorbital edema is also a common sign of hypothyroidism due to mucopolysaccharide deposition in the skin.
Choice D reason: Tremors and dyskinesias are more commonly associated with hyperthyroidism, not hypothyroidism. Elevated levels of thyroid hormones can lead to these neurological symptoms.
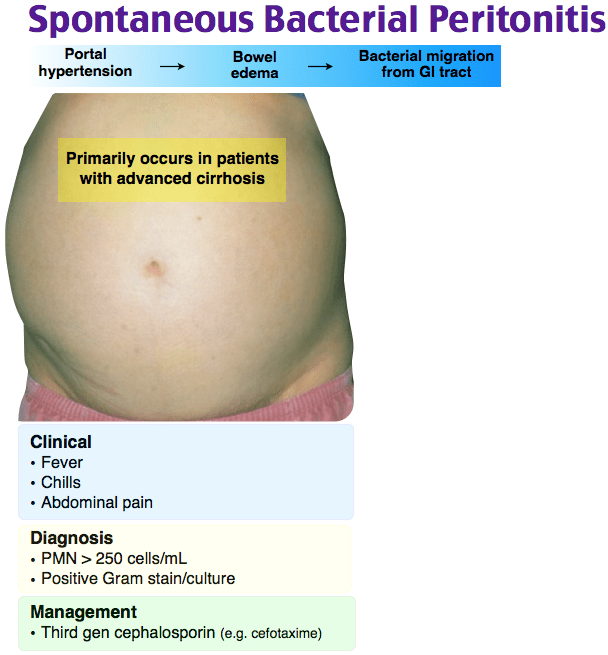
The client with cirrhosis has developed spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP). Which data indicates this complication of cirrhosis is occurring?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Petechiae are small red or purple spots caused by bleeding into the skin, typically associated with platelet disorders, and are not a direct indicator of SBP.
Choice B reason: Increased abdominal pain is a common symptom of SBP, as the condition causes inflammation and irritation of the peritoneum, which can lead to significant discomfort.
Choice C reason: Jaundice is a sign of liver dysfunction but is not specific to SBP. It results from high levels of bilirubin in the blood and can occur in various liver diseases.
Choice D reason: Blood in emesis (vomiting) may indicate gastrointestinal bleeding, which can be a complication of cirrhosis but is not specific to SBP.
The nurse recognizes that a patient with sepsis is at risk to develop hypotension. Which pathophysiological process is responsible for this symptom?
Explanation
Choice A reason: In sepsis, inflammatory mediators cause vasodilation and increased capillary permeability, leading to fluid leaking out of the vascular space, resulting in hypotension.
Choice B reason: Platelet aggregation and thrombus formation can occur in sepsis but are more related to disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) rather than directly causing hypotension.
Choice C reason: Decreased blood glucose and oliguria can be consequences of sepsis but are not the primary pathophysiological processes responsible for hypotension.
Choice D reason: Hypoxemia and anaerobic metabolism may result from the effects of sepsis on the body, including hypotension, but they are not the direct cause of hypotension.
The nurse is reviewing laboratory results for a client with sepsis. The results are as follows:
- WBC: 11,000/mm³ (normal range: 5,000-10,000 mm³)
- PaO2: 90 mm Hg (normal range: 80-100 mm Hg)
- aPTT: 50 seconds (normal range: 30-40 seconds)
- Platelet count: 98,000/mm³ (normal range: 150,000-400,000 mm³)
What is the nurse's priority action?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Assessing for hematuria is important but not the priority action. Hematuria can be a symptom of various conditions and does not directly address the abnormal laboratory results.
Choice B reason: Monitoring temperature is a routine action in sepsis management but does not address the immediate concern of the abnormal laboratory results, specifically the elevated aPTT and low platelet count.
Choice C reason: Evaluating skin turgor is a method to assess dehydration, which is not the immediate concern indicated by the laboratory results.
Choice D reason: The elevated aPTT and low platelet count suggest a potential coagulopathy, which could be a sign of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), a complication of sepsis. Administering heparin may be part of the treatment for DIC to prevent further clotting and is a priority action in this context.
A client with thyroid disease is being treated with propylthiouracil (PTU). Which statement made by the client indicates the medication therapy is effective?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Less constipation is not a direct indicator of effective PTU therapy, as constipation can be associated with hypothyroidism, and PTU is used to treat hyperthyroidism.
Choice B reason: Weight loss is expected in hyperthyroidism, and PTU is used to reduce thyroid hormone levels, not to promote weight loss.
Choice C reason: A reduction in facial puffiness can indicate that the PTU is effectively reducing thyroid hormone levels, as puffiness can be associated with hyperthyroidism.
Choice D reason: Improvement in vision is not a typical outcome of PTU therapy and does not directly indicate its effectiveness.
The nurse is caring for a client with sepsis. Which intervention would the nurse include to monitor for decreased tissue perfusion?
Explanation
Choice A reason: Evaluating pupil reactions every shift is important for neurological assessment but is not directly related to monitoring tissue perfusion.
Choice B reason: Assessing temperature every 4 hours is a standard monitoring procedure for sepsis but does not specifically address tissue perfusion.
Choice C reason: Monitoring for cyanosis is a direct method to assess tissue perfusion. Cyanosis, a bluish discoloration of the skin, indicates poor oxygenation and is a sign of decreased tissue perfusion.
Choice D reason: Checking reflexes is part of a neurological assessment and, while important, it does not directly monitor tissue perfusion.
When assessing a client with sepsis, which finding would be consistent with the late phase of septic shock?
Explanation
Choice A reason: A temperature of 99.6°F is a mild fever and not specifically indicative of the late phase of septic shock.
Choice B reason: Skin that is flushed with a capillary refill of less than 3 seconds does not suggest the late phase of septic shock, which would typically present with poor perfusion.
Choice C reason: A renal output of 45 mL/hr is within the normal range (0.5-1 mL/kg/hr for adults) and does not necessarily indicate the late phase of septic shock.
Choice D reason: Arrhythmias can be a sign of the late phase of septic shock as they indicate cardiac dysfunction, which is a result of decreased tissue perfusion and can lead to multiple organ failure.
You just viewed 10 questions out of the 41 questions on the Ati Med Surg n241 exam Exam. Subscribe to our Premium Package to obtain access on all the questions and have unlimited access on all Exams. Subscribe Now



