Anatomy & Physiology Proctored Exam
Anatomy & Physiology Proctored Exam
Total Questions : 73
Showing 10 questions Sign up for moreAnatomy and physiology are difficult to separate because:
Explanation
This is because anatomy and physiology are closely related branches of biology that study the structure and function of living organisms respectively.
Anatomy describes the shape, size, location, and relationships of body parts, while physiology explains how those parts work together to maintain life.
For example, the anatomy of the heart determines how it pumps blood, and the anatomy of the lungs determines how they exchange gases.
Choice B is wrong because our understanding of both anatomy and physiology is constantly changing as new discoveries are made in the field of biology.
Choice C is wrong because body parts take up space regardless of their physiological functions.
Choice D is wrong because physiological functions are not limited to an organism, but can also occur at the cellular, tissue, organ, and system levels.
A hormone that the adrenal medulla secretes is:
Explanation
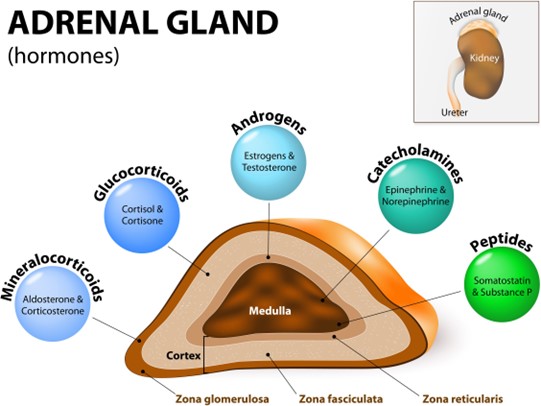
Epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, is a hormone that the adrenal medulla secretes in response to stress or low blood sugar levels.
It helps the body react to stress by increasing blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen delivery to muscles, and blood sugar levels.
Choice A is wrong because mineralocorticoids are hormones that the adrenal cortex secretes, not the adrenal medulla.
They help regulate the balance of sodium and potassium in the body.
Choice C is wrong because glucocorticoids are also hormones that the adrenal cortex secretes, not the adrenal medulla.
They help control the body’s use of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates, suppress inflammation, and regulate blood pressure and blood sugar.
Choice D is wrong because aldosterone is a specific type of mineralocorticoid that the adrenal cortex secretes, not the adrenal medulla.
It helps regulate the balance of sodium and water in the body.
After an infection, many dead and fragmented bacterial cells must be filtered from the body.
Which of the following cells will clear out the cell debris?
Explanation
Macrophages are the main cells that clear out the cell debris by phagocytosis, a process that involves recognition, engulfment, and degradation of the disposable particles.
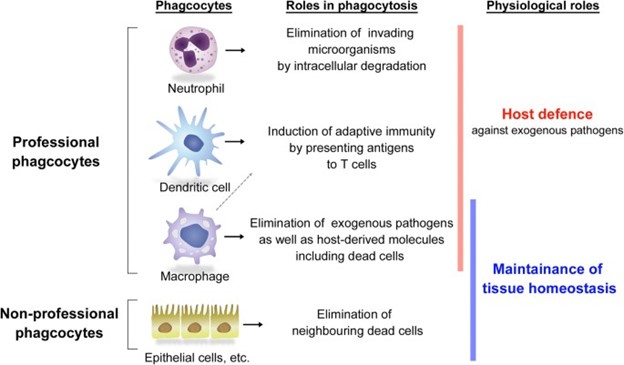
Macrophages are professional phagocytes that can be found in various tissues and organs, where they perform efferocytosis, the removal of dead and dying cells.
Choice A is wrong because lymphocytes are not phagocytes, but rather immune cells that mediate adaptive immunity by producing antibodies or killing infected cells.
Choice B is wrong because cytokines are not cells, but rather soluble molecules that regulate inflammation and immunity by acting as signals between cells.
Choice C is wrong because mast cells are not primarily involved in clearing cell debris, but rather in allergic reactions and innate immunity by releasing histamine and other mediators.
While looking at a sample of blood in a microscope, you see a purple-stained cell that is markedly larger than a red blood cell (about two to three times larger).
It has a large kidney-shaped nucleus.
What type of blood cell is this?
Explanation
A monocyte is a type of white blood cell that is markedly larger than a red blood cell and has a large kidney-shaped nucleus.
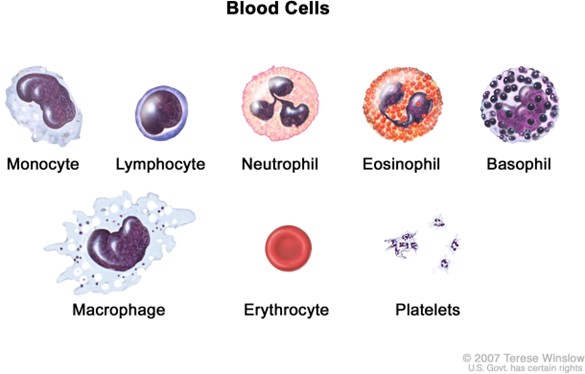
Monocytes are involved in defending the body against infectious diseases and foreign materials.
Choice B is wrong because a basophil is a type of granular white blood cell that has a lobed nucleus and stains purple with basic dyes.
Basophils are involved in allergic reactions and inflammation.
Choice C is wrong because a neutrophil is a type of granular white blood cell that has a multilobed nucleus and stains pale pink with neutral dyes.
Neutrophils are involved in phagocytosis and killing bacteria.
Choice D is wrong because an eosinophil is a type of granular white blood cell that has a bilobed nucleus and stains red-orange with acidic dyes.
Eosinophils are involved in combating parasitic infections and allergic responses. The normal ranges of different types of blood cells are:
Red blood cells: 4.5 to 5.9 million per microliter (mcL) for males, 4.1 to 5.1 million per mcL for females
White blood cells: 4,000 to 11,000 per mcL for both males and females
Platelets: 150,000 to 450,000 per mcL for both males and females
While looking at a sample of blood in a microscope, you see a cell that is markedly larger than a red blood cell.
It has a bi-lobed nucleus and is filled with red granules in the cytoplasm.
What type of blood cell is this?
Explanation
This type of blood cell is a granulocyte that has a bi-lobed nucleus and red granules in the cytoplasm.
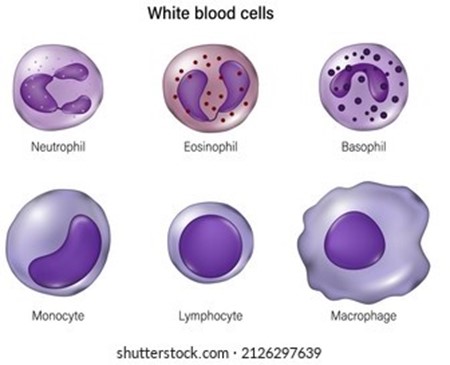
Eosinophils are involved in allergic reactions and parasitic infections.
Choice A is wrong because basophils are granulocytes that have a lobed nucleus and dark blue or purple granules in the cytoplasm.
Basophils are involved in inflammatory responses and histamine release.
Choice B is wrong because lymphocytes are agranulocytes that have a large round nucleus and a thin rim of cytoplasm.
Lymphocytes are involved in immune responses and produce antibodies.
Choice D is wrong because monocytes are agranulocytes that have a kidney-shaped nucleus and a pale blue cytoplasm.
Monocytes are involved in phagocytosis and tissue repair.
Choice E is wrong because neutrophils are granulocytes that have a multi-lobed nucleus and pale pink granules in the cytoplasm.
Neutrophils are involved in bacterial infections and inflammation.
Which of the following usually accounts for the smallest percentage of leukocytes in a blood sample?
Explanation
Basophils usually account for the smallest percentage of leukocytes in a blood sample. Basophils are a type of white blood cell that is involved in allergic reactions and inflammation.
Choice A is wrong because eosinophils are not the least common type of leukocyte.
Eosinophils are another type of white blood cell that is involved in allergic responses and parasitic infections.
They typically make up about 1-6% of the total leukocyte count.
Choice B is wrong because monocytes are not the least common type of leukocyte.
Monocytes are a type of white blood cell that can differentiate into macrophages and dendritic cells, which are important for phagocytosis and antigen presentation.
They typically make up about 2-10% of the total leukocyte count.
Choice D is wrong because neutrophils are not the least common type of leukocyte.
Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell that are the first responders to bacterial infections and tissue damage.
They typically make up about 55-70% of the total leukocyte count.
Which type of blood vessel holds the greatest volume of blood?
Explanation
Veins are the type of blood vessel that holds the greatest volume of blood and serve as reservoirs for blood.
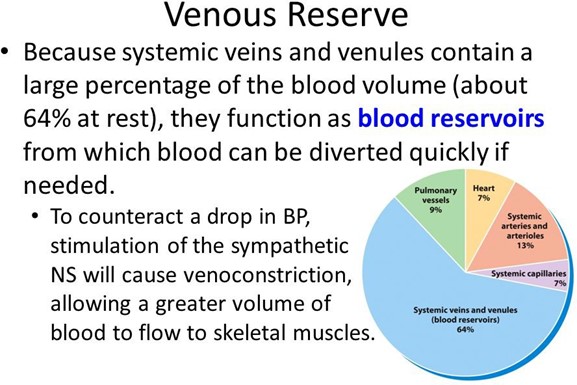
According to 1, veins contain about 70-80% of the blood volume in circulation.
Veins are also called capacitance vessels because they can expand and store more blood when needed.
Choice A. Capillary is wrong because capillaries are very thin and narrow vessels that allow the exchange of gases and nutrients between the blood and the tissues.
Capillaries have a very small volume compared to veins.
Choice C. Arteriole is wrong because arterioles are small branches of arteries that regulate blood pressure and blood flow to the capillaries.
Arterioles have a higher resistance and lower volume than veins.
Choice D. Artery is wrong because arteries are thick and muscular vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to the rest of the body.
Arteries have a higher pressure and lower volume than veins.
Normal ranges for blood volume vary depending on age, sex, weight, and health status, but generally range from 4 to 6 liters for adults.
The smooth, thin membrane that lines the chambers of the heart and forms the surface of the heart valves is the:
Explanation
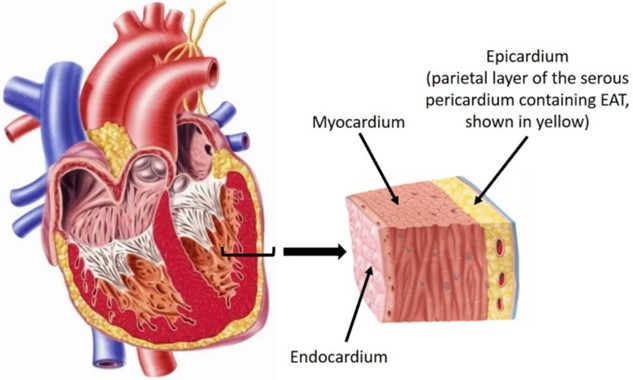
The endocardium is the thin inner lining of the heart chambers and also forms the surface of the heart valves.
Some possible explanations for the other choices are:
Choice A is wrong because the pericardium is the sac that surrounds the heart and consists of two layers: the fibrous pericardium and the serous pericardium.
Choice C is wrong because the myocardium is the thick middle layer of muscle that allows the heart chambers to contract and relax to pump blood to the body.
Choice D is wrong because epicardium is another name for the visceral layer of the serous pericardium that is fused to the heart and is part of the heart wall.
Which of the following lists best illustrates the idea of increasing levels of complexity?
Explanation
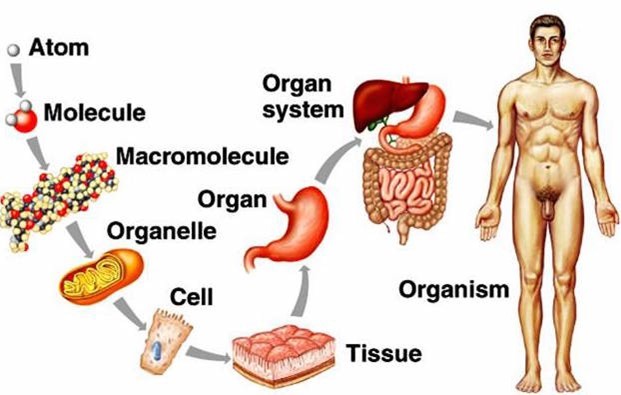
This list best illustrates the idea of increasing levels of complexity because it follows the biological hierarchy of organization from the simplest to the most complex units of matter.
Each level is composed of units from the previous level and has emergent properties that are not present in the lower levels.
Choice A is wrong because it reverses the order of organelles and cells. Organelles are subcellular structures that perform specific functions within cells.
Cells are the basic units of life that can carry out all the processes of living organisms.
Choice B is wrong because it reverses the order of tissues and organelles. Tissues are groups of similar cells that work together to perform a common function. Organelles are more basic than tissues and are found within cells.
Choice D is wrong because it reverses the order of organs and organelles.
Organs are structures composed of two or more types of tissues that perform a specific function or function.
Organelles are more basic than organs and are found within cells.
Which of the following is not an example of a negative homeostatic mechanism in the human body?
Explanation
This is because it is an example of a positive feedback loop, which amplifies the change and moves the system away from its normal state.
A negative feedback loop is a mechanism that reverses a deviation from the set point and maintains homeostasis.
Choice A is wrong because increasing heart rate and force of contraction when blood pressure falls is a negative feedback loop that restores blood pressure to normal.
Choice B is wrong because secreting insulin after a meal to return blood sugar concentration toward normal is a negative feedback loop that regulates glucose levels.
Choice D is wrong because shivering when body temperature falls below normal is a negative feedback loop that increases heat production and raises body temperature.
Normal ranges for blood pressure are 90/60 mmHg to 120/80 mmHg, for blood glucose, are 70 mg/dL to 140 mg/dL, and for body temperature are 36.5°C to 37.5°C or 97.7°F to 99.5°F.
You just viewed 10 questions out of the 73 questions on the Anatomy & Physiology Proctored Exam Exam. Subscribe to our Premium Package to obtain access on all the questions and have unlimited access on all Exams. Subscribe Now



