Rn Hesi Mental Health Proctored Exam
Total Questions : 38
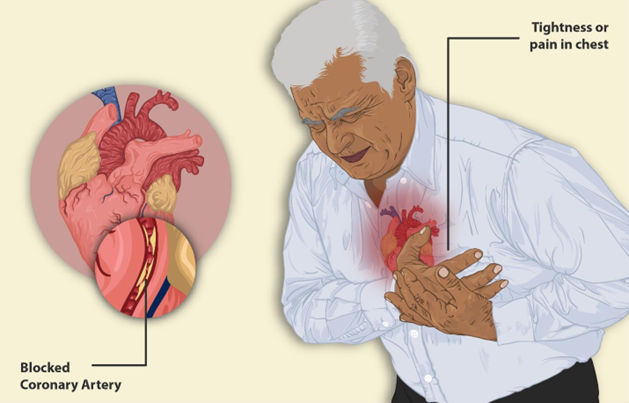
Showing 10 questions, Sign in for moreThe nurse is developing a plan of care for an older client with hypertension who reports chest pain on exertion. Which outcome should the nurse include in the plan of care for this client?
During a routine assessment at an outpatient clinic, the nurse notes that a client has abdominal obesity and a high waist-hip ratio, with a body mass index of 32 kg/m2.
Which action(s) should the nurse take in response to these findings? (Select all that apply.)
Result
- Glucose
- 75 mg/dL (4.2 mmol/L)
- Reference Range
- 74 to 106 mg/dim (4.1 to 5.9 mmol/L)
Click to highlight the assessment findings that require IMMEDIATE follow-up by the nurse.
The client is a 68-year-old with a history of diabetes, hypertension (HTN), coronary artery disease (CAD), and recently diagnosed with end-stage renal disease (ERSD). She has been on hemodialysis three times a week for one month and presents to the emergency department (ED) with:
- Fatigue
- Generalized weakness
- Muscle cramps
- Tingling sensation in her arms and legs
- Lightheadedness
She also reports having missed her scheduled dialysis for the past 2 days, coupled with complaints of nausea, poor appetite, and an inability to attend the dialysis sessions.
Initial Vital Signs:
- Blood Pressure: 146/82 mmHg
- Heart Rate: 114 bpm
- Respiratory Rate: 18 bpm
- SpO₂: 98% on room air
- Temperature: 98.2 °F (36.8 °C) orally
Explanation
The assessment findings that require immediate follow-up by the nurse are: muscle cramps, tingling sensation in arms and legs, and lightheadedness.
These are signs of electrolyte imbalance, which can be caused by missed dialysis sessions, dehydration, or infection. Electrolyte imbalance can lead to serious complications such as cardiac arrhythmias, seizures, or coma.
The nurse should monitor the client's vital signs, neurological status, and cardiac rhythm, and notify the physician for further orders. The nurse should also assess the client's fluid status, hydration, and nutritional intake, and provide education on the importance of adhering to the dialysis schedule and dietary restrictions.
A client is admitted to the mental health unit and sits in the corner of the day room. When the nurse begins the admission assessment interview, the client is guarded, suspicious, and resists talking.
Which action should the nurse implement?
A young adult client with a recent diagnosis of bipolar disorder takes lithium carbonate daily. The client informed the school nurse of the desire to live away from home to attend college after graduating in one month. Which information is most important for the nurse to provide the client and his family?
A preschool-aged girl tells the school nurse that her hair hurts. The nurse finds that the child's hair has been arranged to cover several small bald spots. Which finding indicates to the nurse that the hair loss is not disease-related?
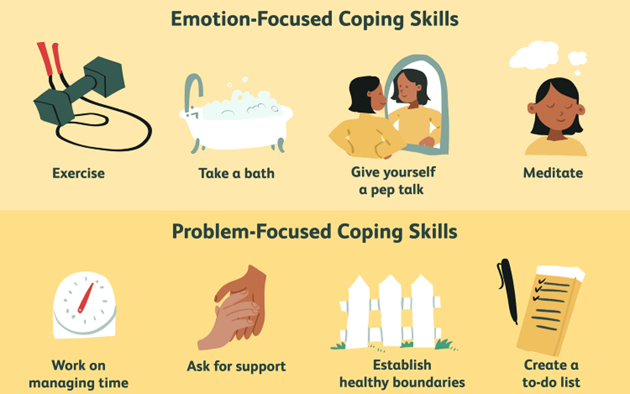
A client with depression does not want to communicate with friends, uses television watching as a means of escaping responsibilities, and describes the inability to handle personal circumstances. Which coping strategy should the nurse include in the plan of care?
Prior to initiating a treatment regimen with the antidepressant sertraline, it is most important for the nurse to obtain which information?
The nurse is assessing a client who reports using cocaine several times in the past week. Which observations should the nurse expect on assessment?
The client is a 68-year-old with a history of diabetes, hypertension (HTN), coronary artery disease (CAD), and was recently diagnosed with end-stage renal disease (ERSD). She has been placed on hemodialysis three times a week for one month. She presents to the emergency department (ED) with fatigue, generalized weakness, muscle cramps, tingling sensation in arms and legs, and lightheadedness following 3 days of illness during which her husband reports she has complained of nausea and had poor appetite and was not able to go for her scheduled dialysis 2
- BP 146/82 mmHg
- HR 114 bpm
- RR 18 bpm
- SpO, 98% on room air
- Temperature 98.2 °F (36.8 °C) orally
Patient Data
The nurse is reviewing the history and physical.
Choose the most likely options for the information missing from the statement below by selecting from the list of options provided.
Based on the client's subjective and objectives data, the nurse recognizes that she is having signs and symptoms of a .
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Sinus tachycardia is not a cause, but a consequence of hyperkalemia.
Choice B rationale:
The client has a history of diabetes, hypertension, coronary artery disease, and end-stage renal disease, which are all risk factors for developing hyperkalemia (high levels of potassium in the blood). She also missed her scheduled dialysis session, which could have caused a buildup of potassium in her blood. Some of the signs and symptoms of hyperkalemia include fatigue, weakness, muscle cramps, tingling sensation in arms and legs, and cardiac arrhythmias such as sinus tachycardia (a fast heart rate). The other options are not consistent with the client's data or condition.
Choice C rationale:
Hypermagnesemia can also cause muscle weakness and cardiac arrhythmias, but they are less likely in this scenario since magnesium is not affected by dialysis
Choice D rationale:
Hypokalemia can also cause muscle weakness and cardiac arrhythmias, but they is less likely in this scenario since potassium is usually elevated in ESRD.
Sign Up or Login to view all the 38 Questions on this Exam
Join over 100,000+ nursing students using Naxlex’s science-backend flashcards, practice tests and expert solutions to improve their grades and reach their goals.
Sign Up Now


