Which conditions can cause hypovolemic shock? Select all that apply.
Diarrhea
Vomiting
Lower GI bleed
Tension pneumothorax
Diabetes insipidus
Valvular stenosis
Correct Answer : A,B,C,D
These conditions can lead to fluid loss, either through increased gastrointestinal output (diarrhea, vomiting, lower GI bleeding) or accumulation of air in the pleural space (tension pneumothorax), resulting in a decrease in blood volume and subsequent hypovolemic shock.
E. Diabetes insipidus in (option E) is incorrect because it is not directly associated with hypovolemic shock. Diabetes insipidus is a condition characterized by excessive thirst and the production of large volumes of dilute urine due to insufficient production or response to antidiuretic hormone (ADH). While diabetes insipidus can lead to dehydration and potential hypovolemia, it is not a direct cause of hypovolemic shock.
F. Valvular stenosis in (option F) is incorrect because it is a condition characterized by the narrowing or obstruction of one or more heart valves. While it can cause problems with cardiac output and circulation, it is not specifically related to hypovolemic shock, which is caused by a decrease in blood volume.
Therefore, the conditions that can cause hypovolemic shock include diarrhea, vomiting, lower GI bleeding, and tension pneumothorax.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Assessing the patient's level of consciousness is a critical initial step in evaluating a patient with shock. Altered mental status or decreased level of consciousness can be indicative of inadequate cerebral perfusion and may require immediate interventions to address compromised brain function and ensure patient safety.
While all the options mentioned are important in the assessment and management of a patient in shock, checking the level of consciousness takes priority as it provides essential information about the patient's neurological status and helps guide further interventions.
A. Obtaining the blood pressure in (option A) is incorrect because Assessing blood pressure is crucial in evaluating a patient in shock, but it can be done in conjunction with checking the level of consciousness and other vital signs.
C. Administering oxygen in (option C) is incorrect because: Administering oxygen is important in managing shock, as tissue hypoxia is a key concern. However, it can be done simultaneously with assessing the level of consciousness and initiating other interventions.
D. Obtaining a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) in (option D) is incorrect because While an ECG may provide valuable information about the patient's cardiac function, it is not the first priority in a patient with shock of unknown etiology. Assessing the level of consciousness and vital signs takes precedence.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
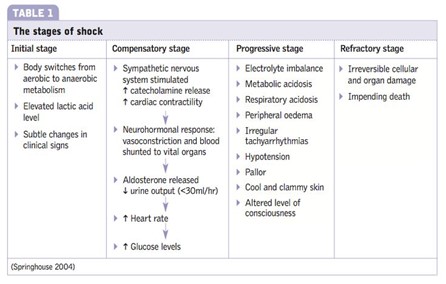
In the compensatory stage of shock, the body initiates various mechanisms to maintain perfusion to vital organs and restore homeostasis. Activation of the renin-angiotensin system is one of the compensatory responses. The decreased blood flow and oxygen delivery to the kidneys stimulate the release of renin from the kidneys. Renin acts on angiotensinogen, converting it into angiotensin I, which is further converted to angiotensin II by the action of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor and also stimulates the release of aldosterone, leading to sodium and water retention. These mechanisms aim to increase blood pressure and cardiac output and restore fluid balance.
A. The initial stage of shock in (option A) is incorrect because it is characterized by inadequate tissue perfusion and the activation of various compensatory mechanisms, including the release of stress hormones. However, the renin-angiotensin system is not specifically mentioned as activated in this stage.
B. The progressive stage of shock in (option B) is incorrect because it occurs when compensatory mechanisms fail to maintain adequate perfusion, leading to worsening hypoperfusion and organ dysfunction. The renin-angiotensin system continues to be activated during this stage, but it is primarily associated with the compensatory stage.
C. The refractory stage of shock in (option C) is incorrect because it is the stage of severe and prolonged hypoperfusion, where organ failure becomes irreversible. The renin-angiotensin system may still be activated, but it is not the primary focus of this stage.
Therefore, the activation of the renin-angiotensin system occurs during the compensatory stage of shock.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
