How does the emergency department nurse caring for a critically ill with septic shock recognize that severe tissue hypoxia is present?
Partial thromboplastin time 64 seconds
Lactate 9.0 mmol/L
Potassium 2.8 mEq/L (2.8 mmol/L)
PaCO2 58 mm Hg
The Correct Answer is B
Lactate is a by-product of anaerobic metabolism that accumulates when there is insufficient oxygen supply to meet cellular metabolic demands. In the context of severe tissue hypoxia, such as in septic shock, the body may resort to anaerobic metabolism, leading to increased lactate production and elevated lactate levels in the blood.
Elevated lactate levels, typically above 4.0 mmol/L, are indicative of tissue hypoxia and inadequate oxygenation at the cellular level. Higher lactate levels, such as 9.0 mmol/L, suggest more severe tissue hypoxia and increased anaerobic metabolism.
A. Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) 64 seconds in (option A) is incorrect because: PTT is a laboratory test that evaluates the intrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade. While coagulation abnormalities may occur in septic shock, PTT alone does not specifically indicate severe tissue hypoxia.
C. Potassium 2.8 mEq/L (2.8 mmol/L) (option C) is incorrect because Low potassium levels (hypokalemia) can be a concern in septic shock, but it does not directly indicate severe tissue hypoxia.
D. PaCO2 58 mm Hg in (option D) is incorrect because: PaCO2 refers to the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in arterial blood and is a measure of the respiratory status. While an elevated PaCO2 can be a sign of respiratory acidosis, it is not specific to severe tissue hypoxia.
Therefore, in a critically ill patient with septic shock, an elevated lactate level, such as 9.0 mmol/L, indicates severe tissue hypoxia and inadequate oxygenation at the cellular level
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
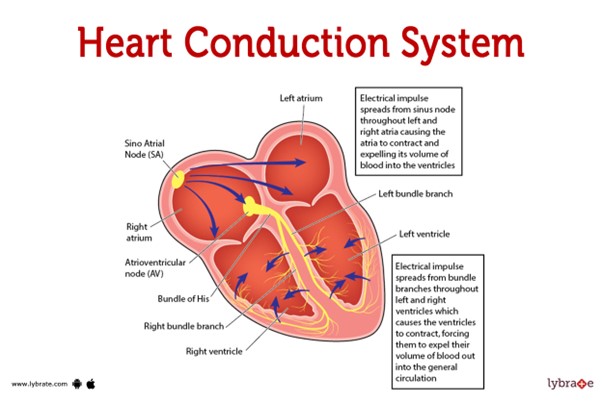 This pathway represents the normal sequence of electrical impulses that coordinate the contraction and relaxation of the heart chambers.
This pathway represents the normal sequence of electrical impulses that coordinate the contraction and relaxation of the heart chambers.
The electrical signal originates from the sinoatrial (SA) node, which is often referred to as the natural pacemaker of the heart. It is located in the right atrium and generates the electrical impulses that initiate each heartbeat. From the SA node, the electrical signal travels to the atrioventricular (AV) node, which is located at the junction between the atria and ventricles.
After passing through the AV node, the electrical impulse travels through the bundle of His (also known as the atrioventricular bundle) and divides into the right and left bundle branches. These branches continue the conduction pathway and deliver the electrical signal to the Purkinje fibers.
The Purkinje fibers spread the electrical impulse rapidly throughout the ventricles, stimulating the contraction of the ventricular muscle and allowing for efficient pumping of blood out of the heart.
Therefore, the correct sequence of the normal conduction pathway in the heart is:
A. SA node - AV node - bundle of His - bundle branches - Purkinje fibers.
Correct Answer is ["18"]
Explanation
Step 1: Convert the patient's weight from pounds to kilograms. 130 pounds ÷ 2.205 (1 pound = 0.453592 kilograms) ≈ 58.97 kilograms
Step 2: Calculate the total dosage of Dobutamine required per hour based on the weight-specific dose. 2.5 mcg/kg/min × 58.97 kg = 147.425 mcg/min
Step 3: Calculate the infusion rate (mL/hr) using the concentration of Dobutamine in the prepared solution. The solution contains 250 mg of Dobutamine in 500 mL, which means there are 250,000 mcg of Dobutamine in 500 mL. To determine the mL/hr, divide the required dosage (147.425 mcg/min) by the amount of Dobutamine in 500 mL (250,000 mcg) and multiply by 500 mL (volume of the solution).
(147.425 mcg/min ÷ 250,000 mcg) × 500 mL ≈ 0.295 mL/min
To get the mL/hr, we convert the rate from minutes to hours (60 minutes = 1 hour):
0.295 mL/min × 60 min/hr ≈ 17.7 mL/hr
Round the answer to the nearest whole number:
Approximately 18 mL/hr of Dobutamine should be administered to the patient.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
