When caring for a patient weighing 60 kg who has just been admitted with septic shock, which of these assessment data greatest concern to the nurse?
Arterial oxygen saturation is 90%.
Urine output 15 ml for 2 hours.
Apical pulse 110 beats/min.
BP 94/56 mm Hg.
The Correct Answer is D
Septic shock is a life-threatening condition characterized by severe infection, systemic inflammation, and inadequate tissue perfusion. Hypotension, as indicated by a low blood pressure reading, is a significant concern in septic shock. It reflects inadequate perfusion to vital organs and tissues, leading to potential organ dysfunction and damage.
While all the assessment data provided may be important and require attention, the low blood pressure (BP) reading indicates impaired systemic perfusion and can contribute to end-organ damage. The nurse should prioritize interventions aimed at improving perfusion and stabilizing the patient's blood pressure.
A. Arterial oxygen saturation is 90% in (option A) is incorrect because While an arterial oxygen saturation of 90% is below the desired range, it is not as immediately life-threatening as low blood pressure. Oxygen therapy and interventions to improve oxygenation should still be initiated, but addressing hypotension takes priority.
B. Urine output of 15 ml for 2 hours in (option B) is incorrect because Decreased urine output is a concerning sign, as it may indicate impaired renal perfusion. However, the immediate concern in septic shock is addressing the low blood pressure to improve overall perfusion, including renal perfusion.
C. Apical pulse 110 beats/min in (option C) is incorrect because: Tachycardia is a common finding in septic shock and represents the body's compensatory response to maintain cardiac output. While it requires monitoring and consideration, low blood pressure is a more significant concern.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
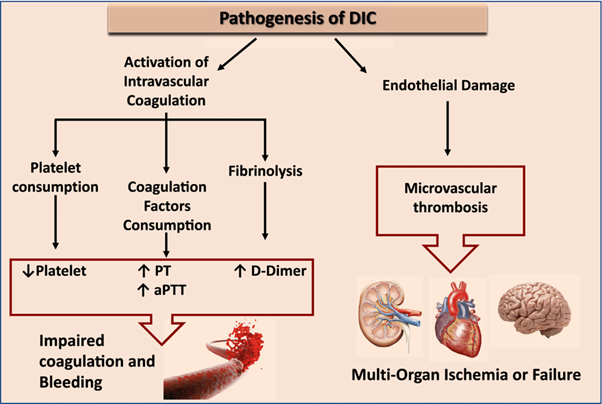
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition characterized by both widespread activation of the coagulation system and excessive clotting, leading to the consumption of clotting factors and platelets. This results in a prothrombotic state, which can lead to organ dysfunction and bleeding manifestations.
Elevated D-dimer levels are a characteristic finding in DIC. D-dimer is a fibrin degradation product that is elevated when there is excessive fibrin formation and breakdown. Elevated D-dimer indicates ongoing fibrinolysis and activation of the clotting system.
B. Decreased prothrombin time in (option B) is incorrect because: DIC is characterized by consumption of clotting factors, which can result in prolongation of the prothrombin time (PT) as well as other coagulation tests.
C. Decreased partial thromboplastin time in (option C) is incorrect because Similar to the prothrombin time, the partial thromboplastin time (PTT) can also be prolonged in DIC due to the consumption of clotting factors.
D. Elevated fibrinogen level in (option D) is incorrect because, In DIC, there is consumption of fibrinogen along with other clotting factors. Therefore, elevated fibrinogen levels are not consistent with the pathophysiology of DIC.
Correct Answer is ["18"]
Explanation
Step 1: Convert the patient's weight from pounds to kilograms. 130 pounds ÷ 2.205 (1 pound = 0.453592 kilograms) ≈ 58.97 kilograms
Step 2: Calculate the total dosage of Dobutamine required per hour based on the weight-specific dose. 2.5 mcg/kg/min × 58.97 kg = 147.425 mcg/min
Step 3: Calculate the infusion rate (mL/hr) using the concentration of Dobutamine in the prepared solution. The solution contains 250 mg of Dobutamine in 500 mL, which means there are 250,000 mcg of Dobutamine in 500 mL. To determine the mL/hr, divide the required dosage (147.425 mcg/min) by the amount of Dobutamine in 500 mL (250,000 mcg) and multiply by 500 mL (volume of the solution).
(147.425 mcg/min ÷ 250,000 mcg) × 500 mL ≈ 0.295 mL/min
To get the mL/hr, we convert the rate from minutes to hours (60 minutes = 1 hour):
0.295 mL/min × 60 min/hr ≈ 17.7 mL/hr
Round the answer to the nearest whole number:
Approximately 18 mL/hr of Dobutamine should be administered to the patient.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
