A patient is admitted to the emergency department (ED) for shock of unknown etiology. The first action by the nurse should be to
obtain the blood pressure.
Check the level of consciousness.
administer oxygen.
obtain a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG).
The Correct Answer is B
Assessing the patient's level of consciousness is a critical initial step in evaluating a patient with shock. Altered mental status or decreased level of consciousness can be indicative of inadequate cerebral perfusion and may require immediate interventions to address compromised brain function and ensure patient safety.
While all the options mentioned are important in the assessment and management of a patient in shock, checking the level of consciousness takes priority as it provides essential information about the patient's neurological status and helps guide further interventions.
A. Obtaining the blood pressure in (option A) is incorrect because Assessing blood pressure is crucial in evaluating a patient in shock, but it can be done in conjunction with checking the level of consciousness and other vital signs.
C. Administering oxygen in (option C) is incorrect because: Administering oxygen is important in managing shock, as tissue hypoxia is a key concern. However, it can be done simultaneously with assessing the level of consciousness and initiating other interventions.
D. Obtaining a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) in (option D) is incorrect because While an ECG may provide valuable information about the patient's cardiac function, it is not the first priority in a patient with shock of unknown etiology. Assessing the level of consciousness and vital signs takes precedence.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
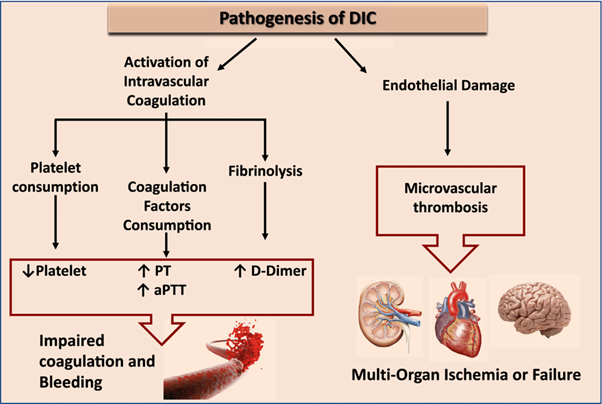
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition characterized by both widespread activation of the coagulation system and excessive clotting, leading to the consumption of clotting factors and platelets. This results in a prothrombotic state, which can lead to organ dysfunction and bleeding manifestations.
Elevated D-dimer levels are a characteristic finding in DIC. D-dimer is a fibrin degradation product that is elevated when there is excessive fibrin formation and breakdown. Elevated D-dimer indicates ongoing fibrinolysis and activation of the clotting system.
B. Decreased prothrombin time in (option B) is incorrect because: DIC is characterized by consumption of clotting factors, which can result in prolongation of the prothrombin time (PT) as well as other coagulation tests.
C. Decreased partial thromboplastin time in (option C) is incorrect because Similar to the prothrombin time, the partial thromboplastin time (PTT) can also be prolonged in DIC due to the consumption of clotting factors.
D. Elevated fibrinogen level in (option D) is incorrect because, In DIC, there is consumption of fibrinogen along with other clotting factors. Therefore, elevated fibrinogen levels are not consistent with the pathophysiology of DIC.
Correct Answer is ["A","B","D","E"]
Explanation
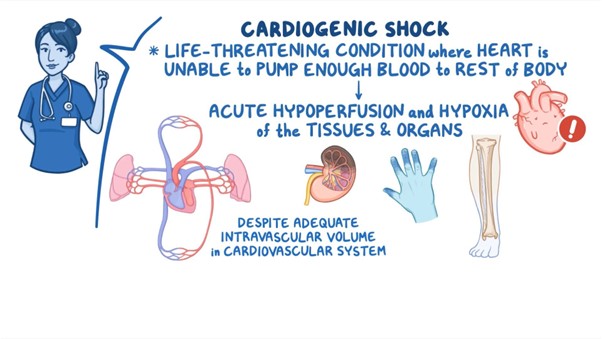
A. Narrowed pulse pressure: In cardiogenic shock, the cardiac output is compromised, resulting in reduced stroke volume and subsequent narrowed pulse pressure. The pulse pressure is the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
B. Tachycardia: Tachycardia is a compensatory response in cardiogenic shock, as the body attempts to increase cardiac output to maintain tissue perfusion despite decreased stroke volume. Increased heart rate is a common finding in this condition.
D. Pulmonary congestion: Cardiogenic shock is often associated with impaired left ventricular function, leading to an inadequate pump mechanism. This can result in fluid accumulation and congestion in the pulmonary circulation, leading to pulmonary edema and congestion. Patients may experience symptoms such as dyspnea, crackles on lung auscultation, and increased work of breathing.
E. Elevated pulmonary artery wedge pressure (PAWP): PAWP is a measurement obtained during invasive hemodynamic monitoring. In cardiogenic shock, the impaired left ventricular function leads to increased left atrial pressure, which is reflected by an elevated PAWP. Elevated PAWP indicates increased fluid volume and congestion in the left side of the heart.
C. Elevated SBP in (option C) is incorrect because Elevated systolic blood pressure (SBP) is not a typical finding in cardiogenic shock. Instead, hypotension or decreased blood pressure is commonly observed due to reduced cardiac output.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
