Four hours after mechanical ventilation is initiated for a patient with a suspected drug overdose, the patient's arterial blood gas (ABG) results include a pH of 7.50, Pa0 2 of 80 mm Hg. PaCO2 of 29 mmHg, and HCO3 of 23 mEq/L (23 mmo/L). The nurse will anticipate the need to:
decrease the respiratory rate.
Leave the ventilator at the current settings.
increase the tidal volume (VT).
Increase the F102
The Correct Answer is A
The ABG results show a pH of 7.50, PaCO2 of 29 mmHg, and HCO3 of 23 mEq/L, indicating respiratory alkalosis. In respiratory alkalosis, there is a decrease in PaCO2 (hypocapnia), which can be caused by excessive ventilation.
To address the respiratory alkalosis, the nurse should decrease the respiratory rate. This would help reduce the amount of ventilation provided and allow the patient to retain more carbon dioxide (CO2), thereby increasing the PaCO2 levels and restoring acid-base balance.
B. Leaving the ventilator at the current settings in (option B) is incorrect because it may exacerbate respiratory alkalosis as it would maintain the same level of ventilation.
C. Increasing the tidal volume (VT) in (option C) is incorrect because it would not address the respiratory alkalosis. Tidal volume refers to the volume of air delivered with each breath, while the issue in this case is excessive ventilation leading to hypocapnia.
D. Increasing the FiO2 (fraction of inspired oxygen) in (option D) is incorrect because it is not indicated based on the given ABG results. The oxygenation (PaO2) level is within normal limits (80 mmHg), suggesting adequate oxygenation.
It is important to consult with the healthcare provider or respiratory therapist for further guidance on adjusting the ventilator settings based on the patient's condition and response to therapy.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
The absence of palpable pulses suggests a lack of effective cardiac output, and the patient is in cardiac arrest. In this situation, immediate initiation of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is crucial to maintain circulation and provide oxygenation to vital organs.
CPR consists of chest compressions and rescue breaths to circulate oxygenated blood to the brain and other vital organs. It is the primary intervention in cardiac arrest to provide temporary life support until advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) measures, such as defibrillation or medication administration, can be initiated.
A. Administering the prescribed Beta-Blocker in (option A) is incorrect because Administering a beta-blocker is not the initial action in a patient who is in cardiac arrest and requires immediate resuscitation.
B. Prepare for Cardioversion per hospital protocol (option B) is incorrect because Cardioversion, which is the delivery of an electric shock to the heart, may be considered in certain situations like unstable ventricular tachycardia or certain supraventricular tachycardias. However, in the given scenario, the patient is unresponsive and has no pulses, indicating cardiac arrest where CPR takes precedence over cardioversion.
C. Give 100% oxygen per non-rebreather mask in (option C) is incorrect because: While oxygenation is important, it should not delay or replace the initiation of CPR, which is the immediate priority in a patient without palpable pulses.
Therefore, the first action that the nurse should take in this scenario is to start CPR.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
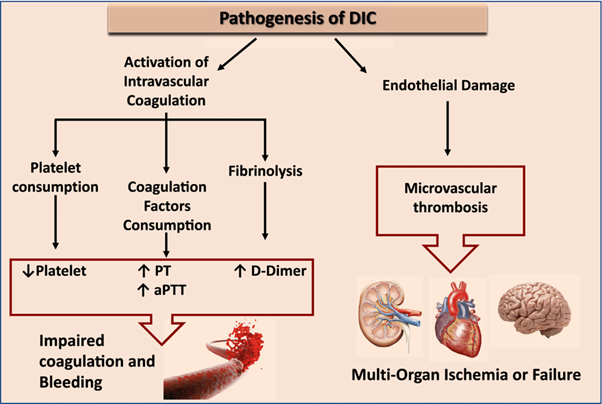
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition characterized by both widespread activation of the coagulation system and excessive clotting, leading to the consumption of clotting factors and platelets. This results in a prothrombotic state, which can lead to organ dysfunction and bleeding manifestations.
Elevated D-dimer levels are a characteristic finding in DIC. D-dimer is a fibrin degradation product that is elevated when there is excessive fibrin formation and breakdown. Elevated D-dimer indicates ongoing fibrinolysis and activation of the clotting system.
B. Decreased prothrombin time in (option B) is incorrect because: DIC is characterized by consumption of clotting factors, which can result in prolongation of the prothrombin time (PT) as well as other coagulation tests.
C. Decreased partial thromboplastin time in (option C) is incorrect because Similar to the prothrombin time, the partial thromboplastin time (PTT) can also be prolonged in DIC due to the consumption of clotting factors.
D. Elevated fibrinogen level in (option D) is incorrect because, In DIC, there is consumption of fibrinogen along with other clotting factors. Therefore, elevated fibrinogen levels are not consistent with the pathophysiology of DIC.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
