The emergency department nurse provides care for a 50-year-old male patient with septic shock. The nurse recalls that the renin- angiotensin system is activated during which stage of shock?
Initial stage
Progressive stage
Refractory stage
Compensatory stage
The Correct Answer is D
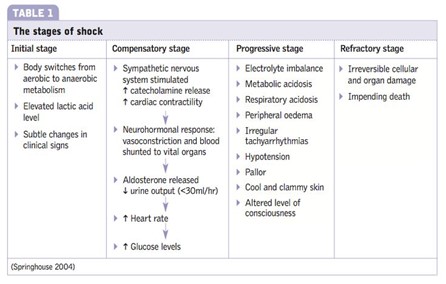
In the compensatory stage of shock, the body initiates various mechanisms to maintain perfusion to vital organs and restore homeostasis. Activation of the renin-angiotensin system is one of the compensatory responses. The decreased blood flow and oxygen delivery to the kidneys stimulate the release of renin from the kidneys. Renin acts on angiotensinogen, converting it into angiotensin I, which is further converted to angiotensin II by the action of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). Angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor and also stimulates the release of aldosterone, leading to sodium and water retention. These mechanisms aim to increase blood pressure and cardiac output and restore fluid balance.
A. The initial stage of shock in (option A) is incorrect because it is characterized by inadequate tissue perfusion and the activation of various compensatory mechanisms, including the release of stress hormones. However, the renin-angiotensin system is not specifically mentioned as activated in this stage.
B. The progressive stage of shock in (option B) is incorrect because it occurs when compensatory mechanisms fail to maintain adequate perfusion, leading to worsening hypoperfusion and organ dysfunction. The renin-angiotensin system continues to be activated during this stage, but it is primarily associated with the compensatory stage.
C. The refractory stage of shock in (option C) is incorrect because it is the stage of severe and prolonged hypoperfusion, where organ failure becomes irreversible. The renin-angiotensin system may still be activated, but it is not the primary focus of this stage.
Therefore, the activation of the renin-angiotensin system occurs during the compensatory stage of shock.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Septic shock is a life-threatening condition characterized by severe infection, systemic inflammation, and inadequate tissue perfusion. Hypotension, as indicated by a low blood pressure reading, is a significant concern in septic shock. It reflects inadequate perfusion to vital organs and tissues, leading to potential organ dysfunction and damage.
While all the assessment data provided may be important and require attention, the low blood pressure (BP) reading indicates impaired systemic perfusion and can contribute to end-organ damage. The nurse should prioritize interventions aimed at improving perfusion and stabilizing the patient's blood pressure.
A. Arterial oxygen saturation is 90% in (option A) is incorrect because While an arterial oxygen saturation of 90% is below the desired range, it is not as immediately life-threatening as low blood pressure. Oxygen therapy and interventions to improve oxygenation should still be initiated, but addressing hypotension takes priority.
B. Urine output of 15 ml for 2 hours in (option B) is incorrect because Decreased urine output is a concerning sign, as it may indicate impaired renal perfusion. However, the immediate concern in septic shock is addressing the low blood pressure to improve overall perfusion, including renal perfusion.
C. Apical pulse 110 beats/min in (option C) is incorrect because: Tachycardia is a common finding in septic shock and represents the body's compensatory response to maintain cardiac output. While it requires monitoring and consideration, low blood pressure is a more significant concern.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Heart rate: 72 beats per minute Stroke volume: 90 mL/contraction
Cardiac output = Heart rate × Stroke volume
Cardiac output = 72 beats/minute × 90 mL/contraction
To simplify the calculation, you can convert the units:
72 beats/minute × 90 mL/contraction = (72 × 90) beats/minute × mL/contraction
Now, perform the multiplication:
72 × 90 = 6,480
Therefore, the cardiac output is 6,480 mL per minute.
The correct answer is:
C. 6,480 mL
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
