The nurse needs to estimate quickly the heart rate of a patient with a regular heart rhythm. Which method will be best to use?
Print a 1-minute electrocardiogram (ECG) strip and count the number of QRS complexes.
Calculate the number of small squares between one QRS complex and the next and divide it into 1500.
Use the 3-second markers to count the number of QRS complexes in 6 seconds and multiply by 10.
Count the number of large squares in the R-R interval and divide by 300.
The Correct Answer is C
This method, known as the 6-second method, involves counting the number of QRS complexes in a 6-second interval on the electrocardiogram (ECG) strip and then multiplying that number by 10 to calculate the heart rate per minute. The advantage of this method is that it provides a relatively quick estimate of the heart rate.
A. Printing a 1-minute ECG strip and counting the number of QRS complexes in (option A) is incorrect because it can be time-consuming and may not be practical in situations where a quick estimate is needed.
B. Calculating the number of small squares between one QRS complex and the next and dividing into 1500 in (option B) is incorrect because it is a method used to calculate heart rate, known as the "1500 method," but it is not as quick as the 6-second method and requires more time and measurement precision.
D. Counting the number of large squares in the R-R interval and dividing by 300 is another method used to calculate heart rate, known as the "300 method," but it is also less quick and less accurate for assessing heart rate in patients with regular rhythms.
It's important to note that if the heart rhythm is irregular, these methods may not provide an accurate estimate of the heart rate, and a longer monitoring period or a different approach may be necessary.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["18"]
Explanation
Step 1: Convert the patient's weight from pounds to kilograms. 130 pounds ÷ 2.205 (1 pound = 0.453592 kilograms) ≈ 58.97 kilograms
Step 2: Calculate the total dosage of Dobutamine required per hour based on the weight-specific dose. 2.5 mcg/kg/min × 58.97 kg = 147.425 mcg/min
Step 3: Calculate the infusion rate (mL/hr) using the concentration of Dobutamine in the prepared solution. The solution contains 250 mg of Dobutamine in 500 mL, which means there are 250,000 mcg of Dobutamine in 500 mL. To determine the mL/hr, divide the required dosage (147.425 mcg/min) by the amount of Dobutamine in 500 mL (250,000 mcg) and multiply by 500 mL (volume of the solution).
(147.425 mcg/min ÷ 250,000 mcg) × 500 mL ≈ 0.295 mL/min
To get the mL/hr, we convert the rate from minutes to hours (60 minutes = 1 hour):
0.295 mL/min × 60 min/hr ≈ 17.7 mL/hr
Round the answer to the nearest whole number:
Approximately 18 mL/hr of Dobutamine should be administered to the patient.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
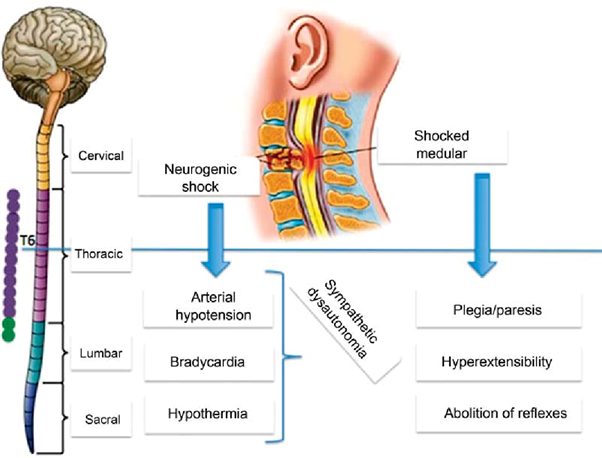
Neurogenic shock is a type of distributive shock that occurs due to the loss of sympathetic nervous system tone after a spinal cord injury or other traumatic brain injuries. This loss of sympathetic tone leads to vasodilation and decreased systemic vascular resistance, resulting in inadequate perfusion to vital organs.
One of the hallmark signs of neurogenic shock is bradycardia (a heart rate less than 60 beats/min) due to the unopposed parasympathetic activity. The parasympathetic system becomes dominant when sympathetic activity is impaired. Therefore, a heart rate of 48 beats/min in this patient suggests the possibility of neurogenic shock.
A. Cool, clammy skin in (option A) is incorrect because Cool, clammy skin is a characteristic of hypovolemic shock, where reduced blood volume leads to vasoconstriction to redirect blood flow to vital organs.
B. BP of 82/40 mm Hg in (option B) is incorrect because: Hypotension is a common finding in both neurogenic shock and hypovolemic shock. A low blood pressure reading alone does not specifically indicate neurogenic shock.
D. Shortness of breath in (option D) is incorrect because Shortness of breath is not specific to neurogenic shock but can occur in various types of shock, including hypovolemic shock. It may result from inadequate oxygenation or impaired respiratory function due to the underlying condition or associated injuries.
Therefore, the heart rate of 48 beats/min suggests the possibility of neurogenic shock in addition to hypovolemic shock in this patient.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
