The medical-surgical nurse is caring for a 55-year-old female patient after surgery. The patient's respiratory rate has increased from 12 to 22 breaths/min, and the pulse rate has increased from 86 to 110 beats/min since the patient was last assessed 4 hours ago. What action by the nurse is best?
Assess the patient's tissue perfusion further.
Ask if the patient needs pain medication.
Document the findings in the patient's chart.
Increase the rate of the patient's IV infusion.
The Correct Answer is A
The increased respiratory rate and pulse rate can be indicators of physiological changes or potential complications in the patient's condition. These changes may suggest alterations in tissue perfusion or other underlying issues that require further assessment.
Assessing the patient's tissue perfusion includes evaluating additional vital signs, such as blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and capillary refill time. Assessing skin color, temperature, and moisture, as well as peripheral pulses, can also provide important information regarding tissue perfusion.
B. Pain medication (option B) is incorrect because the increased respiratory and pulse rates could also indicate other factors that require assessment before administering pain medication.
C. Documenting the findings in the patient's chart (option C) is incorrect because it should not be the primary action at this point. Assessing the patient's condition and determining appropriate interventions take priority.
D. Increasing the rate of the patient's IV infusion (option D) is incorrect because may not be the most appropriate action without further assessment. The patient's increased respiratory and pulse rates may not necessarily be related to hydration status, and it is important to assess the patient comprehensively before making changes to the IV infusion rate.
Therefore, the best action by the nurse in this situation is to further assess the patient's tissue perfusion to gather more information and determine the appropriate course of action.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The characteristics described in the monitor strip analysis suggest ventricular tachycardia. The absence of a visible P wave and the wide and distorted QRS complex indicates that the electrical impulse is originating in the ventricles rather than the atria. The ventricular rate of 196 and regular R-R intervals further support the diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia.
B. Atrial fibrillation in (option B) is incorrect because it is characterized by irregularly irregular R-R intervals and the absence of discernible P waves. The QRS complex is typically narrow
C. Atrial tachycardia in (option C) is incorrect because it would have a rapid atrial rate with regular R-R intervals, and P waves may or may not be discernible. The QRS complex is typically narrow.
D. Ventricular fibrillation in (option D) is incorrect because it would present as a chaotic, rapid, and irregular electrical activity with no discernible P waves, QRS complexes, or regular R-R intervals. It is a life-threatening emergency that requires immediate defibrillation.
Therefore, based on the provided information, the nurse would interpret the patient's cardiac rhythm as ventricular tachycardia. However, it is important to note that an accurate interpretation should be made by a qualified healthcare professional, and the patient's clinical context should also be considered.
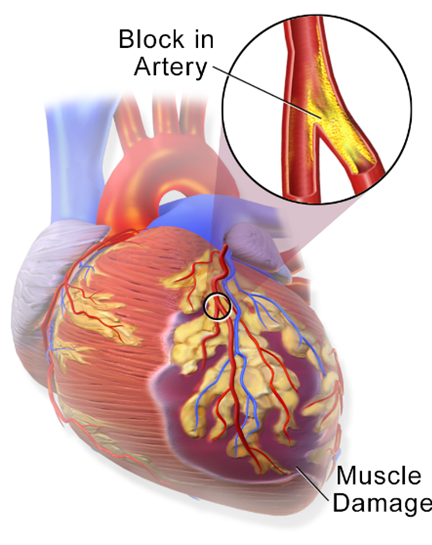
Correct Answer is ["A","B","D","E"]
Explanation
A. Narrowed pulse pressure: In cardiogenic shock, the cardiac output is compromised, resulting in reduced stroke volume and subsequent narrowed pulse pressure. The pulse pressure is the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
B. Tachycardia: Tachycardia is a compensatory response in cardiogenic shock, as the body attempts to increase cardiac output to maintain tissue perfusion despite decreased stroke volume. Increased heart rate is a common finding in this condition.
D. Pulmonary congestion: Cardiogenic shock is often associated with impaired left ventricular function, leading to an inadequate pump mechanism. This can result in fluid accumulation and congestion in the pulmonary circulation, leading to pulmonary edema and congestion. Patients may experience symptoms such as dyspnea, crackles on lung auscultation, and increased work of breathing.
E. Elevated pulmonary artery wedge pressure (PAWP): PAWP is a measurement obtained during invasive hemodynamic monitoring. In cardiogenic shock, the impaired left ventricular function leads to increased left atrial pressure, which is reflected by an elevated PAWP. Elevated PAWP indicates increased fluid volume and congestion in the left side of the heart.
C. Elevated SBP in (option C) is incorrect because Elevated systolic blood pressure (SBP) is not a typical finding in cardiogenic shock. Instead, hypotension or decreased blood pressure is commonly observed due to reduced cardiac output.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
