A patient who has been involved in a motor vehicle crash arrives in the emergency department (ED) with cool, clammy skin; tachycardia; and hypotension. ordered by the health care provider should the nurse implement first?
Insert two large-bore IV catheters.
Provide oxygen at 100% per non-rebreather mask.
Draw blood to type and crossmatch for transfusions. Initiate continuous
electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring.
The Correct Answer is B
Cool, clammy skin, tachycardia, and hypotension are signs of shock, indicating inadequate tissue perfusion and oxygenation. The immediate priority is to ensure adequate oxygen delivery to the tissues. Providing oxygen at 100% via a non-rebreather mask helps increase the patient's oxygen saturation and improve tissue oxygenation.
While all the options mentioned are important in the management of a patient in shock, oxygenation takes priority as it directly addresses compromised tissue perfusion and oxygenation.
A. Inserting two large-bore IV catheters in (option A) is incorrect because: Establishing intravenous access is crucial for fluid resuscitation and administration of medications, but it can be done after ensuring adequate oxygenation.
C. Drawing blood to type and crossmatch for transfusions in (option C) is incorrect because Blood typing and crossmatching are important for potential blood transfusions but should not be the first action in this critical situation.
D. Initiating continuous electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring in (option D) is incorrect because Continuous ECG monitoring is important for assessing cardiac rhythm and detecting any dysrhythmias, but ensuring oxygenation should be the initial priority.
Therefore, in a patient presenting with cool, clammy skin, tachycardia, and hypotension, the nurse should first provide oxygen at 100% via a non-rebreather mask to address inadequate tissue perfusion and oxygenation.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
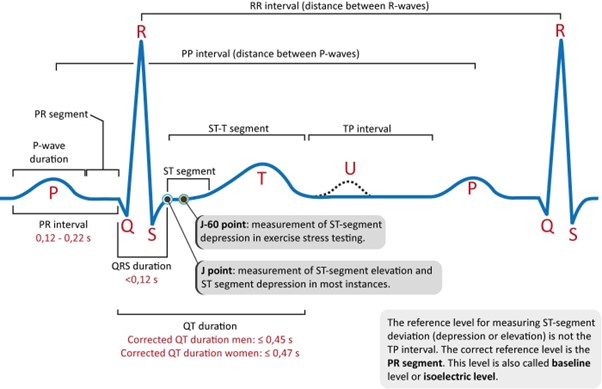
The QTc (corrected QT) interval is a measure of the time it takes for the ventricles to depolarize and repolarize during a cardiac cycle. It is corrected for heart rate (HR) to account for variations in the cardiac cycle length.
The normal range for the QTc interval varies depending on the calculation method used but generally falls within 0.36 to 0.44 seconds. In the given options, the range of 0.33 to 0.47 seconds for the QTc interval is wider than the normal range, suggesting a prolonged QTc interval, which can be indicative of a potential risk for arrhythmias, including ventricular tachycardia and torsades de pointes.
B. QT interval that varies with HR in (option B) is normal because The QT interval alone can vary with heart rate, and this is considered a normal physiological adaptation.
C. QRS interval <0.12 seconds in (option C) is normal because The QRS interval represents the time it takes for ventricular depolarization and is normally less than 0.12 seconds.
D. PR interval 0.12 to 0.24 seconds in (option D) is normal because The PR interval represents the time it takes for atrial depolarization and conduction through the AV node. The normal range is typically 0.12 to 0.20 seconds.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Assessing the patient's level of consciousness is a critical initial step in evaluating a patient with shock. Altered mental status or decreased level of consciousness can be indicative of inadequate cerebral perfusion and may require immediate interventions to address compromised brain function and ensure patient safety.
While all the options mentioned are important in the assessment and management of a patient in shock, checking the level of consciousness takes priority as it provides essential information about the patient's neurological status and helps guide further interventions.
A. Obtaining the blood pressure in (option A) is incorrect because Assessing blood pressure is crucial in evaluating a patient in shock, but it can be done in conjunction with checking the level of consciousness and other vital signs.
C. Administering oxygen in (option C) is incorrect because: Administering oxygen is important in managing shock, as tissue hypoxia is a key concern. However, it can be done simultaneously with assessing the level of consciousness and initiating other interventions.
D. Obtaining a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) in (option D) is incorrect because While an ECG may provide valuable information about the patient's cardiac function, it is not the first priority in a patient with shock of unknown etiology. Assessing the level of consciousness and vital signs takes precedence.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
