The ICU nurse provides care for a 67-year-old female patient experiencing a distributive shock. Assessment findings are indicative of decreasing cardiac output, decreased peripheral perfusion, and increased capillary permeability. The nurse identifies that the patient is in which stage of shock.
Progressive stage
Compensatory stage
Initial stage
Refractory stage
The Correct Answer is A
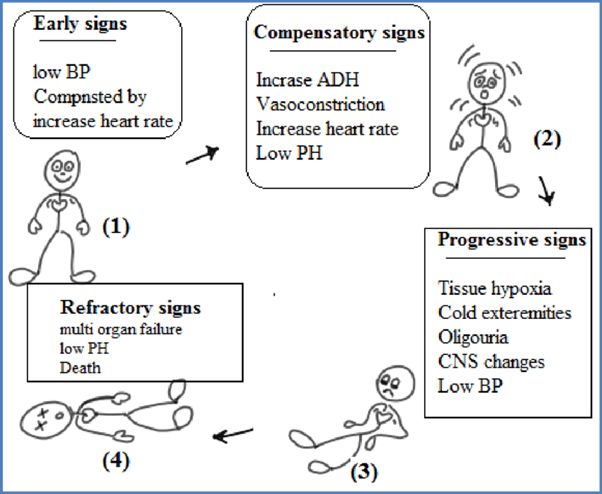
The stages of shock are commonly described as the initial, compensatory, progressive, and refractory stages. Here is an explanation of each stage and why the patient's assessment findings correspond to the progressive stage:
B. The compensatory stage in (option B) is incorrect because, In the compensatory stage, the body continues to activate compensatory mechanisms to maintain perfusion. This includes increased heart rate, peripheral vasoconstriction, and shunting of blood to vital organs. The patient's assessment findings of decreasing cardiac output, decreased peripheral perfusion, and increased capillary permeability suggest that the body's compensatory mechanisms are no longer sufficient to maintain perfusion adequately. Therefore, the patient has progressed beyond the compensatory stage.
C. The initial stage in (option C) is incorrect because, In the initial stage, there is an initial insult or injury that triggers the shock state. The body's compensatory mechanisms are activated, such as increased heart rate and vasoconstriction, to maintain blood pressure and perfusion. However, the patient's assessment findings indicate that they have progressed beyond the initial stage.
D. The refractory stage in (option D) is incorrect because The refractory stage represents a severe and irreversible state of shock where vital organs fail, and despite interventions, the patient's condition does not improve. The patient's assessment findings do not suggest the refractory stage, as there is still potential for intervention and management.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
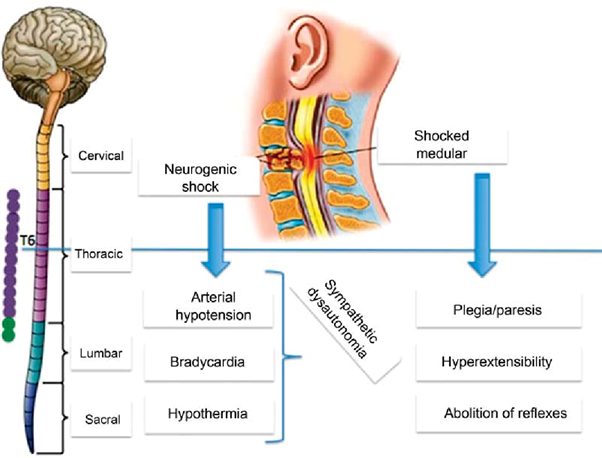
Neurogenic shock is a type of distributive shock that occurs due to the loss of sympathetic nervous system tone after a spinal cord injury or other traumatic brain injuries. This loss of sympathetic tone leads to vasodilation and decreased systemic vascular resistance, resulting in inadequate perfusion to vital organs.
One of the hallmark signs of neurogenic shock is bradycardia (a heart rate less than 60 beats/min) due to the unopposed parasympathetic activity. The parasympathetic system becomes dominant when sympathetic activity is impaired. Therefore, a heart rate of 48 beats/min in this patient suggests the possibility of neurogenic shock.
A. Cool, clammy skin in (option A) is incorrect because Cool, clammy skin is a characteristic of hypovolemic shock, where reduced blood volume leads to vasoconstriction to redirect blood flow to vital organs.
B. BP of 82/40 mm Hg in (option B) is incorrect because: Hypotension is a common finding in both neurogenic shock and hypovolemic shock. A low blood pressure reading alone does not specifically indicate neurogenic shock.
D. Shortness of breath in (option D) is incorrect because Shortness of breath is not specific to neurogenic shock but can occur in various types of shock, including hypovolemic shock. It may result from inadequate oxygenation or impaired respiratory function due to the underlying condition or associated injuries.
Therefore, the heart rate of 48 beats/min suggests the possibility of neurogenic shock in addition to hypovolemic shock in this patient.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
When the low-pressure alarm sounds, it indicates that the pressure being detected by the arterial line is below the set threshold. This could be due to a variety of reasons, such as a loose connection, air bubbles, or a shift in the zero-reference point.
Rezeroing the monitoring equipment involves recalibrating or resetting the baseline reference point for the arterial pressure waveform. This ensures accurate measurement and monitoring of the patient's arterial pressure.
A. Checking the right hand for a rash in (option A) is incorrect because While assessing the patient for any skin changes or rashes is important, it is not the first action to take in response to a low-pressure alarm.
B. Assessing the waveform for under-dampening in (option B) is incorrect because Assessing the waveform characteristics is important in arterial line monitoring, but it may not be the initial action when the low-pressure alarm sounds. Rezeroing the equipment should be performed before assessing waveform characteristics.
C. Assessing for cardiac dysrhythmias in (option C) is incorrect because Assessing for dysrhythmias is an important aspect of patient care, but it may not be directly related to the low-pressure alarm from the arterial line. Rezeroing the monitoring equipment takes precedence.
Therefore, when the low-pressure alarm sounds for a patient with an arterial line, the nurse should first re-zero the monitoring equipment to ensure accurate measurement of arterial pressure.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
