An arterial catheter is inserted in the right radial artery to monitor a patient's blood pressure. Which information obtained by the nurse indicates that a complication of arterial pressure monitoring may be occurring?
Allen's test is positive.
The mean arterial pressure (MAP) is 90 mm Hg.
The dicrotic notch is visible in the waveform.
The right hand is numb.
The Correct Answer is D
Arterial pressure monitoring involves the insertion of an arterial catheter, typically in the radial artery, to directly measure blood pressure. Complications can arise from this invasive procedure, and one potential complication is inadequate blood flow to the hand, leading to numbness or ischemia.
A. The Allen's test is positive in (option A) is incorrect because The Allen's test is performed before arterial catheter insertion to assess the collateral circulation of the hand. A positive Allen test indicates adequate collateral circulation, which is desirable before performing the procedure. However, it does not directly indicate a complication during or after arterial pressure monitoring.
B. The mean arterial pressure (MAP) is 90 mm Hg in (option B) is incorrect because The mean arterial pressure (MAP) represents the average pressure in the arterial system during one cardiac cycle. While changes in MAP can be significant for patient management, it does not specifically indicate a complication of arterial pressure monitoring.
C. The dicrotic notch visible in the waveform in (option C) is incorrect because The dicrotic notch represents the closure of the aortic valve and is a normal finding in arterial waveforms. Its presence does not indicate a complication.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
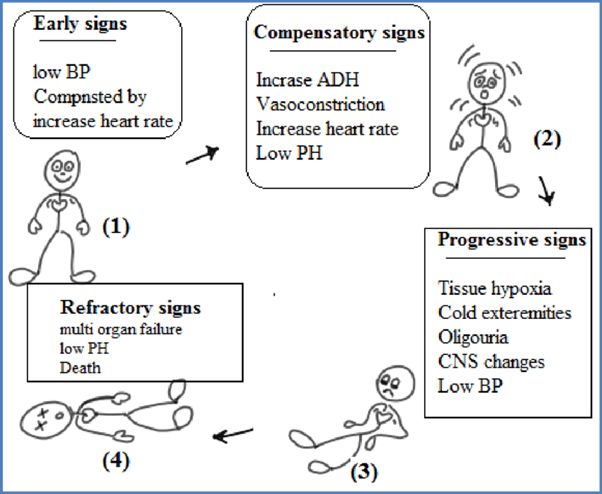
The stages of shock are commonly described as the initial, compensatory, progressive, and refractory stages. Here is an explanation of each stage and why the patient's assessment findings correspond to the progressive stage:
B. The compensatory stage in (option B) is incorrect because, In the compensatory stage, the body continues to activate compensatory mechanisms to maintain perfusion. This includes increased heart rate, peripheral vasoconstriction, and shunting of blood to vital organs. The patient's assessment findings of decreasing cardiac output, decreased peripheral perfusion, and increased capillary permeability suggest that the body's compensatory mechanisms are no longer sufficient to maintain perfusion adequately. Therefore, the patient has progressed beyond the compensatory stage.
C. The initial stage in (option C) is incorrect because, In the initial stage, there is an initial insult or injury that triggers the shock state. The body's compensatory mechanisms are activated, such as increased heart rate and vasoconstriction, to maintain blood pressure and perfusion. However, the patient's assessment findings indicate that they have progressed beyond the initial stage.
D. The refractory stage in (option D) is incorrect because The refractory stage represents a severe and irreversible state of shock where vital organs fail, and despite interventions, the patient's condition does not improve. The patient's assessment findings do not suggest the refractory stage, as there is still potential for intervention and management.
Correct Answer is ["9000"]
Explanation
4 mL × body weight in kg × percentage of burn = total fluid volume for the first 24 hours Then, divide the total fluid volume by 2 to determine the fluid volume for the first 8 hours.
In this case, the patient weighs 90 kg and has a 50% burn injury.
4 mL × 90 kg × 50% = 18,000 mL (total fluid volume for 24 hours)
18,000 mL / 2 = 9,000 mL (fluid volume for the first 8 hours)
Therefore, the nurse would infuse the intravenous fluid resuscitation at a rate of 9,000 mL over the first 8 hours.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
