Which of the following clinical manifestations of Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)?
Decreased hematocrit, increased platelet counts, increased D-dimer
Decreased platelet counts, increased D-dimer, increased prothrombin time
Decreased Antithrombin III, increased platelet counts, increased fibrinogen
Decreased D-dimer, increased platelet counts, Increased hemoglobin
The Correct Answer is B
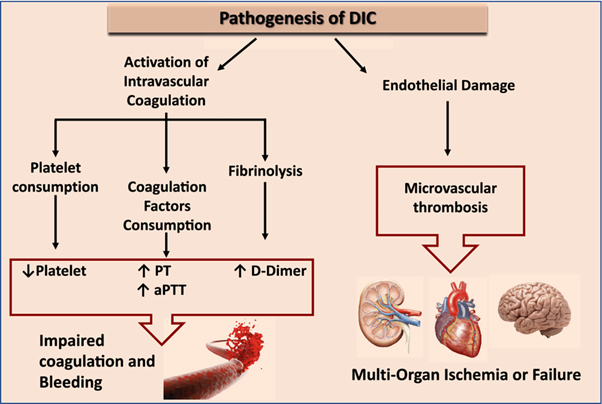
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) is a condition characterized by widespread activation of the coagulation system, leading to both excessive clot formation and consumption of clotting factors and platelets. This process can result in both bleeding and thrombosis.
The manifestations mentioned in option B are commonly seen in DIC:
Decreased platelet counts: DIC leads to platelet consumption and destruction, resulting in low platelet counts (thrombocytopenia).
Increased D-dimer: D-dimer is a fibrin degradation product, and its levels are increased DIC due to the breakdown of fibrin clots.
Increased prothrombin time (PT): DIC can lead to the depletion of clotting factors, resulting in prolonged prothrombin time, indicating impaired coagulation.
The other options mentioned do not represent the typical clinical manifestations of DIC:
A. Decreased hematocrit, increased platelet counts, and increased D-dimer in (option A) are incorrect because While platelet counts and D-dimer are increased in DIC, decreased hematocrit is not a characteristic finding.
C. Decreased Antithrombin III, increased platelet counts, and increased fibrinogen in (option C) is incorrect because: Decreased Antithrombin III can be seen in DIC, but increased platelet counts and fibrinogen levels are not specific to DIC.
D. Decreased D-dimer, increased platelet counts, and increased hemoglobin in (option D) is incorrect because Decreased D-dimer and increased hemoglobin are not typical findings in DIC, while increased platelet counts can be seen in some cases.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Heart rate: 72 beats per minute Stroke volume: 90 mL/contraction
Cardiac output = Heart rate × Stroke volume
Cardiac output = 72 beats/minute × 90 mL/contraction
To simplify the calculation, you can convert the units:
72 beats/minute × 90 mL/contraction = (72 × 90) beats/minute × mL/contraction
Now, perform the multiplication:
72 × 90 = 6,480
Therefore, the cardiac output is 6,480 mL per minute.
The correct answer is:
C. 6,480 mL
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Central venous pressure (CVP) is a measurement of the pressure in the central veins, which reflects the blood volume and right-sided cardiac function. High CVP readings may indicate fluid overload or impaired cardiac function, and intervention is necessary to address the underlying cause.
Administering IV diuretic medications can help reduce fluid volume by increasing urine output and promoting fluid elimination. By removing excess fluid, the diuretic medications can help lower the CVP and alleviate the high pressures.
The other options mentioned are not the anticipated actions for addressing high CVP:
A. Increasing the IV fluid infusion rate in (option A) is incorrect because: If the CVP is already indicating high pressures, increasing the IV fluid infusion rate would further contribute to fluid overload and exacerbate the problem. This action would not be appropriate for high CVP readings.
C. Elevating the head of the patient's bed to 45 degrees in (option C) is incorrect because Positioning the patient with the head of the bed elevated is commonly done to prevent complications such as aspiration or improve respiratory function. While it may have other benefits, it does not directly address the high CVP.
D. Documenting the CVP and continuing to monitor in (option D) is incorrect because Documenting the CVP and continuing to monitor is important for ongoing assessment and evaluation. However, in the presence of high CVP readings, intervention is necessary to address the underlying issue rather than solely documenting and monitoring.
Therefore, when a patient's CVP monitor indicates high pressures following surgery, the nurse would anticipate administering IV diuretic medications to help reduce fluid volume and lower the CVP.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
