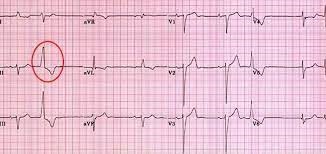
Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) occur while the nurse is suctioning a patient's endotracheal tube. Which action by the nurse is best?
Stop and ventilate the patient with 100% oxygen.
Check the patient's potassium level
Give prescribed PRN antidysrhythmic medications.
Decrease the suction pressure to 80 mm Hg.
The Correct Answer is A
Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) are abnormal heart rhythms originating from the ventricles. They can be triggered by various factors, including irritation or stimulation of the airway during suctioning.
In this situation, the priority is to ensure adequate oxygenation and ventilation for the patient. Stopping the suctioning procedure and providing ventilatory support with 100% oxygen helps maintain oxygen levels and minimizes further cardiac dysrhythmias.
B. Check the patient's potassium level in (option B) is incorrect because While electrolyte imbalances, including low potassium levels (hypokalemia), can contribute to cardiac dysrhythmias, checking the potassium level is not the immediate priority when PVCs occur during suctioning.
C. Give prescribed PRN antidysrhythmic medications in (option C) is incorrect because: Administering antidysrhythmic medications without further assessment or evaluation may not be appropriate in this situation.
D. Decrease the suction pressure to 80 mm Hg in (option D) is incorrect because: While adjusting suction pressure may help prevent further irritation, it is not the initial priority when PVCs are present during suctioning.
E. Documenting the dysrhythmia in the patient's chart in (option E) is incorrect because: Documentation is important but should not be the initial action when a patient experiences PVCs during suctioning. Patient safety and immediate intervention take precedence.
Therefore, when PVCs occur during suctioning, the nurse should stop the procedure, provide ventilatory support with 100% oxygen, and assess the patient's response to intervention.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
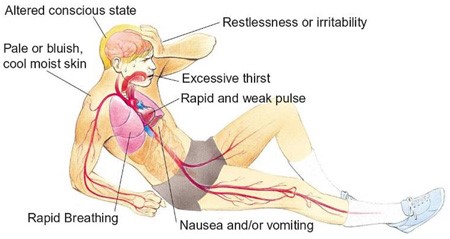
Hypovolemic shock is a life-threatening condition resulting from severe blood or fluid loss. The patient in this scenario exhibits signs of hypovolemic shock, such as low blood pressure, tachycardia, cool and clammy skin, and decreased urine output.
When assessing the prescription options, the nurse should consider the appropriateness of each intervention for hypovolemic shock. Plasmanate is a type of plasma protein fraction that is used for volume expansion in certain situations. However, in hypovolemic shock, the primary intervention is to restore intravascular volume promptly. Plasmanate alone may not be sufficient for rapid-volume resuscitation.
In hypovolemic shock, the initial management typically involves the administration of crystalloid solutions, such as Lactated Ringers or Normal Saline, to restore intravascular volume. Therefore, the prescription of Plasmanate as the primary intervention raises concerns and should be questioned by the nurse.
A. Dopamine (Intropin) 12 mcg/min in (option A) is incorrect because: Dopamine is a vasopressor medication used to increase blood pressure and cardiac output. It is a suitable option for hypovolemic shock to support blood pressure and tissue perfusion.
B. Dobutamine (Dobutrex) 5 mcg/kg/min in (option B) is incorrect because: Dobutamine is an inotropic medication that helps improve cardiac contractility and cardiac output. It can be beneficial in cases of hypovolemic shock with signs of poor cardiac function.
D. Bumetanide (Bumex) 1 mg IV in (option D) is incorrect because: Bumetanide is a loop diuretic used to promote diuresis. However, in the context of hypovolemic shock, diuretics are generally not the first-line treatment as they can further reduce intravascular volume and worsen the patient's condition.
It is essential for the nurse to consult with the healthcare provider regarding the prescription order of Plasmanate and consider alternative interventions for rapid volume resuscitation in hypovolemic shock.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The ABG results show a pH of 7.50, PaCO2 of 29 mmHg, and HCO3 of 23 mEq/L, indicating respiratory alkalosis. In respiratory alkalosis, there is a decrease in PaCO2 (hypocapnia), which can be caused by excessive ventilation.
To address the respiratory alkalosis, the nurse should decrease the respiratory rate. This would help reduce the amount of ventilation provided and allow the patient to retain more carbon dioxide (CO2), thereby increasing the PaCO2 levels and restoring acid-base balance.
B. Leaving the ventilator at the current settings in (option B) is incorrect because it may exacerbate respiratory alkalosis as it would maintain the same level of ventilation.
C. Increasing the tidal volume (VT) in (option C) is incorrect because it would not address the respiratory alkalosis. Tidal volume refers to the volume of air delivered with each breath, while the issue in this case is excessive ventilation leading to hypocapnia.
D. Increasing the FiO2 (fraction of inspired oxygen) in (option D) is incorrect because it is not indicated based on the given ABG results. The oxygenation (PaO2) level is within normal limits (80 mmHg), suggesting adequate oxygenation.
It is important to consult with the healthcare provider or respiratory therapist for further guidance on adjusting the ventilator settings based on the patient's condition and response to therapy.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
