Which of the following findings is most consistent with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)?
elevated D-dimer
decreased prothrombin time
decreased partial thromboplastin time
elevated fibrinogen level
The Correct Answer is A
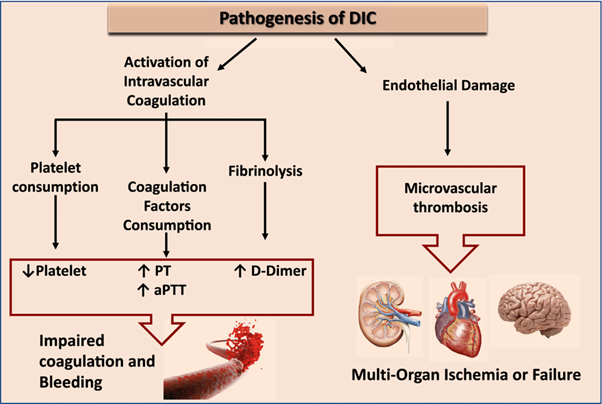
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition characterized by both widespread activation of the coagulation system and excessive clotting, leading to the consumption of clotting factors and platelets. This results in a prothrombotic state, which can lead to organ dysfunction and bleeding manifestations.
Elevated D-dimer levels are a characteristic finding in DIC. D-dimer is a fibrin degradation product that is elevated when there is excessive fibrin formation and breakdown. Elevated D-dimer indicates ongoing fibrinolysis and activation of the clotting system.
B. Decreased prothrombin time in (option B) is incorrect because: DIC is characterized by consumption of clotting factors, which can result in prolongation of the prothrombin time (PT) as well as other coagulation tests.
C. Decreased partial thromboplastin time in (option C) is incorrect because Similar to the prothrombin time, the partial thromboplastin time (PTT) can also be prolonged in DIC due to the consumption of clotting factors.
D. Elevated fibrinogen level in (option D) is incorrect because, In DIC, there is consumption of fibrinogen along with other clotting factors. Therefore, elevated fibrinogen levels are not consistent with the pathophysiology of DIC.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
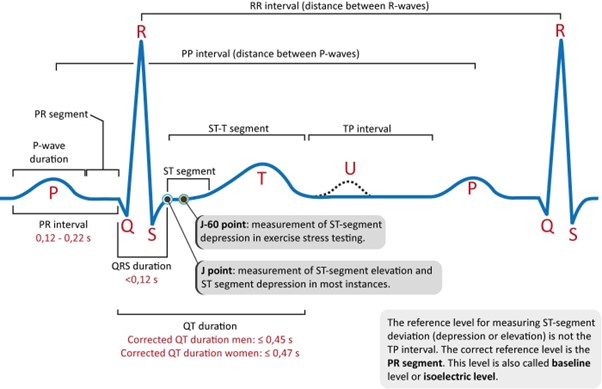
The QTc (corrected QT) interval is a measure of the time it takes for the ventricles to depolarize and repolarize during a cardiac cycle. It is corrected for heart rate (HR) to account for variations in the cardiac cycle length.
The normal range for the QTc interval varies depending on the calculation method used but generally falls within 0.36 to 0.44 seconds. In the given options, the range of 0.33 to 0.47 seconds for the QTc interval is wider than the normal range, suggesting a prolonged QTc interval, which can be indicative of a potential risk for arrhythmias, including ventricular tachycardia and torsades de pointes.
B. QT interval that varies with HR in (option B) is normal because The QT interval alone can vary with heart rate, and this is considered a normal physiological adaptation.
C. QRS interval <0.12 seconds in (option C) is normal because The QRS interval represents the time it takes for ventricular depolarization and is normally less than 0.12 seconds.
D. PR interval 0.12 to 0.24 seconds in (option D) is normal because The PR interval represents the time it takes for atrial depolarization and conduction through the AV node. The normal range is typically 0.12 to 0.20 seconds.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Mean arterial pressure (MAP) is a measure of the average pressure within the arteries during one cardiac cycle. It represents the perfusion pressure that drives blood flow to organs and tissues. In the context of shock, a MAP of 50 mm Hg is considered low and indicates inadequate tissue perfusion.
To improve tissue perfusion and restore blood pressure, the nurse would anticipate administering large volumes of intravenous fluids, such as Lactated Ringers (LR). Fluid resuscitation aims to increase intravascular volume and improve cardiac output, ultimately leading to improved tissue perfusion.
B. Cardiac Output (CO) is 4 L/min in (option A) is incorrect because Cardiac output represents the volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute. While a low cardiac output may require intervention, it does not specifically indicate the need for large volumes of fluid administration.
C. Stroke volume is 70 ml/beat in (option C) is incorrect because Stroke volume refers to the volume of blood ejected by the heart with each contraction. While stroke volume can be an important determinant of cardiac output, it alone does not indicate the need for large fluid volumes.
D. The heart rate is 80 bpm in (option D) is incorrect because: Heart rate is the number of heartbeats per minute. While the heart rate can impact cardiac output, it does not provide direct information about fluid resuscitation needs.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
