Penicillin has cross-sensitivity to which of the following drug classes?
Aminoglycosides
Erythromycins
Quinolones
Cephalosporins
The Correct Answer is D
A. Aminoglycosides: Aminoglycosides are a different class of antibiotics. They do not have cross-sensitivity with penicillin. People who are allergic to penicillin can usually take aminoglycosides without a problem.
B. Erythromycins: Erythromycins are macrolide antibiotics. They are not related to penicillin structurally, so there is no cross-sensitivity between penicillin and erythromycins. People allergic to penicillin can generally take erythromycin without issues.
C. Quinolones: Quinolones, also known as fluoroquinolones, are a different class of antibiotics. They do not share a structural similarity with penicillin, so there is usually no cross-sensitivity between penicillin and quinolones. People allergic to penicillin can usually take quinolones without problems.
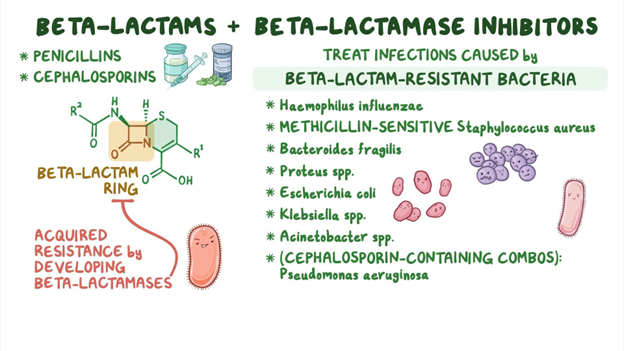
D. Cephalosporins: Cephalosporins are beta-lactam antibiotics, just like penicillins. They have a similar chemical structure to penicillins, which can lead to cross-sensitivity. Individuals who are allergic to penicillin might also have an allergic reaction to cephalosporins due to this structural resemblance. However, it's important to note that not all cephalosporins are the same, and the risk of cross-reactivity varies among different generations of cephalosporins. Healthcare providers need to assess the specific situation and choose an appropriate antibiotic if there is a known penicillin allergy.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. "The antibiotic I have been taking doesn't work as well as it used to."
This statement shows awareness of decreased effectiveness, which can occur due to drug resistance. Bacteria can become resistant to antibiotics, leading to reduced efficacy of the medication over time.
B. "The bacteria in my body have become resilient."
This statement correctly attributes resistance to the bacteria. Resilience in this context means that bacteria have developed mechanisms to survive the effects of antibiotics, making the treatment less effective.
C. "Over time, an organism that had once been highly sensitive to an antibiotic may become less susceptible, or it may lose drug sensitivity entirely."
This statement accurately describes the concept of drug resistance. Bacteria can lose sensitivity to antibiotics, rendering the drugs ineffective against them.
D. "My body has become resistant to the antibiotic."
This statement is incorrect. It's the bacteria that develop resistance, not the patient's body. Patients don't become resistant to antibiotics; instead, bacteria evolve and adapt, making the drugs less effective against them.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Dermatitis and headaches: Prednisone use can sometimes cause skin issues, but dermatitis is not a common side effect. Headaches can also occur, but they are not specific to long-term prednisone therapy.
B. Heart failure and headaches: Prednisone does not directly cause heart failure. Headaches can occur but are not specific indicators of prednisone side effects.
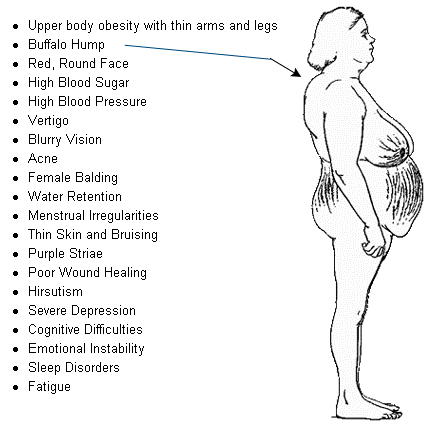
C. Hyperglycemia and osteoporosis: Prednisone can lead to elevated blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia) and increased bone loss (osteoporosis) when used long-term. Regular monitoring is essential to manage these potential side effects.
D. Weight loss and hypoglycemia: Prednisone can cause weight gain rather than weight loss. Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) is not a common side effect of prednisone; it typically causes hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) instead.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
