A nurse is caring for a client whose throat culture is positive for group A streptococcus 24 hours after a rapid strep test (RST) was negative. Which of the following actions is the nurse's priority?
Reinforce teaching about gargling with warm saline several times daily.
Ask the client to identify friends and family who have been in close contact.
Instruct the client to take antipyretics as directed for elevated temperature.
Notify the client to return to the clinic for initiation of antibiotic therapy.
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A reason:
While gargling with warm saline can provide symptomatic relief for a sore throat, it does not address the underlying bacterial infection. Therefore, it is not the priority action once a diagnosis of group A streptococcus has been confirmed.
Choice B reason:
Identifying close contacts is important for public health tracking and potentially preventing the spread of the infection. However, the immediate priority for the client is the initiation of treatment to address the infection.
Choice C reason:
Taking antipyretics can help manage fever and provide comfort to the client. While managing symptoms is important, it is secondary to initiating antibiotic therapy, which addresses the cause of the symptoms.
Choice D reason:
The priority action is to notify the client to return to the clinic for initiation of antibiotic therapy. Group A streptococcus is a bacterial infection that requires antibiotics for treatment. Prompt initiation of antibiotics is crucial to prevent complications and promote recovery.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is the most common type of antibody found in blood circulation and is involved in the body's immune response to fight infections. However, IgG is not typically associated with allergic reactions, which are immediate hypersensitivity reactions.
Choice B reason:
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) plays a critical role in mucosal immunity and is found in high concentrations in the mucous membranes, particularly those lining the respiratory passages and gastrointestinal tract. Like IgG, IgA is not primarily responsible for the allergic response seen in conditions such as seasonal allergies.
Choice C reason:
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is usually the first antibody produced by the immune system when it detects an infection. IgM antibodies are larger and are involved in the primary immune response but are not the antibodies that mediate typical allergic reactions.
Choice D reason:
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is the antibody that plays a central role in the pathophysiology of allergic diseases, including seasonal allergies. IgE antibodies are produced as a response to allergens and are responsible for the symptoms of an allergic reaction. An elevation in IgE levels typically indicates a positive result for an allergy test such as RAST.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason:
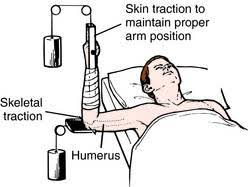
Skin traction is indeed less restrictive than skeletal traction, allowing for more mobility. It is applied using bandages or adhesive material to the skin, which can be removed or adjusted more easily than the pins or screws used in skeletal traction. This type of traction is typically used for short-term treatment before surgery or when the injury is less severe.
Choice B reason:
Discomfort levels can vary depending on the individual and the specific circumstances of the traction. However, skin traction is generally considered to be less painful than skeletal traction because it is less invasive and applies less force. Skeletal traction, which involves the insertion of pins or wires directly into the bone, is likely to cause more discomfort due to the invasive nature of the procedure.
Choice C reason:
Skeletal traction is more appropriate for reducing fractures, especially in cases where a greater force is needed to align the bones. It involves the surgical insertion of pins or wires directly into the bone, allowing for a stronger and more stable pull that is necessary for the realignment of complex fractures.
Choice D reason:
Skeletal traction carries a higher risk of infection compared to skin traction because it is more invasive. The insertion of pins or wires into the bone creates a potential entry point for bacteria, which can lead to infection at the site of insertion.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
