A nurse is assessing the reflexes of a client who has an unrepaired femur fracture and has suddenly become stuporous. For which of the following findings should the nurse identify that the client exhibits Babinski's sign?
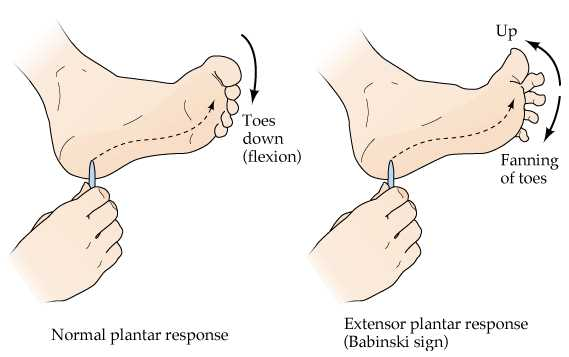
Dorsiflexion of the great toe
Pronation of the arms
Pinpoint pupils
Jerking contractions of the head and neck
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A reason:
Babinski's sign is a neurological reflex that's tested by stroking the sole of the foot. A positive Babinski's sign, which is normal in infants but abnormal in adults, is indicated by dorsiflexion of the great toe (the toe points up) while the other toes fan out. This reflex suggests dysfunction of the corticospinal tract, which may be due to various neurological conditions. In the context of a stuporous patient with an unrepaired femur fracture, a positive Babinski's sign could indicate an acute neurological change possibly related to the injury or a secondary complication such as a fat embolism syndrome, which can occur after fractures and may affect the brain.
Choice B reason:
Pronation of the arms is not associated with Babinski's sign. Pronation is a rotational movement where the hand and upper arm are turned inwards. While arm movements are part of the neurological examination, they do not constitute a response to the plantar reflex test used to elicit Babinski's sign.
Choice C reason:
Pinpoint pupils may indicate opioid overdose or damage to the pons due to various causes, but they are not a component of Babinski's sign. Pupil size and reaction to light are important in neurological assessments, but they are separate from the reflexes tested by the Babinski sign.
Choice D reason:
Jerking contractions of the head and neck are not related to Babinski's sign. These could be indicative of seizure activity or other neurological disorders but are not a response to the plantar reflex test.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason:
A reddened area over the sacrum is a sign of potential pressure ulcer development, which is a common complication of immobility, especially in bedridden or wheelchair-bound individuals. The sacrum is a prominent bony area that bears weight when a person is sitting or lying down, making it susceptible to pressure ulcers if proper preventative measures, such as regular repositioning, are not taken.
Choice B reason:
Difficulty hearing some types of sounds is not typically a direct complication of immobility. Hearing issues may be related to other health conditions or age-related changes but are not caused by the lack of movement associated with post-stroke immobility.
Choice C reason:
Stiffness in the lower extremities can occur due to immobility, as muscles and joints may become tight when not used regularly. However, this is more of a long-term effect and may not be as immediately concerning as pressure ulcer prevention. Regular range-of-motion exercises can help prevent stiffness.
Choice D reason:
Difficulty moving the upper extremities may be a result of the stroke itself rather than a complication of immobility. While maintaining mobility in all limbs is important, the focus of monitoring should be on complications that arise specifically due to immobility, such as pressure ulcers.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason:Scheduling the procedure five days before the expected menses would place it in the late proliferative phase, which risks missing ongoing menstrual bleeding and could coincide with implantation if the client ovulated early. Best practice is to perform the test after menstruation ends but before ovulation—usually within 12 days of the first day of the last period—to ensure the client is not pregnant.
Choice B reason:
Diarrhea is not a common side effect of HSG. The procedure involves the insertion of a dye into the uterine cavity to visualize the fallopian tubes and uterus via X-ray. While some discomfort, cramping, or spotting may occur, diarrhea is not typically expected.
Choice C reason:
There is no requirement for a client to be on a liquid diet following an HSG procedure. The client can usually resume normal activities and diet immediately after the procedure unless otherwise instructed by their healthcare provider.
Choice D reason:
Referred shoulder pain can occur when contrast fluid spills through a patent tube into the peritoneal cavity, irritating the diaphragm’s undersurface and eliciting pain perceived at the shoulder via the phrenic nerve. Clients should be advised this is normal, short-lived, and relieved by positioning or mild analgesics.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
