A nurse is assisting with the care of a client who has metabolic alkalosis. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Place the client on seizure precautions.
Have the client breath into a paper bag.
Encourage the client to breath slowly,
Plan to administer sodium bicarbonate to the client
The Correct Answer is A
A. Placing the client on seizure precautions is important as metabolic alkalosis can cause neurological symptoms, such as confusion and increased risk for seizures due to electrolyte imbalances (e.g., low calcium levels). Therefore, seizure precautions are warranted.
B. Breathing into a paper bag is used in respiratory alkalosis to increase CO2 levels, but it is not appropriate in metabolic alkalosis, where the issue is not primarily related to CO2 imbalance.
C. Encouraging the client to breathe slowly is generally more appropriate for respiratory alkalosis, not metabolic alkalosis. Slow breathing would not directly address the underlying issue of metabolic alkalosis.
D. Administering sodium bicarbonate would worsen metabolic alkalosis, as it would further increase the alkalotic state. Sodium bicarbonate is used in metabolic acidosis, not alkalosis.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Furosemide use is more commonly associated with hyponatremia rather than hypernatremia due to its diuretic effect.
B. Furosemide does not typically cause hypercalcemia; instead, it may lead to hypocalcemia.
C. Hyperchloremia is not a primary concern with furosemide, as the drug can cause a loss of chloride ions alongside sodium.
D. Furosemide can cause an increase in uric acid levels by reducing its excretion through the kidneys.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
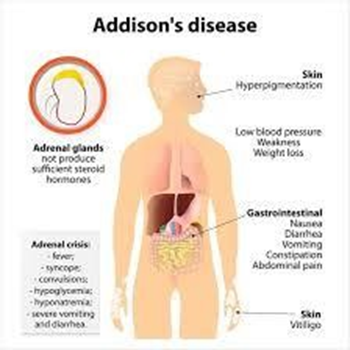
A. Intention tremors are not typically associated with Addison's disease.
B. Hyperpigmentation, particularly in sun-exposed areas and pressure points, is a characteristic finding in Addison's disease due to increased melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) production.
C. Purple striations are typically associated with Cushing's syndrome, not Addison's disease.
D. Hirsutism (excessive hair growth) is not a common manifestation of Addison's disease. It is more associated with Cushing’s disease.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
