A nurse is assisting with the admission of a child who has measles. Which of the following isolation precautions should the nurse initiate?
Contact
Airborne
Protective environment
Droplet
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A: Contact isolation is not appropriate for a child who has measles, which is a highly contagious viral infection that causes fever, rash, cough, runny nose, and red eyes. Contact isolation is used for patients who have infections that can be spread by direct or indirect contact with the patient or their environment, such as wound infections, scabies, or Clostridioides difficile. Contact isolation requires wearing gloves and gowns and using dedicated equipment.
Choice B: Airborne isolation is appropriate for a child who has measles, as it is used for patients who have infections that can be spread by small droplets that can remain suspended in the air and travel over long distances, such as tuberculosis, chickenpox, or measles. Airborne isolation requires wearing a respirator mask and placing the patient in a negative pressure room with the door closed.
Choice C: Protective environment isolation is not appropriate for a child who has measles, as it is used for patients who have compromised immune systems and are at high risk of acquiring infections from others, such as transplant recipients, cancer patients, or patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy. Protective environment isolation requires wearing gloves, gowns, masks, and eye protection and placing the patient in a positive pressure room with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters.
Choice D: Droplet isolation is not appropriate for a child who has measles, as it is used for patients who have infections that can be spread by large droplets that can travel up to 6 feet from the source, such as influenza, pertussis, or meningitis. Droplet isolation requires wearing a surgical mask and eye protection and placing the patient in a private room or cohorting with other patients with the same infection.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A: This instruction is correct, as iron supplements can cause a change in the color and consistency of stools, making them dark, green, or black. This is not a sign of bleeding or infection, but a normal side effect of iron therapy. The parents should be informed of this possibility and reassured that it is harmless.
Choice B: This instruction is incorrect, as iron supplements should not be administered at bedtime, but rather one hour before or two hours after meals. This is because iron absorption is reduced by food, especially dairy products, antacids, or calcium supplements. The parents should be instructed to give the medication on an empty stomach or with a small amount of food if it causes nausea.
Choice C: This instruction is incorrect, as iron supplements should not be given with milk, as milk contains calcium, which can interfere with iron absorption and reduce its effectiveness. The parents should be instructed to avoid giving milk or other dairy products within two hours of the medication.
Choice D: This instruction is incorrect, as iron supplements should not be administered at mealtimes, but rather one hour before or two hours after meals. This is because iron absorption is reduced by food, especially dairy products, antacids, or calcium supplements. The parents should be instructed to give the medication on an empty stomach or with a small amount of food if it causes nausea.
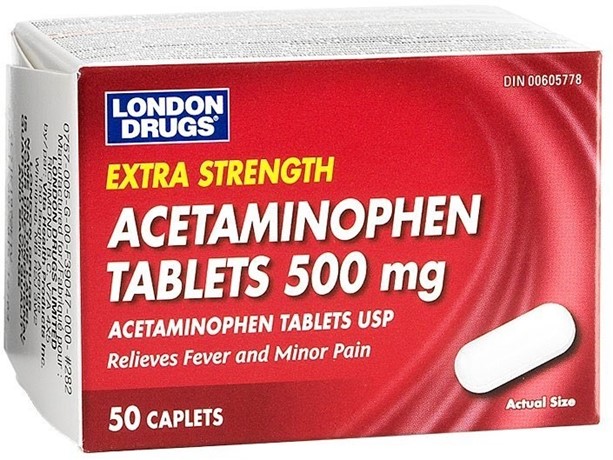
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A: This instruction is not correct, as the child should avoid taking a tub bath for the first 3 days after a cardiac catheterization, which is a procedure that involves inserting a thin tube into a blood vessel and advancing it to the heart to diagnose or treat heart problems. Taking a tub bath can increase the risk of infection or bleeding at the insertion site, which is usually in the groin or arm. The child should take a shower instead and keep the insertion site clean and dry.
Choice B: This instruction is correct, as the child may experience some discomfort or soreness at the insertion site after a cardiac catheterization. Giving the child acetaminophen can help relieve the pain and reduce inflammation. The child should avoid taking aspirin or ibuprofen, as they can increase the risk of bleeding.
Choice C: This instruction is not correct, as the child does not need to stay home for 1 week after a cardiac catheterization unless there are complications or specific instructions from the provider. The child can resume normal activities within 2 to 3 days after the procedure, as long as they avoid strenuous exercise, heavy lifting, or contact sports.
Choice D: This instruction is not correct, as the child does not need to limit their diet to clear liquids for the first 24 hours after a cardiac catheterization unless there are complications or specific instructions from the provider. The child can resume their regular diet as soon as they feel hungry and drink plenty of fluids to flush out the contrast dye used during the procedure.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
