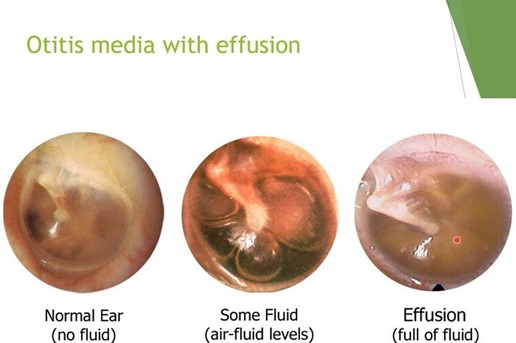
A nurse is caring for a child who has otitis media with effusion. The nurse should identify which of the following manifestations indicates a tympanic membrane rupture.
Popping sensation when swallowing
Green-blue discharge in the ear canal
Sudden pain relief
Increased temperature
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A: A popping sensation when swallowing is not a sign of a tympanic membrane rupture, as it is a normal phenomenon that occurs when the eustachian tube opens and closes to equalize the pressure between the middle ear and the atmosphere. A popping sensation when swallowing may be associated with otitis media with effusion, which is a condition that causes fluid accumulation behind the eardrum, but it does not indicate a rupture.
Choice B: Green-blue discharge could be indicative of infection but is not as directly related to the rupture event as the sudden pain relief is.
Choice C: The correct answer is sudden relief of pain. This is because the rupture of the tympanic membrane releases the pressure and fluid that has built up in the middle ear, leading to an immediate decrease in pain.
Choice D: An increased temperature is not a sign of a tympanic membrane rupture, as it is a nonspecific symptom that may indicate various conditions, such as inflammation, infection, or fever. An increased temperature may be associated with otitis media with effusion, which is a condition that causes fluid accumulation behind the eardrum, but it does not indicate a rupture.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A: A barking cough is not a finding that indicates that the treatment has been effective, but rather a symptom of acute laryngotracheobronchitis, which is also known as croup. Croup is a condition that causes inflammation and narrowing of the upper airway and produces a characteristic barking or seal-like cough. A barking cough may persist for several days after the onset of croup and does not reflect the severity of the airway obstruction.
Choice B: Decreased stridor is a finding that indicates that the treatment has been effective, as stridor is a sign of airway obstruction caused by acute laryngotracheobronchitis. Stridor is a high-pitched, noisy breathing sound that occurs when the air passes through the narrowed airway. Stridor may be inspiratory, expiratory, or biphasic,
depending on the level of obstruction. Decreased stridor means that the airway is less obstructed and the child can breathe more easily.
Choice C: Improved hydration is not a finding that indicates that the treatment has been effective, but rather a goal of treatment for acute laryngotracheobronchitis. Dehydration can worsen the symptoms and complications of croup by thickening the mucus and increasing the risk of infection. Improved hydration can help thin out the mucus and prevent dehydration. Hydration can be improved by encouraging oral fluids, administering intravenous fluids, or providing humidified air.
Choice D: Decreased temperature is not a finding that indicates that the treatment has been effective, but rather a possible outcome of treatment for acute laryngotracheobronchitis. Fever may or may not be present in croup, depending on the cause and severity of the condition. Fever can be caused by viral or bacterial infection, inflammation, or dehydration. Decreased temperature can indicate that the infection or inflammation is resolving or that the dehydration is corrected.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A: Lice cannot survive for more than 48 hours away from the host. This statement is false and should not be included in the teaching, as it can cause unnecessary anxiety or confusion.
Choice B: Washing your child's hair daily will not prevent lice, as lice do not depend on hair cleanliness or hygiene.
This statement is false and should not be included in the teaching, as it can create a false sense of security or stigma.
Choice C: Lice cannot jump or fly from one child to another, as they only crawl. This statement is false and should not be included in the teaching, as it can cause unnecessary fear or panic.
Choice D: Encouraging your child to avoid sharing hats with other children can prevent lice, as lice can be transmitted by direct contact or by sharing personal items. This statement is true and should be included in the teaching, as it can help prevent lice infestation or spread.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
