A parent tells a nurse that her toddler drinks a quart of milk a day and has a poor appetite for solid foods. The nurse should explain that the toddler is at risk for which of the following disorders?
Obesity
Diabetes mellitus
Iron deficiency anemia
Rickets
The Correct Answer is C
Consuming a large amount of milk, such as a quart a day, can lead to iron deficiency anemia in toddlers. Milk is a poor source of iron, and excessive milk intake can displace other iron-rich foods from the toddler's diet.
Iron deficiency anemia occurs when the body lacks sufficient iron to produce enough hemoglobin, which is essential for oxygen transport in the blood. Toddlers are particularly vulnerable to iron deficiency anemia because they have increased iron needs for growth and development.
Option A (Obesity) and option B (Diabetes mellitus) are not directly related to the toddler's milk consumption. Obesity may be a concern if the child consumes excessive calories overall, but it is not specifically associated with milk intake. Similarly, diabetes mellitus is not directly related to milk consumption.
Option D (Rickets) is caused by a deficiency of vitamin D, not iron. Rickets results in weakened and deformed bones, and it is usually associated with inadequate sunlight exposure and insufficient dietary vitamin D. While milk is often fortified with vitamin D, excessive milk intake can displace other vitamin D sources in the diet and contribute to an increased risk of rickets, but the primary concern with excessive milk intake is iron deficiency anemia.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Consuming a large amount of milk, such as a quart a day, can lead to iron deficiency anemia in toddlers. Milk is a poor source of iron, and excessive milk intake can displace other iron-rich foods from the toddler's diet.
Iron deficiency anemia occurs when the body lacks sufficient iron to produce enough hemoglobin, which is essential for oxygen transport in the blood. Toddlers are particularly vulnerable to iron deficiency anemia because they have increased iron needs for growth and development.
Option A (Obesity) and option B (Diabetes mellitus) are not directly related to the toddler's milk consumption. Obesity may be a concern if the child consumes excessive calories overall, but it is not specifically associated with milk intake. Similarly, diabetes mellitus is not directly related to milk consumption.
Option D (Rickets) is caused by a deficiency of vitamin D, not iron. Rickets results in weakened and deformed bones, and it is usually associated with inadequate sunlight exposure and insufficient dietary vitamin D. While milk is often fortified with vitamin D, excessive milk intake can displace other vitamin D sources in the diet and contribute to an increased risk of rickets, but the primary concern with excessive milk intake is iron deficiency anemia.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Rheumatic fever (RF) is a complication that can occur after an untreated or inadequately treated streptococcal throat infection (strep throat). It can affect the heart, joints, skin, and brain. One important aspect of managing RF is to prevent further episodes of strep throat, as it can trigger recurrent RF. Therefore, the child with a history of RF will require prophylactic antibiotics (usually penicillin or a related antibiotic) before certain invasive procedures, dental work, or surgeries to prevent strep throat and subsequent recurrence of RF.
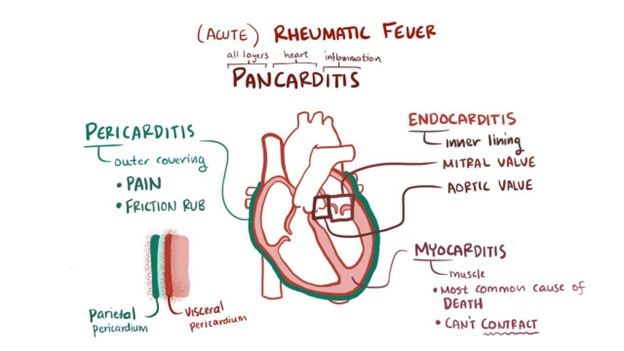
Option A is not specific to rheumatic fever, and while electrolyte imbalances may be monitored and managed in certain cases of severe illness, it is not a core aspect of managing RF.
Option B is not accurate. While many children with RF do recover fully with appropriate treatment, they may be at risk of developing rheumatic heart disease, which can lead to long-term complications if not managed properly.
Option D is not a direct implication of RF. Rheumatic fever is not a genetically inherited condition, but a complication of strep throat caused by a bacterial infection. There is no evidence to suggest that having RF would directly affect the genetic implications for future offspring.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
