Which of the following is the most accurate assessment of tissue perfusion in a patient in shock?
Pupil response, pulse pressure, urine output.
Level of consciousness, urine output, lactate level
Blood pressure, pulse, respirations.
Breath sounds, heart rate, pupil response
The Correct Answer is B
Assessing tissue perfusion is crucial in evaluating the adequacy of oxygen and nutrient delivery to the body's tissues. While multiple factors contribute to tissue perfusion, the options provided in choice B are key indicators:
Level of consciousness: Altered mental status or changes in the patient's level of consciousness can be a sign of impaired cerebral perfusion, which reflects overall tissue perfusion.
Urine output: Monitoring urine output provides information about renal perfusion and kidney function. Decreased urine output can be indicative of inadequate tissue perfusion.
Lactate level: Lactate is a by-product of anaerobic metabolism that accumulates when there is insufficient oxygen delivery to tissues. Elevated lactate levels indicate tissue hypoperfusion and cellular oxygen debt.
A. Pupil response, pulse pressure, and urine output in (option A) are incorrect because While pupil response and pulse pressure may provide some information about perfusion, they do not encompass a comprehensive assessment of tissue perfusion. Additionally, assessing urine output is important, but it alone may not provide a complete picture of tissue perfusion status.
C. Blood pressure, pulse, and respirations in (option C) are incorrect because Blood pressure, pulse, and respirations are important vital signs to monitor, but they do not solely indicate tissue perfusion. Hypotension, for example, can be a late sign of inadequate tissue perfusion.
D. Breath sounds, heart rate, and pupil response in (option D) are incorrect because: Although breath sounds and heart rate can be affected by changes in tissue perfusion, they are not specific or comprehensive indicators of tissue perfusion status. Pupil response alone does not provide a complete assessment of tissue perfusion.
Therefore, the most accurate assessment of tissue perfusion in a patient in shock involves evaluating the level of consciousness, urine output, and lactate levels.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Norepinephrine is a vasopressor medication commonly used in the management of septic shock. It acts as a potent vasoconstrictor to increase systemic vascular resistance and improve blood pressure. By constricting blood vessels, norepinephrine helps restore tissue perfusion and improve organ function.
A. Nitroglycerine (Tridil) in (option A) is incorrect because: Nitroglycerine is a vasodilator and would further lower blood pressure. It is not suitable for a patient with septic shock who already has low blood pressure.
B. Atenolol (Tenormin) in (option B) is incorrect because: Atenolol is a beta-blocker and would further decrease heart rate and blood pressure. It is not appropriate for a patient in septic shock who requires intervention to increase blood pressure.
C. Dobutamine (Dobutrex) in (option C) is incorrect because: Dobutamine is an inotropic medication used to increase cardiac output. While it can be helpful in certain types of shock, such as cardiogenic shock, it is not the first-line choice for septic shock when there is inadequate blood pressure response.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
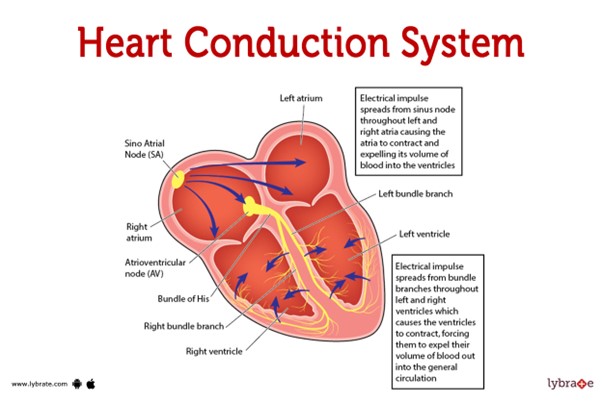 This pathway represents the normal sequence of electrical impulses that coordinate the contraction and relaxation of the heart chambers.
This pathway represents the normal sequence of electrical impulses that coordinate the contraction and relaxation of the heart chambers.
The electrical signal originates from the sinoatrial (SA) node, which is often referred to as the natural pacemaker of the heart. It is located in the right atrium and generates the electrical impulses that initiate each heartbeat. From the SA node, the electrical signal travels to the atrioventricular (AV) node, which is located at the junction between the atria and ventricles.
After passing through the AV node, the electrical impulse travels through the bundle of His (also known as the atrioventricular bundle) and divides into the right and left bundle branches. These branches continue the conduction pathway and deliver the electrical signal to the Purkinje fibers.
The Purkinje fibers spread the electrical impulse rapidly throughout the ventricles, stimulating the contraction of the ventricular muscle and allowing for efficient pumping of blood out of the heart.
Therefore, the correct sequence of the normal conduction pathway in the heart is:
A. SA node - AV node - bundle of His - bundle branches - Purkinje fibers.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
