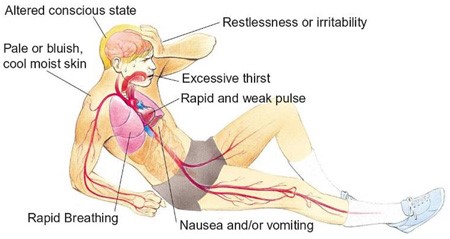
A 61-year-old female patient with hypovolemic shock has these vital signs: temperature 97.9°F (36.6°C): pulse 123 beats/min: blood pressure 85/48 mamite respirations 24 breaths/min; urine output 20 mL for last 2 hours: skin cool and clammy. Which prescription order for this patient does the nurse question?
Doasive Nitrogen 12m mi
Dobutamine Doubters) 5 mcg/kg/min
Plasmanate 1 unit
Bumetanide (Bumex) 1 mg IV
The Correct Answer is C
Hypovolemic shock is a life-threatening condition resulting from severe blood or fluid loss. The patient in this scenario exhibits signs of hypovolemic shock, such as low blood pressure, tachycardia, cool and clammy skin, and decreased urine output.
When assessing the prescription options, the nurse should consider the appropriateness of each intervention for hypovolemic shock. Plasmanate is a type of plasma protein fraction that is used for volume expansion in certain situations. However, in hypovolemic shock, the primary intervention is to restore intravascular volume promptly. Plasmanate alone may not be sufficient for rapid-volume resuscitation.
In hypovolemic shock, the initial management typically involves the administration of crystalloid solutions, such as Lactated Ringers or Normal Saline, to restore intravascular volume. Therefore, the prescription of Plasmanate as the primary intervention raises concerns and should be questioned by the nurse.
A. Dopamine (Intropin) 12 mcg/min in (option A) is incorrect because: Dopamine is a vasopressor medication used to increase blood pressure and cardiac output. It is a suitable option for hypovolemic shock to support blood pressure and tissue perfusion.
B. Dobutamine (Dobutrex) 5 mcg/kg/min in (option B) is incorrect because: Dobutamine is an inotropic medication that helps improve cardiac contractility and cardiac output. It can be beneficial in cases of hypovolemic shock with signs of poor cardiac function.
D. Bumetanide (Bumex) 1 mg IV in (option D) is incorrect because: Bumetanide is a loop diuretic used to promote diuresis. However, in the context of hypovolemic shock, diuretics are generally not the first-line treatment as they can further reduce intravascular volume and worsen the patient's condition.
It is essential for the nurse to consult with the healthcare provider regarding the prescription order of Plasmanate and consider alternative interventions for rapid volume resuscitation in hypovolemic shock.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Norepinephrine is a vasopressor medication commonly used in the management of septic shock. It acts as a potent vasoconstrictor to increase systemic vascular resistance and improve blood pressure. By constricting blood vessels, norepinephrine helps restore tissue perfusion and improve organ function.
A. Nitroglycerine (Tridil) in (option A) is incorrect because: Nitroglycerine is a vasodilator and would further lower blood pressure. It is not suitable for a patient with septic shock who already has low blood pressure.
B. Atenolol (Tenormin) in (option B) is incorrect because: Atenolol is a beta-blocker and would further decrease heart rate and blood pressure. It is not appropriate for a patient in septic shock who requires intervention to increase blood pressure.
C. Dobutamine (Dobutrex) in (option C) is incorrect because: Dobutamine is an inotropic medication used to increase cardiac output. While it can be helpful in certain types of shock, such as cardiogenic shock, it is not the first-line choice for septic shock when there is inadequate blood pressure response.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Fresh frozen plasma (FFP) is a blood product that contains various clotting factors, including factors II, V, VII, VIII, IX, X, XI, and XIII. These clotting factors are essential for the normal coagulation process. In patients with shock, coagulation abnormalities can occur, and administration of FFP can help replenish the deficient clotting factors and restore proper coagulation function.
The other options mentioned are not the primary components replaced by fresh frozen plasma:
A. Red blood cells are in (option A) is incorrect because Red blood cells carry oxygen and are typically replaced by packed red blood cell transfusions in cases of significant blood loss or anemia. Fresh frozen plasma does not contain a significant amount of red blood cells.
C. Platelets in (option C) is incorrect because: Platelets play a role in blood clotting and are typically replaced by platelet transfusions in cases of thrombocytopenia or platelet dysfunction. Fresh frozen plasma may contain a small number of platelets but is not the primary source for platelet replacement.
D. White blood cells in (option D) is incorrect because White blood cells are part of the immune system and are not typically replaced using fresh frozen plasma. Fresh frozen plasma does not contain a significant amount of white blood cells.
Therefore, fresh frozen plasma is primarily administered to patients in shock to replace clotting factors and help restore proper coagulation function.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
