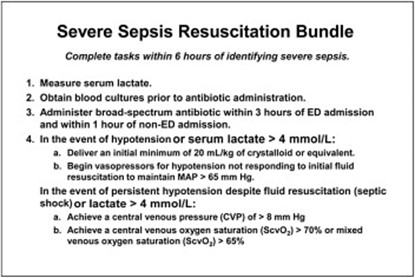
A 29-year-old female patient is admitted to the emergency department with two of the systemic inflammatory response syndrome variables: temperature of 101.2 °F and 14,000 per μL white blood cell count. Which intervention from the sepsis resuscitation bundle does the nurse initiate?
Cooling baths
Broad-spectrum antibiotics
Blood transfusion
NPO status
The Correct Answer is B
The patient's symptoms of fever and elevated white blood cell count suggest a potential infection and sepsis. Broad-spectrum antibiotics should be initiated promptly to cover a wide range of possible pathogens until further diagnostic tests and identification of the specific causative agent are obtained. Early administration of appropriate antibiotics is crucial in sepsis management to target the suspected infection and improve patient outcomes.
A. Cooling baths in (option A) is incorrect because: Cooling baths are typically used in the management of hyperthermia or specific conditions like heatstroke. While the patient has an elevated temperature, it is likely due to the systemic inflammatory response rather than solely hyperthermia.
C. Blood transfusion in (option C) is incorrect because Blood transfusion may be required in certain cases of sepsis if there is evidence of significant anemia or active bleeding. However, based on the information provided, there is no immediate indication of a blood transfusion.
D. NPO status in (option D) is incorrect because NPO status (nothing by mouth) is a general precautionary measure used in various situations, such as prior to surgery or to manage gastrointestinal complications. It is not a specific intervention in the sepsis resuscitation bundle.
Therefore, the nurse should initiate the intervention of administering broad-spectrum antibiotics in this scenario.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Mean arterial pressure (MAP) is a measure of the average pressure within the arteries during one cardiac cycle. It represents the perfusion pressure that drives blood flow to organs and tissues. MAP is calculated using the formula:
MAP = Diastolic blood pressure + 1/3 (Systolic blood pressure - Diastolic blood pressure)
Blood loss, particularly in cases of significant hemorrhage, leads to a decrease in blood volume. When blood volume decreases, there is less circulating blood available to generate pressure within the arterial system. This reduction in blood volume results in decreased MAP.
Therefore, in the case of massive blood loss after trauma, the student can correlate it with a lower blood volume, which in turn leads to a lower MAP. The decrease in blood volume reduces the perfusion pressure, compromising organ and tissue perfusion
A. It causes vasoconstriction and increased MAP in (option A) is incorrect because: While vasoconstriction can occur as a compensatory mechanism to maintain blood pressure, it does not necessarily lead to an increased MAP in the context of significant blood loss.
C. It raises cardiac output and MAP in (option C) is incorrect because Blood loss typically leads to a reduction in cardiac output due to decreased blood volume. Therefore, it does not raise cardiac output and MAP.
D. There is no direct correlation to MAP in (option D) is incorrect because: There is indeed a direct correlation between blood loss and MAP. As blood volume decreases, MAP decreases as well.
Therefore, the correct correlation between blood loss and MAP is that lower blood volume lowers MAP.
Correct Answer is ["A","B","C","D"]
Explanation
These conditions can lead to fluid loss, either through increased gastrointestinal output (diarrhea, vomiting, lower GI bleeding) or accumulation of air in the pleural space (tension pneumothorax), resulting in a decrease in blood volume and subsequent hypovolemic shock.
E. Diabetes insipidus in (option E) is incorrect because it is not directly associated with hypovolemic shock. Diabetes insipidus is a condition characterized by excessive thirst and the production of large volumes of dilute urine due to insufficient production or response to antidiuretic hormone (ADH). While diabetes insipidus can lead to dehydration and potential hypovolemia, it is not a direct cause of hypovolemic shock.
F. Valvular stenosis in (option F) is incorrect because it is a condition characterized by the narrowing or obstruction of one or more heart valves. While it can cause problems with cardiac output and circulation, it is not specifically related to hypovolemic shock, which is caused by a decrease in blood volume.
Therefore, the conditions that can cause hypovolemic shock include diarrhea, vomiting, lower GI bleeding, and tension pneumothorax.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
