The nurse is setting up an intravenous infusion pump to administer a dose of vancomycin [Vancocin] to a patient. What is the fastest rate at which the drug may be infused?
60 minutes
30 minutes
90 minutes
45 minutes
The Correct Answer is A
Vancomycin is often administered over at least 60 minutes to reduce the risk of infusion-related reactions, such as "Red Man Syndrome," which is characterized by flushing, rash, and itching. This reaction is caused by the rapid infusion of vancomycin, leading to the release of histamine.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Antibiotics are prescribed according to culture and sensitivity reports:
When antibiotics are prescribed based on specific tests like cultures and sensitivity reports, it ensures that the right antibiotic is chosen for the specific bacteria causing the infection. This practice helps in targeting the infection more effectively, reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance.
B. Patients stop taking an antibiotic after they feel better:
This scenario is problematic. When patients start feeling better, they might assume the infection is completely gone and stop taking antibiotics before the prescribed course is finished. This premature discontinuation can leave some bacteria alive, which may develop resistance to the antibiotic used. This practice is a significant contributor to antibiotic resistance.
C. Antibiotics are taken with ascorbic acid (vitamin C):
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) doesn't have a significant impact on antibiotic resistance. It is not a factor contributing to antibiotic resistance.
D. Antibiotics are taken with water or juice:
Whether antibiotics are taken with water or juice doesn’t directly influence antibiotic resistance. Proper hydration is essential to support the body's overall health, but it doesn't impact the development of antibiotic resistance.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
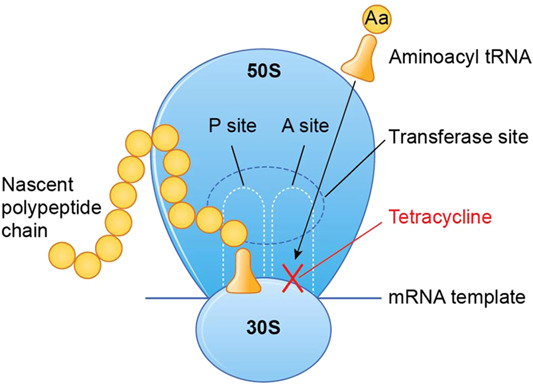
A. "Tetracycline inhibits protein synthesis."
Explanation: Tetracycline antibiotics interfere with bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the bacterial ribosomes. This binding prevents the attachment of transfer RNA (tRNA) to the messenger RNA (mRNA) complex, effectively inhibiting the production of proteins that are crucial for bacterial growth and replication.
B. "Tetracycline blocks RNA synthesis."
Explanation: This statement is incorrect. Tetracycline primarily affects protein synthesis, not RNA synthesis. It doesn't block the creation of RNA molecules in bacteria.
C. "Tetracycline degrades the bacterial cell wall."
Explanation: This statement is incorrect. Tetracycline antibiotics do not target bacterial cell walls. Agents like penicillins and cephalosporins are examples of antibiotics that disrupt bacterial cell walls.
D. "Tetracycline binds to magnesium ions."
Explanation: This statement is incorrect. Tetracycline does bind to certain metal ions, but it's not primarily through magnesium ions. The binding to bacterial ribosomes is a key mechanism of action for tetracyclines.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
