"My doctor said I have an autoimmune disease. What does that mean?" asks a client. How should the nurse respond?
"You have developed urticaria in response to something in your environment."
"Your immune system is creating antibodies that are destroying your own cells."
"Your immune system is not able to create antibodies to help you fight infection."
"You have developed an infection that is destroying your immune cells."
The Correct Answer is B
A. "You have developed urticaria in response to something in your environment."
This statement is incorrect. Urticaria refers to hives, a skin rash usually caused by an allergic reaction, infection, or stress. It's not necessarily indicative of an autoimmune disease.
B. "Your immune system is creating antibodies that are destroying your own cells."
This statement is correct. Autoimmune diseases involve the immune system mistakenly attacking the body's own cells and tissues, leading to various health issues.
C. "Your immune system is not able to create antibodies to help you fight infection."
This statement is incorrect. In autoimmune diseases, the immune system is overactive, producing antibodies that target the body's own cells, not that it can't create antibodies.
D. "You have developed an infection that is destroying your immune cells."
This statement is incorrect. Infections don't typically destroy immune cells; instead, infections often stimulate the immune system to respond and fight against invading pathogens.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Aminoglycosides: Aminoglycosides are a different class of antibiotics. They do not have cross-sensitivity with penicillin. People who are allergic to penicillin can usually take aminoglycosides without a problem.
B. Erythromycins: Erythromycins are macrolide antibiotics. They are not related to penicillin structurally, so there is no cross-sensitivity between penicillin and erythromycins. People allergic to penicillin can generally take erythromycin without issues.
C. Quinolones: Quinolones, also known as fluoroquinolones, are a different class of antibiotics. They do not share a structural similarity with penicillin, so there is usually no cross-sensitivity between penicillin and quinolones. People allergic to penicillin can usually take quinolones without problems.
D. Cephalosporins: Cephalosporins are beta-lactam antibiotics, just like penicillins. They have a similar chemical structure to penicillins, which can lead to cross-sensitivity. Individuals who are allergic to penicillin might also have an allergic reaction to cephalosporins due to this structural resemblance. However, it's important to note that not all cephalosporins are the same, and the risk of cross-reactivity varies among different generations of cephalosporins. Healthcare providers need to assess the specific situation and choose an appropriate antibiotic if there is a known penicillin allergy.
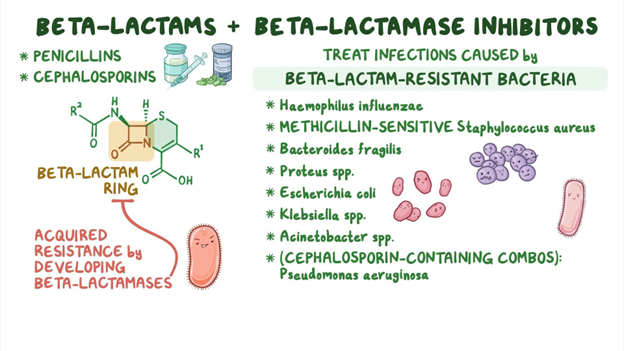
Correct Answer is ["A","B","C","D"]
Explanation
A. Viral Latency: Some viruses, like herpesviruses, can enter a latent phase where they hide in host cells, making it challenging for the immune system to detect and target them.
B. Host Defense Failure: This term encompasses situations where the host's defense mechanisms, including physical barriers and immune responses, are not effective in preventing or controlling infection. For example, pathogens may develop mechanisms to evade detection by the immune system.
C. Immunosuppression: Pathogens can actively suppress the host's immune response. They may produce molecules or proteins that inhibit the immune system's ability to mount an effective defense.
D. Immunodeficiency: Individuals with immunodeficiency disorders have weakened immune systems, which can be congenital (genetic) or acquired. This weakness makes them more susceptible to infections.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
