A nurse is administering a daily dose of vancomycin at 10:00 AM. At which time should the nurse obtain the patient's blood sample to determine the trough level?
8:00 AM
11:00 AM
9:00 AM
12:00 noon
The Correct Answer is C
A. 8:00 AM: This time is too early to draw a trough level for a medication administered at 10:00 AM. The trough level should be drawn just before the next dose is given to get the lowest concentration in the bloodstream.
B. 11:00 AM: This time is after the scheduled dose of vancomycin at 10:00 AM. Waiting until 11:00 AM would not provide an accurate trough level because the patient has already received the medication.
C. 9:00 AM: This is the correct time to obtain the patient's blood sample. It is one hour before the scheduled dose of vancomycin at 10:00 AM. Drawing the trough level at this time ensures it reflects the lowest concentration of the drug in the bloodstream.
D. 12:00 noon: This time is after the scheduled dose of vancomycin at 10:00 AM. Waiting until noon would not provide an accurate trough level because the patient has already received the medication.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
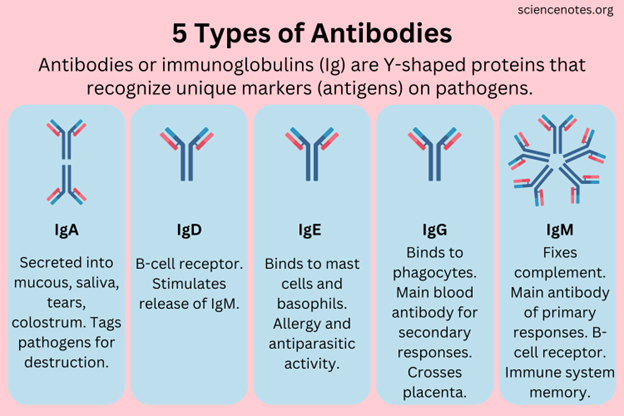
A. IgG: Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is the most abundant antibody in the bloodstream and represents about 75% of all the antibodies in the body. It provides long-term immunity because it can persist in the bloodstream for a long time. IgG antibodies are involved in secondary immune responses and are capable of crossing the placenta, providing passive immunity to newborns.
B. IgE: Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is associated mainly with allergic reactions. When the body is exposed to an allergen, it triggers the release of IgE, leading to the symptoms of an allergic response, such as sneezing or itching.
C. IgM: Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is the largest antibody and is usually the first antibody produced during an initial exposure to an antigen. It is particularly effective at agglutination (clumping together) of pathogens.
D. IgA: Immunoglobulin A (IgA) is found in high concentrations in mucous membranes, particularly those lining the respiratory passages and gastrointestinal tract. It provides localized defense against pathogens. IgA antibodies are also found in saliva, tears, and breast milk, providing immunity to infants.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
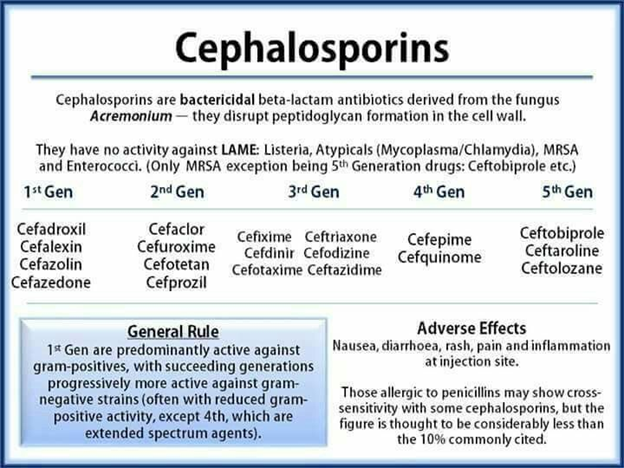
A. Ceftaroline (Teflaro) is a fifth-generation cephalosporin antibiotic that is effective against MRSA (Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus). It's the first cephalosporin in its class with this capability, making it a valuable choice in treating MRSA infections.
B. Cefepime (Maxipime) is a fourth-generation cephalosporin that does not have specific activity against MRSA.
C. Ceftriaxone (Rocephin) is a third-generation cephalosporin, effective against a wide range of bacteria, but not specifically targeted at MRSA.
D. Cephalexin (Keflex) is a first-generation cephalosporin, primarily effective against Gram-positive bacteria, but not effective against MRSA.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
