The antibody class involved in hypersensitivity reaction Type I is:
IgE
IgA
IgG
IgM
The Correct Answer is A
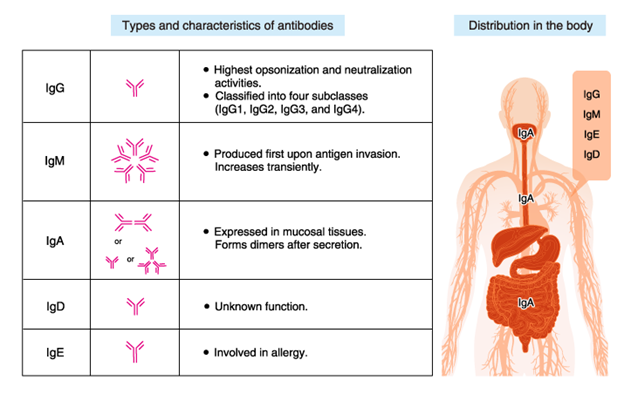
A. IgE (Immunoglobulin E): This class of antibodies is primarily involved in hypersensitivity reactions Type I, which are immediate allergic reactions. When a person is exposed to an allergen they are sensitive to, IgE antibodies on the surface of mast cells and basophils bind to the allergen. This triggers the release of inflammatory mediators like histamine, leading to allergic symptoms such as itching, hives, and in severe cases, anaphylaxis.
B. IgA (Immunoglobulin A): IgA antibodies are primarily found in mucosal areas such as the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. They play a role in immune defense on mucosal surfaces and are important for preventing infections. While IgA is not directly associated with hypersensitivity reactions Type I, deficiencies in IgA can sometimes lead to increased susceptibility to certain infections.
C. IgG (Immunoglobulin G): IgG antibodies are the most common type of antibody in the bloodstream and are involved in various immune responses, including defense against bacterial and viral infections. IgG antibodies are not specific to Type I hypersensitivity reactions; they are part of the immune system's broader defense mechanisms.
D. IgM (Immunoglobulin M): IgM antibodies are the first antibodies to be produced in response to an infection. They are large pentameric molecules and are effective at agglutinating pathogens. IgM antibodies are involved in the primary immune response to infections, but they are not specifically associated with Type I hypersensitivity reactions.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Respiratory Function: Monitoring respiratory function is important for conditions like asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It involves assessing lung sounds, oxygen saturation levels, and breathing patterns. This monitoring is essential to detect any signs of respiratory distress.
B. Cardiac Function: Monitoring cardiac function includes assessing heart rate, blood pressure, and rhythm. It's crucial for patients with heart conditions like heart failure or arrhythmias. This monitoring helps in identifying irregularities in heart function and provides insights into the overall cardiovascular health of the patient.
C. Renal Function: Monitoring renal function involves assessing kidney health, which includes tests like serum creatinine and glomerular filtration rate (GFR). This is vital for patients with kidney diseases or those taking medications that can impact kidney function. Monitoring renal function helps in detecting any signs of kidney impairment or failure.
D. Liver Function: Monitoring liver function involves tests like liver enzymes (AST, ALT), bilirubin levels, and albumin levels. This is essential for patients taking medications that can affect the liver, such as certain antifungals, statins, or pain relievers. Monitoring liver function helps in identifying liver damage or dysfunction early on.
Correct Answer is ["A","B","C","D"]
Explanation
A. Viral Latency: Some viruses, like herpesviruses, can enter a latent phase where they hide in host cells, making it challenging for the immune system to detect and target them.
B. Host Defense Failure: This term encompasses situations where the host's defense mechanisms, including physical barriers and immune responses, are not effective in preventing or controlling infection. For example, pathogens may develop mechanisms to evade detection by the immune system.
C. Immunosuppression: Pathogens can actively suppress the host's immune response. They may produce molecules or proteins that inhibit the immune system's ability to mount an effective defense.
D. Immunodeficiency: Individuals with immunodeficiency disorders have weakened immune systems, which can be congenital (genetic) or acquired. This weakness makes them more susceptible to infections.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
