What is the difference between bactericidal drugs and bacteriostatic drugs?
Bactericidal and bacteriostatic are used interchangeably.
Bactericidal drugs are directly lethal to bacteria, and bacteriostatic drugs work to slow bacterial growth but do not cause cell death.
Bacteriostatic drugs are directly lethal to bacteria, and bactericidal drugs work to slow bacterial growth but do not cause cell death.
A bactericidal drug can cause death to the host, whereas a bacteriostatic drug only affects bacteria.
The Correct Answer is B
A. "Bactericidal and bacteriostatic are used interchangeably."
Explanation: This statement is incorrect. Bactericidal and bacteriostatic are two distinct categories of antibiotics with different mechanisms of action.
B. "Bactericidal drugs are directly lethal to bacteria, and bacteriostatic drugs work to slow bacterial growth but do not cause cell death."
Explanation: This statement is correct. Bactericidal drugs kill bacteria directly, leading to their death, while bacteriostatic drugs inhibit bacterial growth without causing immediate cell death.
C. "Bacteriostatic drugs are directly lethal to bacteria, and bactericidal drugs work to slow bacterial growth but do not cause cell death."
Explanation: This statement is incorrect. It is the opposite of the correct explanation. Bacteriostatic drugs do not directly kill bacteria, and bactericidal drugs do cause bacterial death.
D. "A bactericidal drug can cause death to the host, whereas a bacteriostatic drug only affects bacteria."
Explanation: This statement is not entirely accurate. While some bactericidal drugs can be more toxic to the host, it depends on the specific drug and its dosage. Bacteriostatic drugs, on the other hand, generally do not directly harm the host. The primary distinction between the two categories is their impact on bacterial growth and survival.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. Discoloration of teeth: Tetracycline antibiotics can bind with calcium ions in teeth, leading to the development of yellow-gray-brown stains. This effect is particularly significant in developing teeth in children below the age of 8 and can result in permanent discoloration.
B. Anabolic change: This term doesn't specifically relate to the side effects of tetracycline. "Anabolic" generally refers to processes in the body that build up complex molecules from simpler ones. There's no direct connection between tetracycline and anabolic changes.
C. Cartilage damage: Tetracyclines, especially in high doses or with prolonged use, have been associated with potential adverse effects on cartilage. This is more relevant in individuals whose bones and cartilage are still growing, such as children. It can interfere with skeletal development.
D. Suppression of growth: Long-term use of tetracycline in children can interfere with bone growth and development. It can suppress the growth of bones and affect overall height. This is a significant concern when considering the use of tetracycline in pediatric patients.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Dermatitis and headaches: Prednisone use can sometimes cause skin issues, but dermatitis is not a common side effect. Headaches can also occur, but they are not specific to long-term prednisone therapy.
B. Heart failure and headaches: Prednisone does not directly cause heart failure. Headaches can occur but are not specific indicators of prednisone side effects.
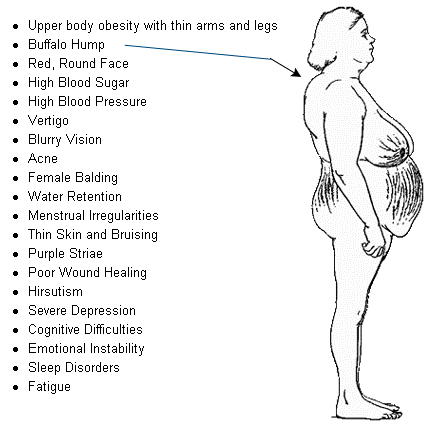
C. Hyperglycemia and osteoporosis: Prednisone can lead to elevated blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia) and increased bone loss (osteoporosis) when used long-term. Regular monitoring is essential to manage these potential side effects.
D. Weight loss and hypoglycemia: Prednisone can cause weight gain rather than weight loss. Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) is not a common side effect of prednisone; it typically causes hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) instead.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
