Which of the following are ways that pathogens can evade the immune system? (Select all that apply)
viral latency
host defense failure
immunosuppression
Immunodeficiency
Correct Answer : A,B,C,D
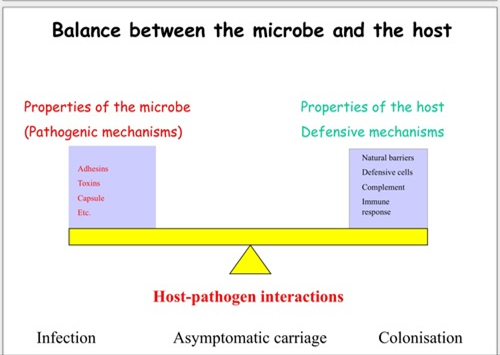
A. Viral Latency: Some viruses, like herpesviruses, can enter a latent phase where they hide in host cells, making it challenging for the immune system to detect and target them.
B. Host Defense Failure: This term encompasses situations where the host's defense mechanisms, including physical barriers and immune responses, are not effective in preventing or controlling infection. For example, pathogens may develop mechanisms to evade detection by the immune system.
C. Immunosuppression: Pathogens can actively suppress the host's immune response. They may produce molecules or proteins that inhibit the immune system's ability to mount an effective defense.
D. Immunodeficiency: Individuals with immunodeficiency disorders have weakened immune systems, which can be congenital (genetic) or acquired. This weakness makes them more susceptible to infections.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. "This drug has a longer duration of action than some of the other antibiotics."
Explanation: Azithromycin, a macrolide antibiotic, has a longer half-life in the body compared to some other antibiotics. Half-life refers to the time it takes for half of the drug to be eliminated from the body. A longer half-life means the drug remains effective for a longer duration, allowing for less frequent dosing.
B. "This is a much more effective drug than what you received previously."
Explanation: While azithromycin is effective against a wide range of bacterial infections, it's not accurate to say it's universally more effective than other antibiotics. The choice of antibiotic depends on the specific type of infection and the susceptibility of the bacteria causing it. Effectiveness varies based on the context of use.
C. "I'll call the pharmacy and ask about the chemical makeup of the drug."
Explanation: While understanding the chemical makeup of drugs is important for healthcare professionals, it might not directly answer the patient's question about the dosing frequency. Explaining the drug's pharmacological properties, such as its duration of action, would provide a more relevant and understandable response to the patient's query.
D. "You'll need to ask your healthcare provider questions like that."
Explanation: This response does not provide the patient with the information they seek. Nurses are valuable resources for medication-related questions and should strive to provide accurate and understandable explanations to patients.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. "Cephalosporins are assigned to generations based on their relative costs to administer."
This statement is incorrect. The classification of cephalosporins into generations is based on their antimicrobial spectrum and activity against specific bacteria, not their cost.
B. "Later generations of cephalosporins have lower resistance to destruction by beta-lactamases."
This statement is not accurate. In fact, later generations of cephalosporins have increased resistance to destruction by beta-lactamases, which are enzymes produced by bacteria that can break down certain antibiotics.
C. "Cephalosporins have increased activity against gram-negative bacteria with each new generation."
This statement is correct. Cephalosporins are grouped into generations (first to fifth) based on their antibacterial spectrum. As the generations progress, there is an increase in activity against gram-negative bacteria, among other improvements in their spectrum.
D. "First-generation cephalosporins have better penetration of the cerebrospinal fluid."
This statement is generally true. First-generation cephalosporins have better penetration into the cerebrospinal fluid, making them useful for treating certain central nervous system infections.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
