The nurse is creating an education plan for a client who has a recent diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Which of the following interventions should the nurse include in the client's plan?
Provide total assistance with all ADLs
Order a low-residue diet
Encourage client to void every hour
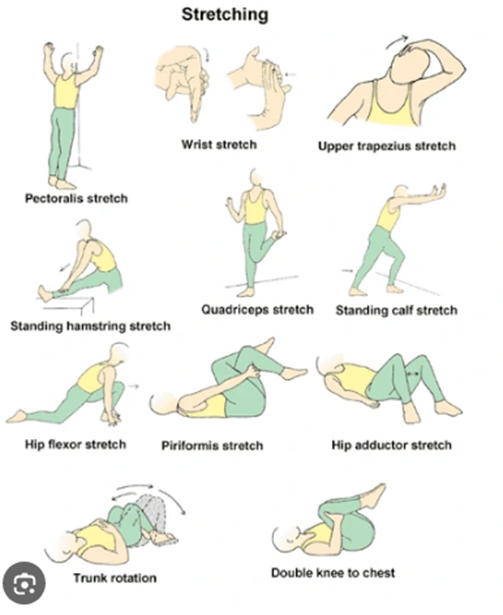
Instruct the client on daily muscle stretching
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A reason: Providing total assistance with all ADLs is not an intervention that should be included in the client's plan. ADLs are activities of daily living, such as bathing, dressing, eating, and toileting. Providing total assistance with all ADLs can reduce the client's independence and self-esteem, and increase their dependence and learned helplessness. The nurse should encourage and assist the client to perform as much as they can by themselves and provide partial or intermittent assistance only when needed.
Choice B reason: Ordering a low-residue diet is not an intervention that should be included in the client's plan. A low-residue diet is a type of diet that limits foods that are high in fiber or indigestible material, such as whole grains, nuts, seeds, fruits, and vegetables. A low-residue diet may be recommended for clients who have inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), diverticulitis, or bowel obstruction, as it can reduce bowel frequency and irritation. However, it is not indicated for clients who have MS, unless they have other comorbidities that require it. A balanced diet that includes adequate fiber, fluids, and nutrients is more beneficial for clients who have MS.
Choice C reason: Encouraging the client to void every hour is not an intervention that should be included in the client's plan. Voiding every hour can be inconvenient and impractical for the client, and may not address their bladder problems effectively. MS can cause bladder dysfunction, such as urinary urgency, frequency, incontinence, or retention, due to nerve damage that affects bladder control. The nurse should assess the type and severity of the bladder dysfunction, and provide appropriate interventions, such as medication, catheterization, pelvic floor exercises, or bladder training.
Choice D reason: Instructing the client on daily muscle stretching is an intervention that should be included in the client's plan. Muscle stretching is a type of exercise that involves extending or elongating a muscle or group of muscles to their full length. Muscle stretching can help prevent or relieve muscle spasticity, stiffness, pain, or contractures that may occur in clients who have MS. The nurse should teach the client how to perform muscle stretching safely and correctly, and encourage them to do it daily or as prescribed.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: The client's financial resources is not the most important factor for the nurse to consider. Although Meals-on-Wheels is a low-cost or free service that provides nutritious meals to homebound seniors and people with disabilities, it does not require a specific income level or financial status to qualify. The nurse should focus on the client's nutritional and functional needs, rather than their economic situation.
Choice B reason: The client's level of family support is not the most important factor for the nurse to consider. Although having family members who can assist with meal preparation and delivery can be helpful and beneficial for the client, it is not a requirement or a guarantee for receiving Meals-on-Wheels. The nurse should assess the client's individual capabilities and preferences, rather than their family availability or involvement.
Choice C reason: The client's access to transportation is not the most important factor for the nurse to consider. Although having access to transportation can enable the client to obtain food and groceries from other sources, such as stores, markets, or restaurants, it is not a criterion or a barrier for receiving Meals-on-Wheels. The nurse should evaluate the client's dietary and health needs, rather than their mobility or transportation options.
Choice D reason: The client's ability to prepare meals is the most important factor for the nurse to consider. Meals-on-Wheels is designed to serve clients who are unable to cook or shop for themselves due to physical, mental, or social limitations. The nurse should determine if the client has any impairments or challenges that prevent them from preparing their own meals, such as vision loss, arthritis, dementia, or isolation. If the client has difficulty or inability to prepare meals, they may be eligible for Meals-on-Wheels.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A: Administer corticosteroids. This is incorrect because corticosteroids are used to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system, but they do not directly affect venous return, stiffness, or muscle strength and endurance.
Choice B: Turn and reposition every 2 hours. This is incorrect because turning and repositioning are important to prevent pressure ulcers and promote circulation, but they are not sufficient to maintain muscle strength and endurance. The client also needs active or passive exercises to prevent muscle atrophy and contractures.
Choice C: Administer interferon. This is incorrect because interferon is a type of immunomodulator that can reduce the frequency and severity of relapses in multiple sclerosis, but it does not directly affect venous return, stiffness, or muscle strength and endurance.
Choice D: Encourage range-of-motion exercises. This is correct because range-of-motion exercises can help increase venous return, prevent stiffness, and maintain muscle strength and endurance in clients with multiple sclerosis. Range-of-motion exercises can be performed actively by the client or passively by the nurse or a caregiver. They should be done at least twice a day to prevent complications such as contractures, spasticity, and pain.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
